Gases, Rainfall and Climate Change - Environment And Ecology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Gases, Rainfall and Climate Change
Medium⏱️ 5 min read
environment and ecology
📖 Introduction
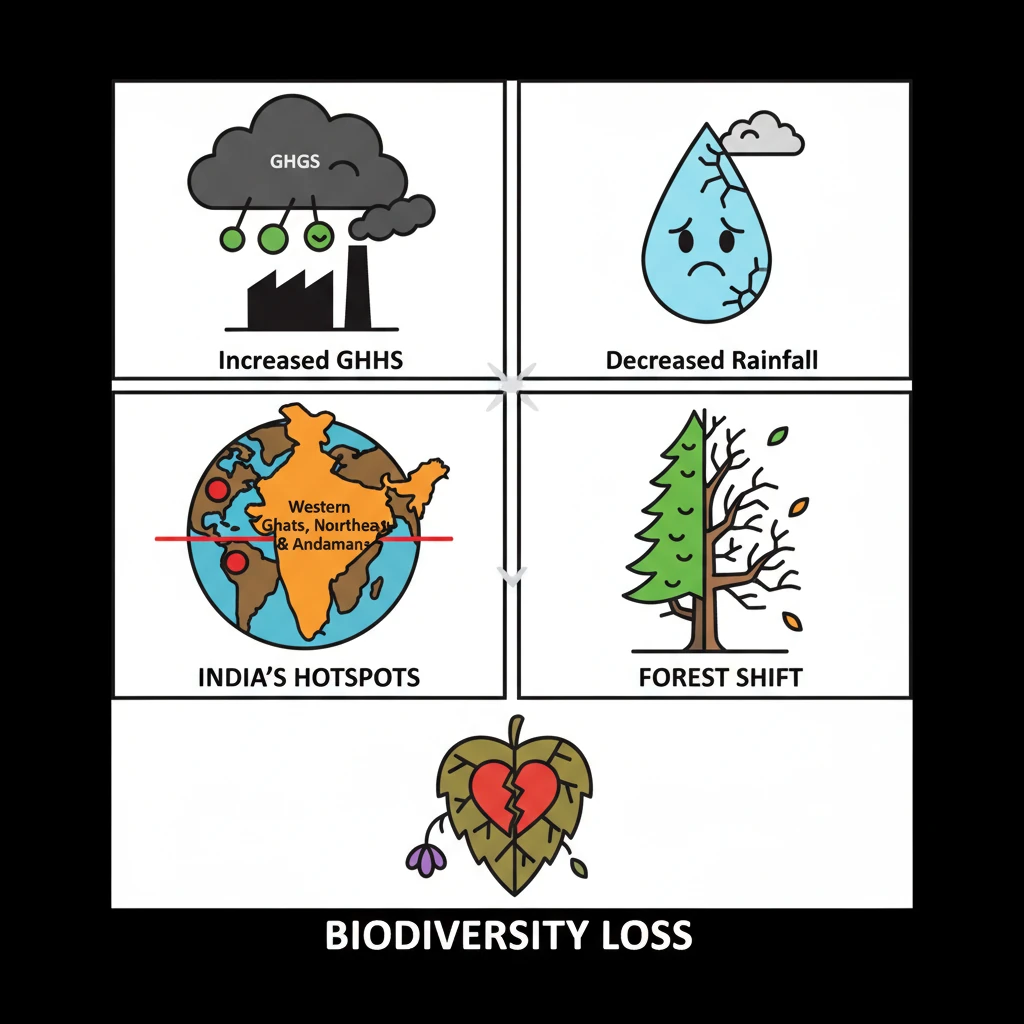
<h4>Recent Study on GHGs and Rainfall</h4><p>A <strong>recent study</strong> has highlighted a critical link between rising <strong>greenhouse gas (GHG)</strong> concentrations and changes in global rainfall patterns.</p><p>The research indicates that an <strong>unprecedented increase</strong> in atmospheric GHGs is projected to lead to a significant <strong>decrease in rainfall</strong> within the crucial <strong>equatorial region</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Greenhouse Gases (GHGs):</strong> Atmospheric gases that absorb and emit radiant energy within the thermal infrared range, causing the greenhouse effect. Key GHGs include <strong>carbon dioxide (CO2)</strong>, <strong>methane (CH4)</strong>, and <strong>nitrous oxide (N2O)</strong>.</p></div><h4>Impact on India's Biodiversity Hotspots</h4><p>This projected decline in equatorial rainfall has severe implications, particularly for <strong>India’s biodiversity hotspots</strong>.</p><p>The study warns of a potential ecological transformation: the existing <strong>evergreen forests</strong> in these regions could be replaced by <strong>deciduous forests</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The shift from <strong>evergreen to deciduous forests</strong> signifies a major ecological change, impacting species composition, water cycles, and overall ecosystem resilience.</p></div><h4>Affected Indian Regions</h4><p>The biodiversity hotspots identified as vulnerable to this transformation include:</p><ul><li>The <strong>Western Ghats</strong>: Known for its high endemism and rich biodiversity.</li><li><strong>Northeast India</strong>: A region characterized by diverse forest types and unique flora and fauna.</li><li>The <strong>Andaman and Nicobar Islands</strong>: Home to pristine rainforests and marine ecosystems.</li></ul><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>Understanding the specific regions affected (<strong>Western Ghats, Northeast India, Andamans</strong>) is crucial for UPSC. Questions often focus on geographical impacts of climate change.</p></div>
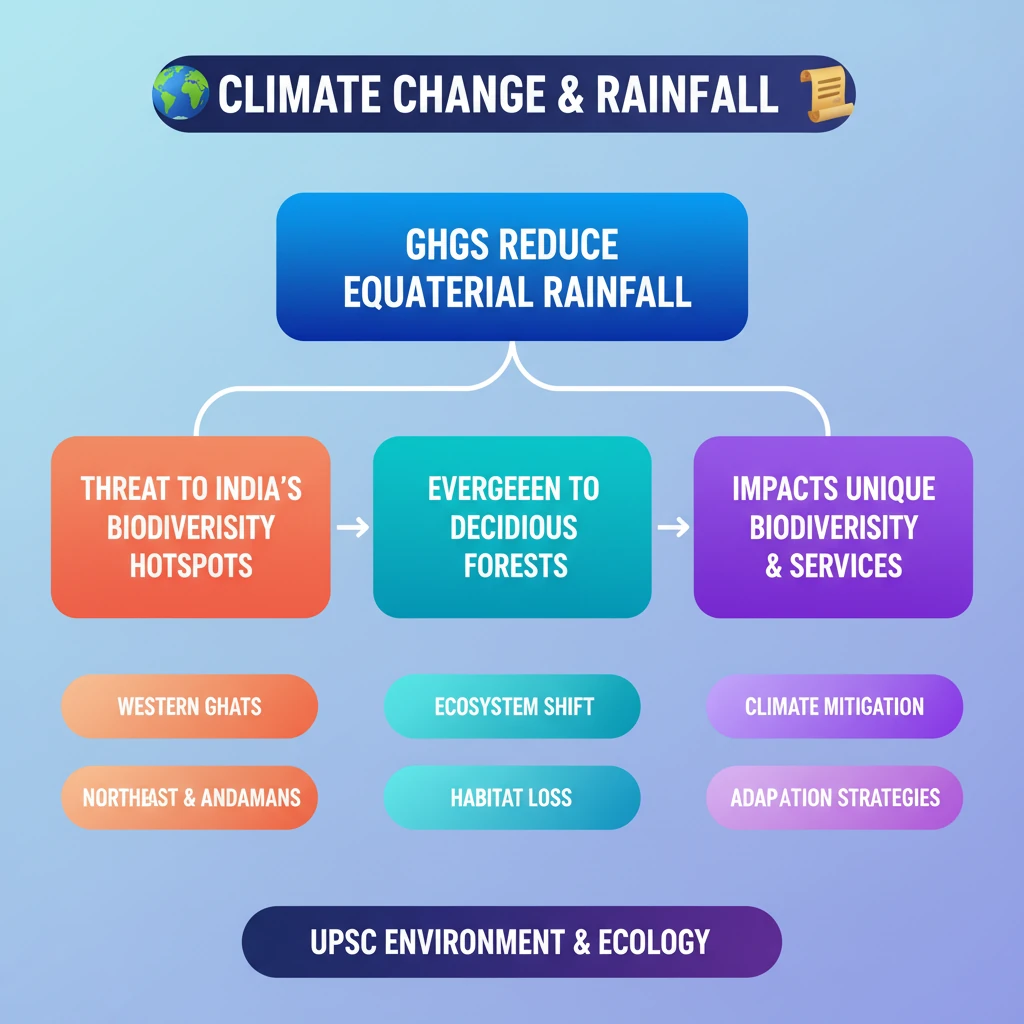
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Increased GHGs can decrease rainfall in equatorial regions.
- •This poses a threat to India's biodiversity hotspots (Western Ghats, Northeast, Andamans).
- •Evergreen forests in these regions could transform into deciduous forests.
- •Such a shift would severely impact unique biodiversity and ecosystem services.
- •Proactive climate mitigation and adaptation strategies are crucial for conservation.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content