Financial mechanisms - Environment And Ecology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
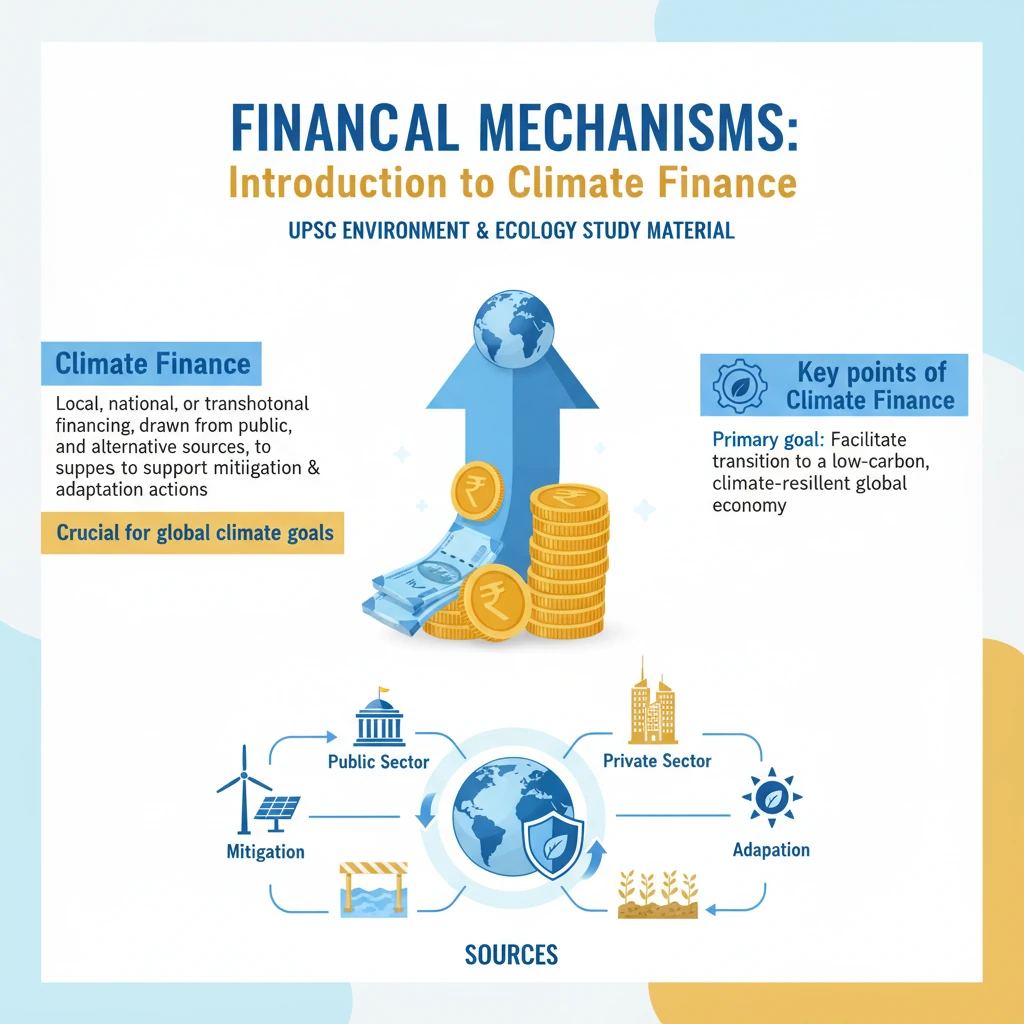
Financial mechanisms
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
environment and ecology
📖 Introduction
<h4>Introduction to Climate Finance</h4><p><strong>Climate finance</strong> refers to local, national, or transnational financing, drawn from public, private, and alternative sources of financing, that seeks to support mitigation and adaptation actions that will address climate change. It is crucial for achieving global climate goals.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The primary goal of <strong>climate finance</strong> is to facilitate the transition to a low-carbon, climate-resilient global economy, especially in developing countries.</p></div><h4>India's Need for Climate Finance</h4><p><strong>India</strong> requires substantial <strong>climate finance</strong> to meet its ambitious climate targets and foster sustainable development. This funding is essential across various sectors to drive transformative change.</p><p>Specifically, India needs significant investment to <strong>scale up renewable energy installations</strong>, such as solar and wind power projects. This transition is vital for reducing reliance on fossil fuels and cutting greenhouse gas emissions.</p><p>Furthermore, finance is needed to <strong>modernise infrastructure</strong>, making it more resilient to climate impacts and less carbon-intensive. This includes green buildings, efficient transportation networks, and sustainable urban planning.</p><p>Improving <strong>energy efficiency</strong> across industries, residential sectors, and transport is another critical area. Financial mechanisms can support the adoption of energy-saving technologies and practices.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Mains (GS-III)</strong> often asks about India's climate change challenges and solutions, where the need for and access to <strong>climate finance</strong> is a crucial point to discuss.</p></div><h4>Key Financial Mechanisms under UNFCCC</h4><p>The <strong>United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC)</strong> has established several dedicated financial mechanisms. These are designed to provide financial resources to developing countries to help them address climate change.</p><p>These mechanisms aim to ensure that developing nations have the means to implement both <strong>mitigation</strong> (reducing emissions) and <strong>adaptation</strong> (adjusting to climate impacts) strategies effectively.</p><ul><li><strong>Adaptation Fund (AF)</strong>: Established under the <strong>Kyoto Protocol</strong> in <strong>2001</strong>, it finances concrete adaptation projects and programmes in developing countries that are particularly vulnerable to the adverse effects of climate change.</li><li><strong>Green Climate Fund (GCF)</strong>: Created in <strong>2010</strong> under the <strong>UNFCCC</strong>, the <strong>GCF</strong> is the largest dedicated climate fund. It supports developing countries in limiting or reducing their greenhouse gas emissions and adapting to climate change.</li><li><strong>Global Environment Facility (GEF)</strong>: While predating the <strong>UNFCCC</strong> (established in <strong>1991</strong>), the <strong>GEF</strong> serves as a financial mechanism for several multilateral environmental agreements, including the <strong>UNFCCC</strong>. It provides grants for projects related to biodiversity, climate change, international waters, land degradation, forest management, and chemicals/waste.</li></ul><div class='info-box'><p>These funds operate on the principle of <strong>Common But Differentiated Responsibilities and Respective Capabilities (CBDR-RC)</strong>, acknowledging that developed countries have a greater historical responsibility and capacity to provide financial support.</p></div>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •Climate finance supports mitigation and adaptation efforts globally.
- •India needs substantial climate finance for renewable energy, infrastructure modernization, and energy efficiency.
- •UNFCCC established key financial mechanisms: Adaptation Fund, Green Climate Fund, and Global Environment Facility.
- •These funds operate on the principle of Common But Differentiated Responsibilities.
- •Access to climate finance is critical for India to achieve its ambitious NDC targets.
- •Historical context shows a progression from UNFCCC commitments to dedicated financial institutions.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Green Climate Fund (GCF) Official Website (greenclimate.fund)
•Adaptation Fund Official Website (adaptation-fund.org)
•Global Environment Facility (GEF) Official Website (thegef.org)
•Drishti IAS Study Material on Environment & Ecology