What is Geoengineering? - Environment And Ecology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
What is Geoengineering?
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
environment and ecology
📖 Introduction
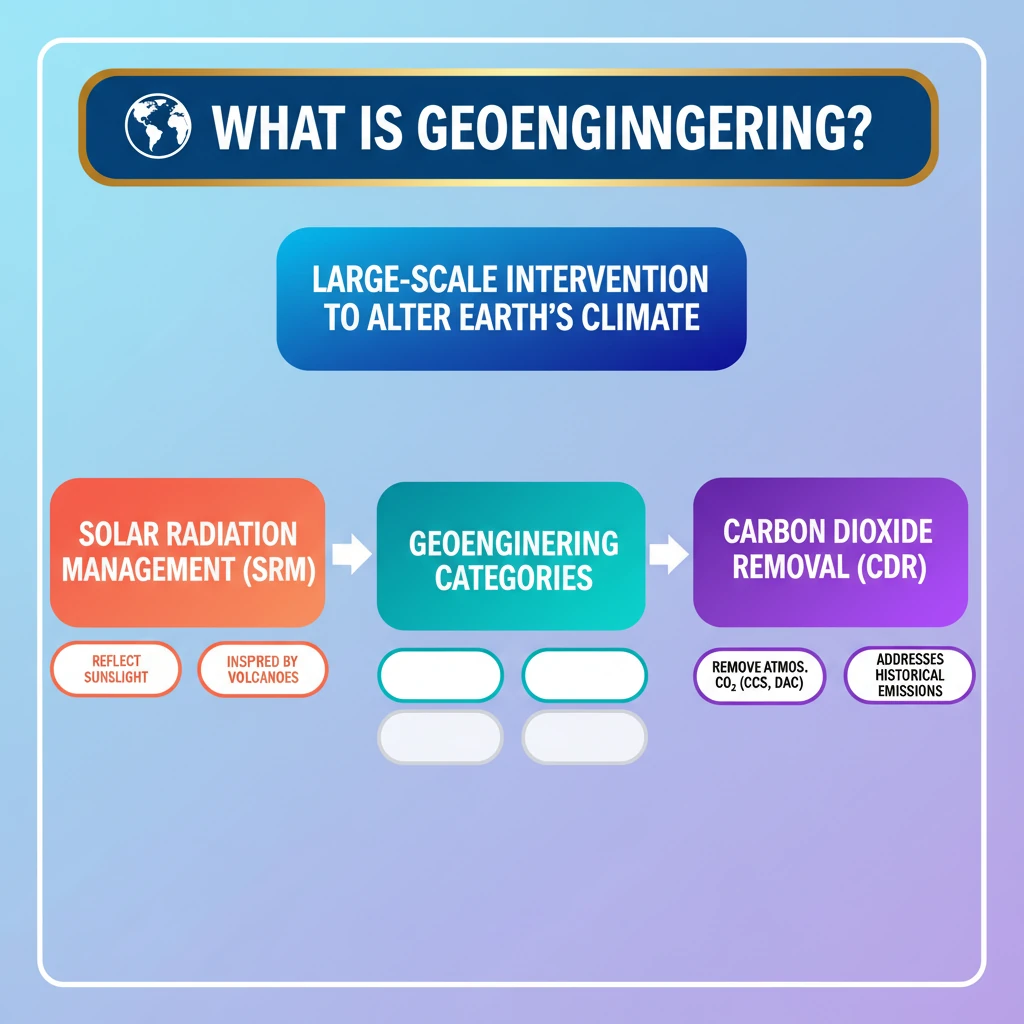
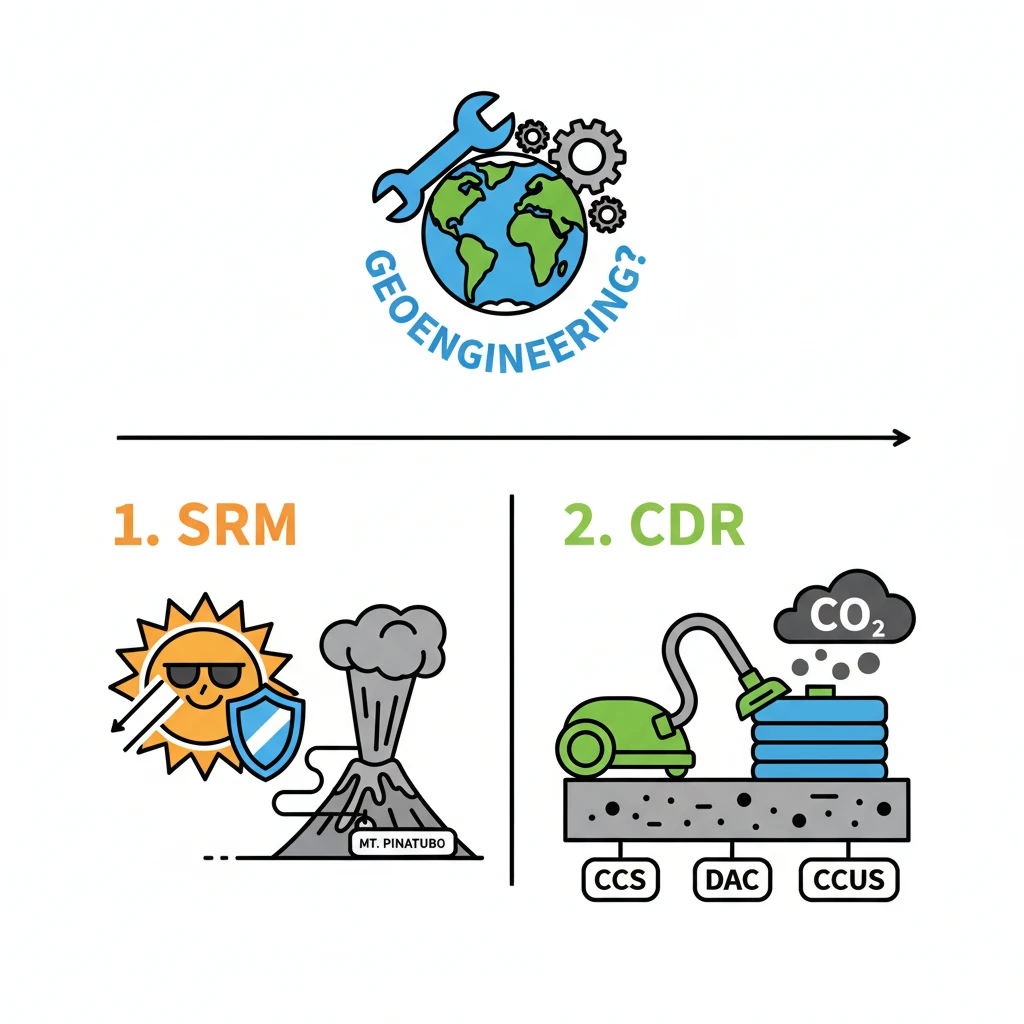
<h4>Understanding Geoengineering: Large-Scale Climate Intervention</h4><p><strong>Geoengineering</strong> refers to large-scale interventions designed to deliberately alter the <strong>Earth’s climate system</strong>. The primary goal is to counteract the adverse effects of <strong>global warming</strong>.</p><p>More specifically, it often focuses on managing <strong>solar radiation</strong> or removing <strong>carbon dioxide</strong> from the atmosphere.</p><h4>Classification of Geoengineering Approaches</h4><p>Geoengineering primarily involves two distinct approaches, each targeting different aspects of the climate system:</p><ul> <li><strong>Solar Radiation Management (SRM)</strong></li> <li><strong>Carbon Dioxide Removal (CDR)</strong></li></ul><h4>Solar Radiation Management (SRM)</h4><p><strong>SRM</strong> techniques aim to reflect a small percentage of the <strong>sun's rays</strong> back into space, thereby reducing the amount of solar energy absorbed by Earth.</p><div class='info-box'> <p><strong>Mechanism:</strong> SRM involves deploying materials or altering atmospheric properties to increase the Earth's <strong>albedo</strong> (reflectivity).</p> <p><strong>Inspiration:</strong> This method draws inspiration from natural phenomena, such as large <strong>volcanic eruptions</strong>, which release aerosols into the stratosphere, temporarily cooling the planet.</p></div><p>A notable example is the <strong>1991 eruption of Mount Pinatubo</strong> in the Philippines, which reportedly reduced Earth's average temperature by approximately <strong>0.5°C</strong> that year.</p><div class='key-point-box'> <p><strong>Key Point:</strong> SRM is considered a rapid-acting approach but does not address the root cause of climate change, which is increased <strong>greenhouse gas concentrations</strong>.</p></div><h4>Carbon Dioxide Removal (CDR)</h4><p><strong>CDR</strong> techniques focus on actively removing <strong>carbon dioxide (CO2)</strong> from the atmosphere and storing it away for long periods. The aim is to reduce the overall concentration of this primary greenhouse gas.</p><div class='info-box'> <p><strong>Objective:</strong> CDR methods are designed for the <strong>long-term reduction</strong> of atmospheric CO2 levels, directly tackling the cause of global warming.</p></div><h4>Carbon Capture and Sequestration (CCS)</h4><p><strong>CCS</strong> is currently the most practiced <strong>CDR method</strong>. It involves capturing CO2 emissions from large industrial sources and preventing them from entering the atmosphere.</p><div class='info-box'> <p><strong>Process:</strong> CO2 is captured from industrial exhaust streams (e.g., power plants, cement factories) and then transported for storage deep underground in suitable <strong>geological formations</strong>.</p></div><p>This process effectively reduces direct industrial <strong>CO2 emissions</strong>.</p><h4>Direct Air Capture (DAC)</h4><p><strong>DAC</strong> is a technology that extracts <strong>CO2 directly from ambient air</strong>, rather than from a concentrated emission source.</p><div class='info-box'> <p><strong>Mechanism:</strong> Large devices, sometimes referred to as "artificial trees," are used to chemically filter CO2 from the air. The captured CO2 can then be stored or utilized.</p></div><div class='key-point-box'> <p><strong>Potential and Challenges:</strong> DAC holds significant potential as it can address <strong>historical CO2 emissions</strong> already in the atmosphere. However, it faces more substantial technological and economic challenges compared to CCS.</p></div><h4>Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage (CCUS)</h4><p><strong>CCUS</strong> is an integrated approach that goes beyond just storage. It involves capturing CO2, then either utilizing it in various industrial processes or storing it permanently.</p><div class='info-box'> <p><strong>Utilization:</strong> Some captured <strong>CO2</strong> is repurposed for applications like enhanced oil recovery, production of fuels, or manufacturing of building materials. The remainder is stored permanently.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Geoengineering involves large-scale interventions to alter Earth's climate.
- •It has two main categories: Solar Radiation Management (SRM) and Carbon Dioxide Removal (CDR).
- •SRM aims to reflect sunlight, inspired by volcanic eruptions like Mount Pinatubo.
- •CDR focuses on removing atmospheric CO2, using techniques like CCS, DAC, and CCUS.
- •DAC can address historical emissions but faces significant challenges.
- •Geoengineering is a complementary, not replacement, strategy for emissions reduction.
🧠 Memory Techniques
98% Verified Content