Climate Finance - Environment And Ecology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
Climate Finance
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
environment and ecology
📖 Introduction
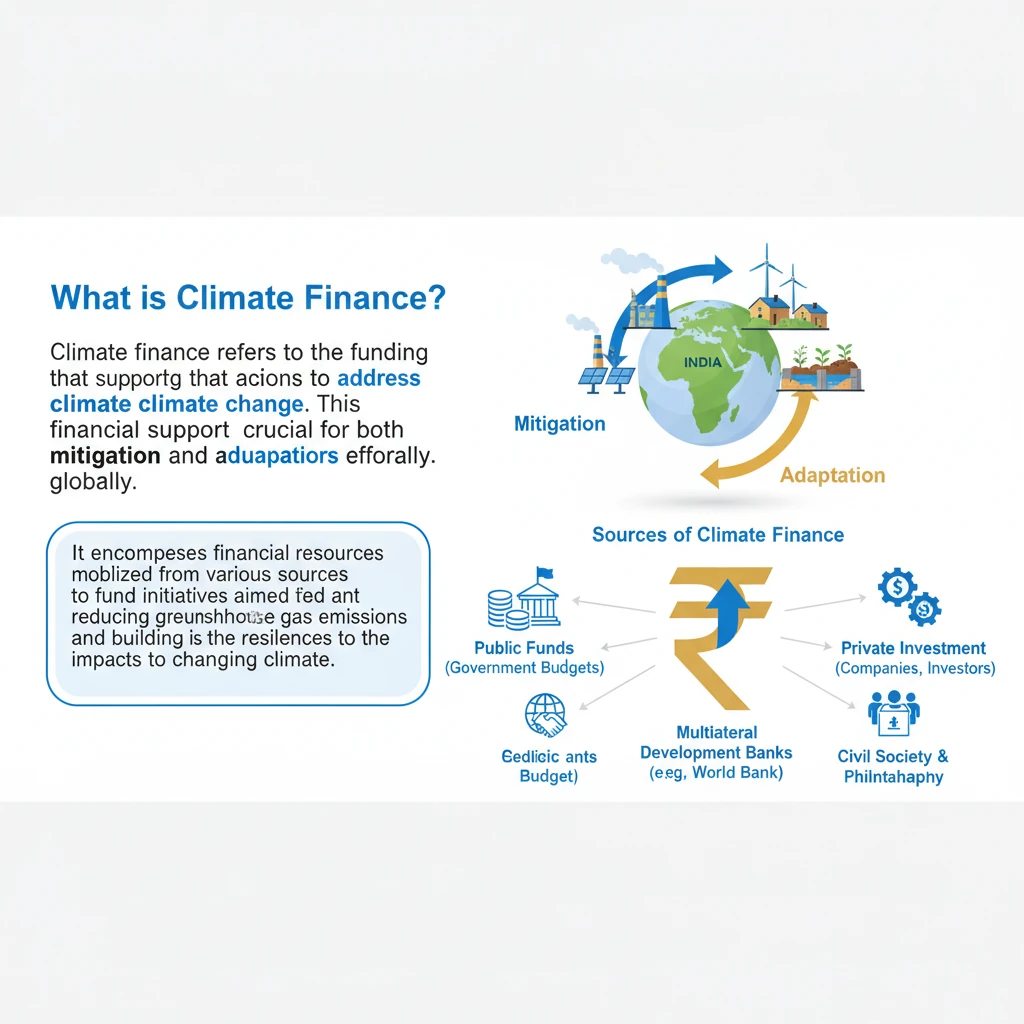
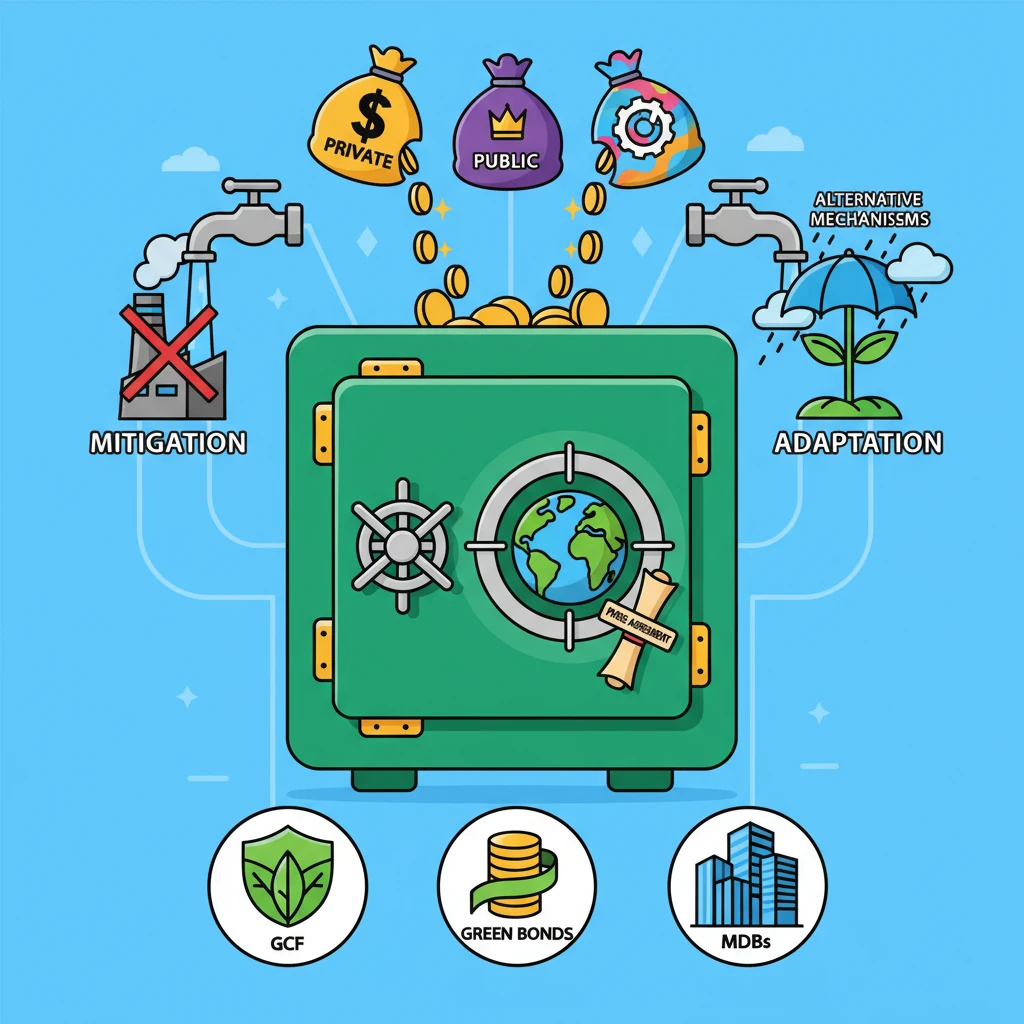
<h4>What is Climate Finance?</h4><p><strong>Climate finance</strong> refers to the funding that supports actions to address <strong>climate change</strong>. This financial support is crucial for both mitigation and adaptation efforts globally.</p><div class='info-box'><p>It encompasses financial resources mobilized from various sources to fund initiatives aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions and building resilience to the impacts of a changing climate.</p></div><h4>Sources of Climate Finance</h4><p>Climate finance can originate from a diverse range of sources, reflecting a global commitment to tackling climate change. These sources include public, private, and alternative mechanisms.</p><ul><li><strong>Public Sources:</strong> This includes national governments, multilateral development banks (MDBs), and international climate funds.</li><li><strong>Private Sources:</strong> This involves investments from commercial banks, institutional investors, and corporations in climate-friendly projects.</li><li><strong>Alternative Sources:</strong> Innovative mechanisms like carbon markets, green bonds, and philanthropic contributions also play a role.</li></ul><h4>Why is Climate Finance Important?</h4><p>Climate finance is paramount for achieving global climate goals and fostering sustainable development. It provides the necessary capital to implement ambitious climate actions.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>It is vital for <strong>reducing emissions</strong> by supporting the transition to renewable energy, energy efficiency, and sustainable land use practices. It also facilitates <strong>adaptation to climate change effects</strong>, helping vulnerable communities build resilience against extreme weather events, sea-level rise, and other impacts.</p></div><p>Moreover, climate finance is critical for enabling countries, especially developing nations, to transition towards <strong>low-carbon economies</strong>. This transition requires significant investment in new technologies and infrastructure.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>Understanding climate finance is essential for UPSC, particularly in <strong>GS Paper 3 (Environment & Economy)</strong>. Questions often focus on its mechanisms, challenges, and India's role in its mobilization and utilization.</p></div><p>Ultimately, robust climate finance flows are indispensable for achieving the ambitious goals outlined in the <strong>Paris Agreement</strong>, particularly limiting global warming to well below 2°C, preferably to 1.5°C, above pre-industrial levels.</p>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •Climate finance is funding for climate change actions (mitigation and adaptation).
- •Sources include public, private, and alternative mechanisms.
- •Crucial for reducing emissions, adapting to climate impacts, and achieving Paris Agreement goals.
- •Key mechanisms include GCF, Green Bonds, and MDBs.
- •Historical context involves UNFCCC, Kyoto, and Paris Agreements establishing financial commitments.
- •Current relevance centers on the USD 100 billion goal, Loss & Damage fund, and India's climate targets.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Green Climate Fund (GCF) official website
•Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) reports
•Ministry of Finance, Government of India reports on green finance
•World Bank and Asian Development Bank publications on climate finance