Black Carbon Emissions and PMUY - Environment And Ecology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Black Carbon Emissions and PMUY
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
environment and ecology
📖 Introduction
<h4>Context: India's Climate Commitments at COP26</h4><p>During the <strong>UNFCCC COP26 climate talks</strong> held in <strong>Glasgow</strong> in <strong>November 2021</strong>, India made a significant pledge. The nation committed to achieving <strong>net-zero emissions</strong> by the year <strong>2070</strong>.</p><p>This ambitious target positions India as a crucial player in the global pursuit of <strong>carbon neutrality</strong>. It underscores the country's dedication to combating climate change on an international platform.</p><h4>India's Renewable Energy Progress</h4><p>According to the <strong>Ministry of New and Renewable Energy</strong>, India has made substantial progress in its renewable energy sector. By <strong>2023</strong>, the country's installed <strong>renewable energy capacity</strong> surpassed <strong>180 GW</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p>India is actively pursuing an even more ambitious target: to reach <strong>500 GW</strong> of renewable energy capacity by <strong>2030</strong>. This rapid expansion is central to its climate mitigation strategy.</p></div><h4>Understanding Black Carbon Emissions</h4><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Black carbon</strong> is a component of fine particulate matter (<strong>PM2.5</strong>) that results from the incomplete combustion of fossil fuels, biofuels, and biomass. It is a powerful <strong>short-lived climate pollutant (SLCP)</strong>.</p><p>Unlike carbon dioxide, black carbon remains in the atmosphere for only a few days to weeks. However, its impact on warming is significant due to its strong light-absorbing properties.</p></div><h4>Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY) and its Role</h4><p>The <strong>Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY)</strong> is a flagship scheme launched by the <strong>Government of India</strong>. Its primary objective is to provide clean cooking fuel, specifically <strong>LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas)</strong>, to women from economically weaker sections.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>PMUY can play a significant role in India's journey towards <strong>net-zero emissions</strong>. By replacing traditional biomass fuels (like wood, cow dung, crop residue) with LPG, it directly contributes to mitigating <strong>black carbon emissions</strong>.</p></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>Understanding the link between social welfare schemes like <strong>PMUY</strong> and environmental goals like <strong>net-zero emissions</strong> is crucial for <strong>UPSC Mains GS-III</strong> (Environment) and <strong>GS-II</strong> (Government Policies and Interventions).</p></div>
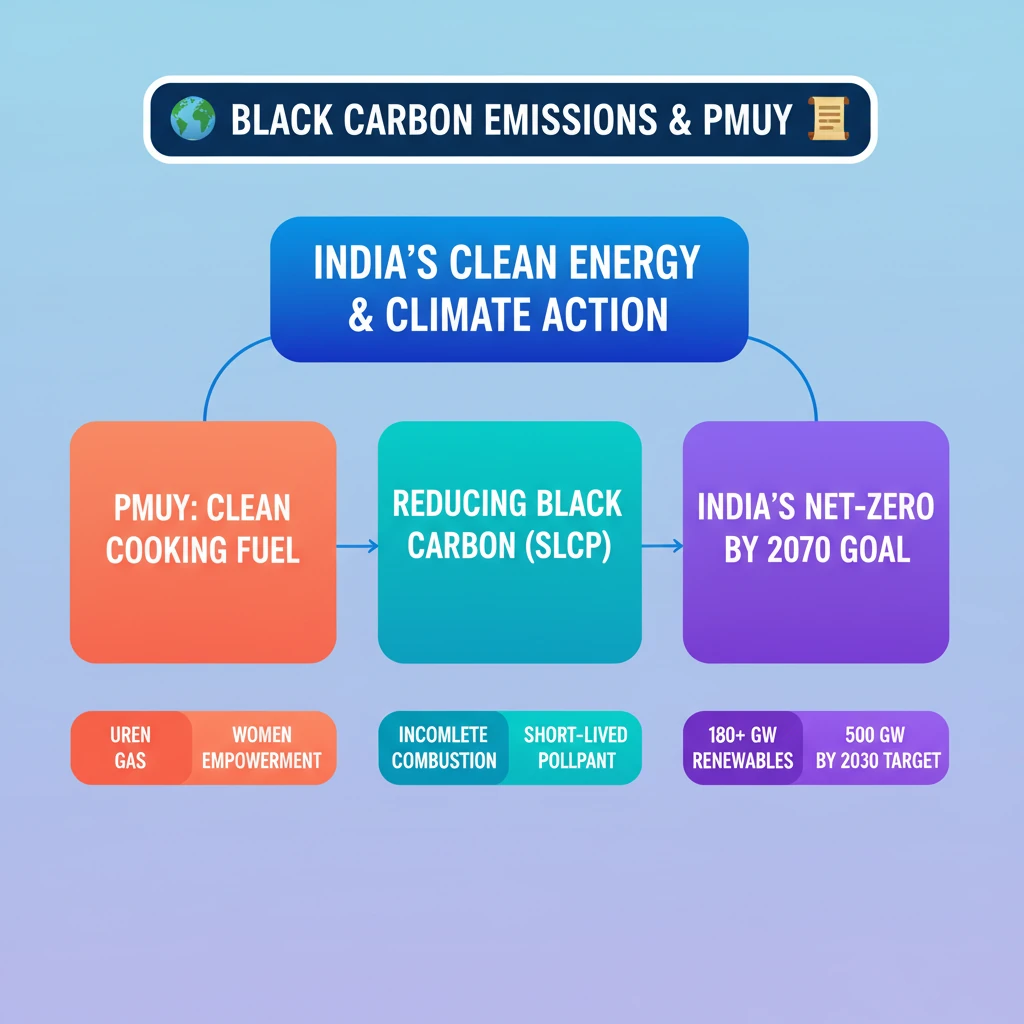
💡 Key Takeaways
- •India committed to achieving net-zero emissions by 2070 at UNFCCC COP26 in Glasgow.
- •Renewable energy capacity surpassed 180 GW by 2023, targeting 500 GW by 2030.
- •Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY) significantly mitigates black carbon emissions by promoting clean cooking fuel.
- •Black carbon is a potent short-lived climate pollutant (SLCP) from incomplete combustion.
- •PMUY is a key example of how social welfare schemes contribute to environmental and climate goals.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•UNFCCC (United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change) COP26 outcomes
•Press Information Bureau (PIB), Government of India - Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana
•NITI Aayog reports on India's energy transition