What Are the Key Facts Regarding Oysters’ Antimicrobial Properties? - Environment And Ecology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

What Are the Key Facts Regarding Oysters’ Antimicrobial Properties?
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
environment and ecology
📖 Introduction
<h4>Introduction to Oyster Antimicrobial Properties</h4><p><strong>Oysters</strong>, often recognized for their culinary value, possess remarkable intrinsic defense mechanisms. These mechanisms include the production of potent <strong>antimicrobial proteins and peptides (AMPs)</strong>.</p><p>These natural compounds are found primarily in the <strong>hemolymph</strong>, which is the circulatory fluid of oysters. They play a crucial role in protecting oysters from a wide array of marine microorganisms.</p><h4>Mechanism of Action and Efficacy</h4><p>The <strong>antimicrobial proteins and peptides</strong> derived from oyster hemolymph exhibit several powerful actions against harmful bacteria and their protective structures.</p><ul><li>They can effectively <strong>kill bacteria</strong>, including significant human pathogens like <strong>Streptococcus spp.</strong>, which are responsible for illnesses such as pneumonia, tonsillitis, and rheumatic fever.</li><li>These compounds possess the ability to <strong>inhibit and penetrate biofilms</strong>. Biofilms are complex communities of bacteria encased in a protective matrix, making them highly resistant to conventional antibiotics and immune responses.</li><li>Beyond direct action, oyster AMPs can significantly <strong>enhance the efficacy of conventional antibiotics</strong>. Studies indicate they can boost antibiotic effectiveness by a remarkable <strong>2 to 32 times</strong>.</li></ul><div class='key-point-box'><p>The dual action of directly killing pathogens and disrupting protective biofilms makes oyster AMPs a promising area for developing new therapeutic agents against drug-resistant infections.</p></div><h4>Oyster Immune Defenses</h4><p>Oysters thrive in marine environments teeming with diverse microorganisms. This constant exposure has led to the evolution of robust and sophisticated <strong>immune defenses</strong> within these bivalves.</p><p>Their <strong>hemolymph</strong> is a rich source of various <strong>antiviral and antibacterial proteins and peptides</strong>. These compounds are effective against a broad spectrum of both human and marine pathogens, highlighting their broad-spectrum activity.</p><h4>Significance for New Antimicrobial Agents</h4><p>The global fight against <strong>antimicrobial resistance (AMR)</strong> urgently requires the discovery of novel therapeutic compounds. Nature has historically been the primary source for such discoveries.</p><div class='info-box'><p>Currently, <strong>over 90% of antibiotics</strong> used by humans are derived from natural sources. Similarly, <strong>over 65% of antibiotics</strong> under recent development also originate from nature.</p></div><p>Oysters, with their potent and diverse AMPs, represent a significant, largely untapped natural resource for the development of the <strong>next generation of antimicrobial agents</strong>.</p><h4>Traditional Relevance</h4><p>The medicinal properties of oysters have been recognized and utilized in various traditional health systems for centuries.</p><ul><li>In <strong>Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)</strong>, oyster extracts have been historically employed to treat various <strong>respiratory and inflammatory conditions</strong>.</li><li>Oysters are also an integral component of the health practices and traditional knowledge systems of <strong>Indigenous Australians</strong>, showcasing their long-standing cultural and medicinal significance.</li></ul><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>Understanding the role of natural sources like oysters in combating <strong>Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)</strong> is crucial for UPSC. This topic can be linked to <strong>GS-III Science & Technology</strong> (biotechnology, health), <strong>Environment & Ecology</strong> (marine biodiversity), and even <strong>Ethics</strong> (traditional knowledge, public health responsibility).</p></div>
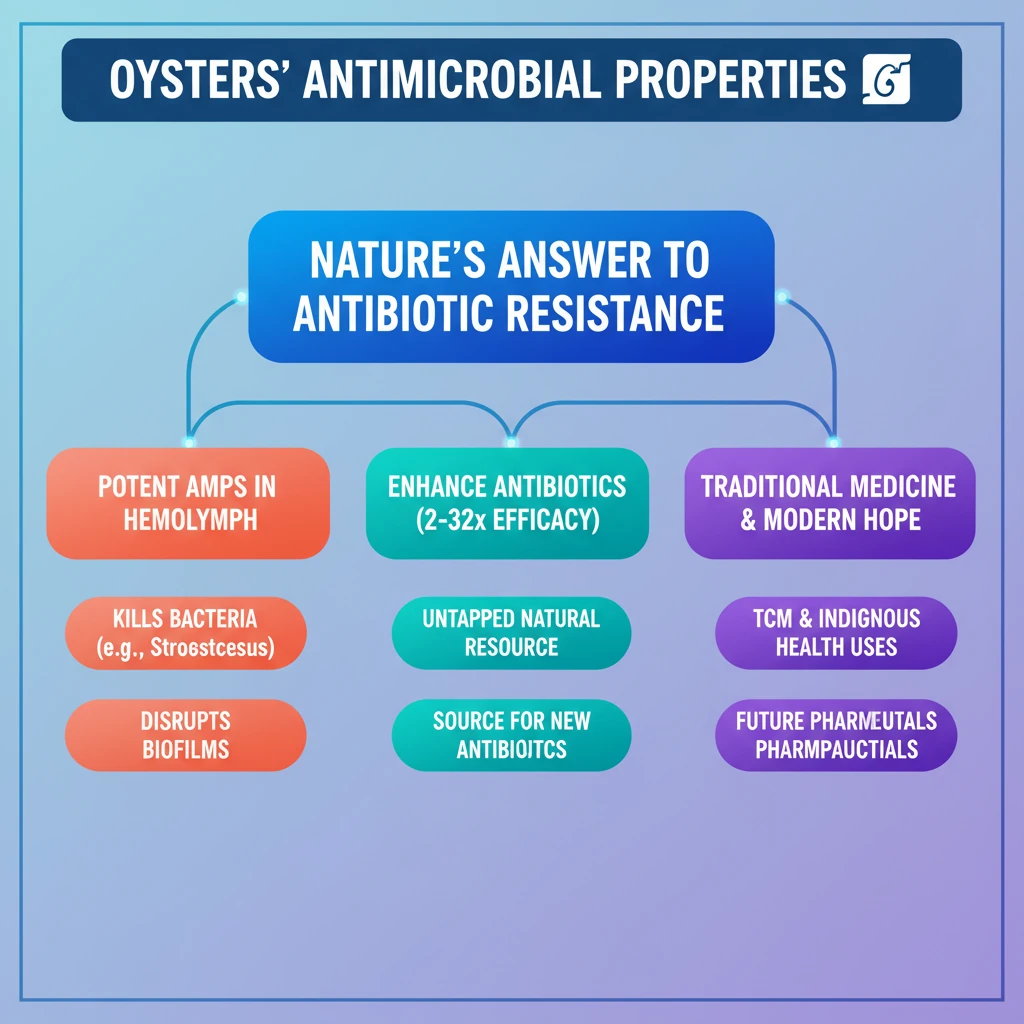
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Oysters produce potent antimicrobial proteins and peptides (AMPs) in their hemolymph.
- •These AMPs kill bacteria like Streptococcus spp. and disrupt protective biofilms.
- •Oyster compounds can enhance conventional antibiotic efficacy by 2 to 32 times.
- •Nature is a primary source for new antibiotics, and oysters represent a vital untapped resource.
- •Traditional Chinese Medicine and Indigenous Australians have historically used oysters for health.
- •Oysters offer a promising avenue in the global fight against the escalating Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) crisis.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content