NGT Imposed Penalty on State Govt of Punjab - Environment And Ecology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

NGT Imposed Penalty on State Govt of Punjab
Medium⏱️ 6 min read
environment and ecology
📖 Introduction
<h4>NGT Imposes Penalty on Punjab Government: Overview</h4><p>The <strong>National Green Tribunal (NGT)</strong> recently imposed a substantial penalty on the <strong>Punjab government</strong>. This action was taken due to the state's persistent failure in effectively managing <strong>solid and liquid wastes</strong> within its jurisdiction.</p><p>This penalty follows multiple warnings issued by the NGT, highlighting a recurring pattern of non-compliance with environmental norms.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Penalty Details:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Amount:</strong> <strong>₹1,000 crore</strong></li><li><strong>Recipient:</strong> <strong>Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB)</strong></li><li><strong>Deadline:</strong> To be deposited within <strong>one month</strong></li></ul></div><h4>Reasons for the Penalty: Waste Management Failure</h4><p>The NGT's decision to impose the penalty was primarily based on the state government's inability to manage both solid and liquid waste efficiently. This failure has led to significant environmental degradation.</p><p>The tribunal meticulously calculated the penalty amount, considering various aspects of the environmental damage caused over a specific period.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Penalty Calculation Basis (over six months):</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Legacy Waste:</strong> For <strong>5.387 million tonnes</strong> of accumulated waste.</li><li><strong>Untreated Sewage:</strong> Due to delays in establishing adequate <strong>sewage treatment capacity</strong>.</li></ul></div><h4>Legal Framework and Non-Compliance</h4><p>The NGT underscored that the state's actions were in direct violation of established environmental laws and regulations. Key among these are the rules governing waste management and broader environmental protection acts.</p><p>The tribunal explicitly cited specific legal provisions that apply to this case, reinforcing the legal grounds for its intervention.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Applicable Legal Provisions:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Solid Waste Management Rules, 2016:</strong> These rules mandate scientific management of solid waste.</li><li><strong>Section 15 of the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986:</strong> This section deals with penalties for contravention of the Act and rules.</li></ul></div><h4>Repeated Violations and Prior Directives</h4><p>The NGT noted that this was not an isolated incident. The <strong>Punjab government</strong> had previously failed to comply with the tribunal's orders issued in <strong>2022</strong>.</p><p>One significant previous directive involved the creation of a <strong>ring-fenced account</strong>, designed to ensure dedicated funds for environmental remediation.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Previous NGT Order (2022):</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Directive:</strong> Create a ring-fenced account.</li><li><strong>Amount:</strong> <strong>₹2,000 crore</strong></li><li><strong>Legal Basis:</strong> Under <strong>Section 26 of the NGT Act, 2010</strong>.</li></ul></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> NGT's role as a statutory body for environmental justice is crucial. Questions often focus on its powers, jurisdiction, and landmark judgments. Understanding cases like this helps illustrate the practical application of environmental laws and the concept of the <strong>'Polluter Pays Principle'</strong>.</p></div>
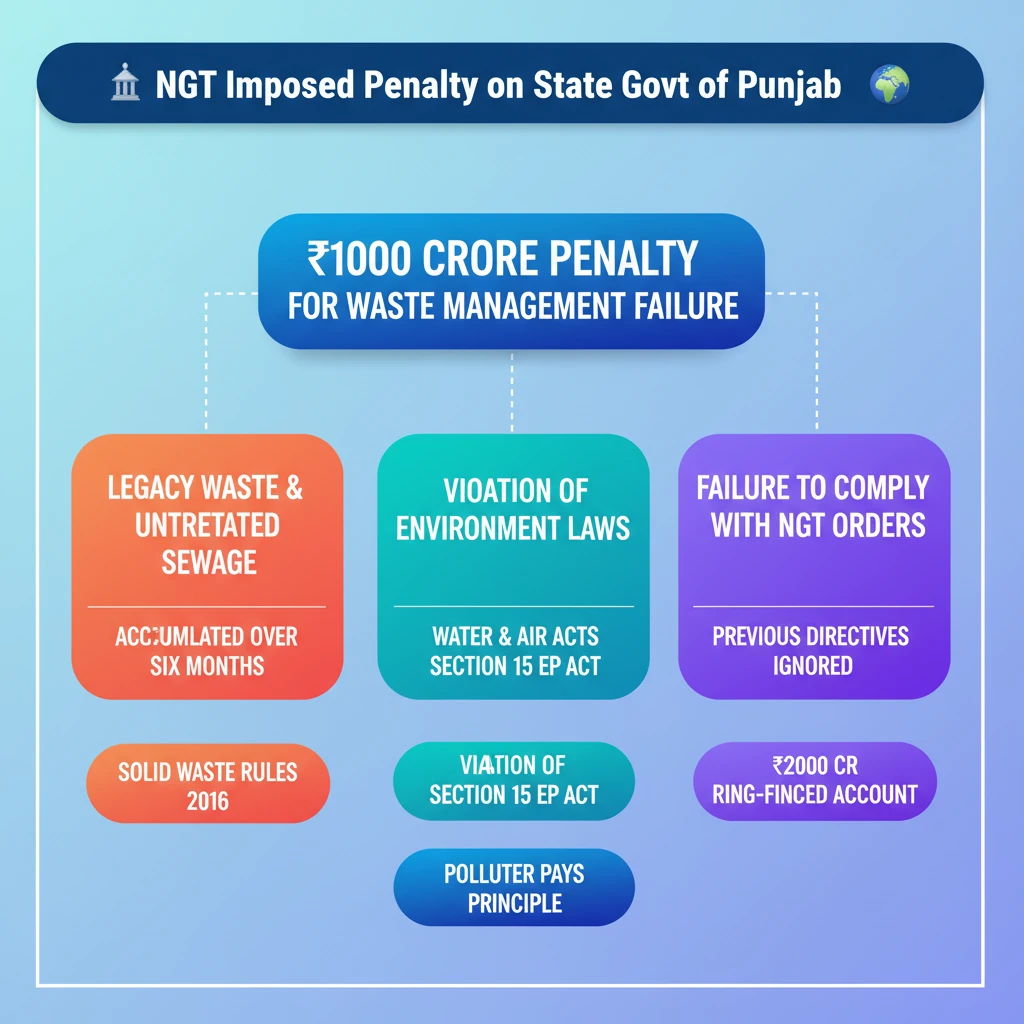
💡 Key Takeaways
- •NGT imposed a ₹1,000 crore penalty on Punjab for failing to manage solid and liquid waste.
- •The penalty was based on accumulated legacy waste and untreated sewage, calculated over six months.
- •Punjab violated Solid Waste Management Rules, 2016, and Section 15 of the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986.
- •The state had also failed to comply with previous NGT orders, including creating a ₹2,000 crore ring-fenced account.
- •NGT's actions underscore its crucial role in environmental enforcement and upholding the 'Polluter Pays Principle'.
🧠 Memory Techniques

98% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•National Green Tribunal Act, 2010
•Environment (Protection) Act, 1986
•Solid Waste Management Rules, 2016
•Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) official reports (general knowledge)