Ground Level Ozone Pollution - Environment And Ecology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Ground Level Ozone Pollution
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
environment and ecology
📖 Introduction
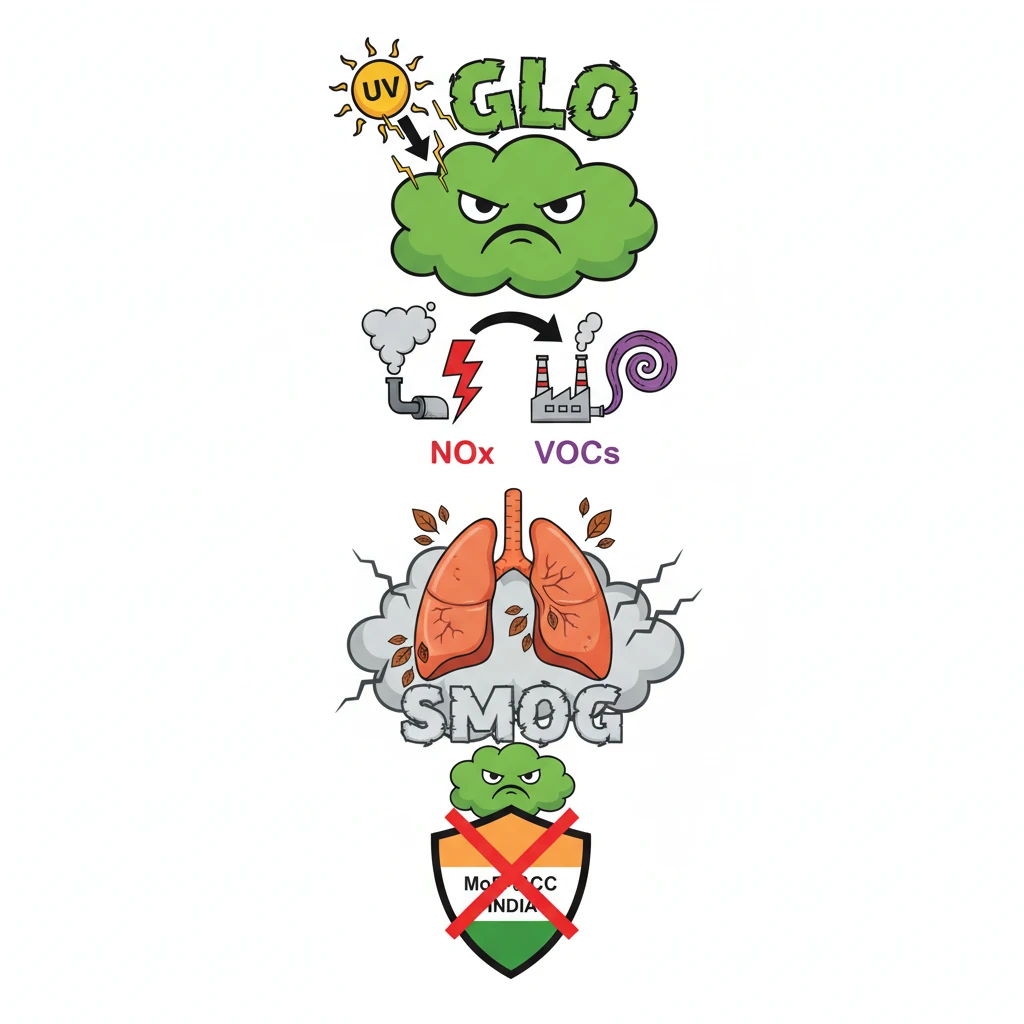
<h4>Introduction to Ground Level Ozone Pollution</h4><p><strong>Ground Level Ozone (GLO)</strong>, also known as <strong>tropospheric ozone</strong>, is a harmful air pollutant that forms near the Earth's surface. Unlike stratospheric ozone, which protects us from UV radiation, GLO is detrimental to human health and ecosystems.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Key Concept:</strong> Ground Level Ozone is a <strong>secondary pollutant</strong>, meaning it is not directly emitted into the air. Instead, it forms through chemical reactions involving other pollutants.</p></div><h4>Formation of Ground Level Ozone</h4><p>GLO forms when precursor pollutants, primarily <strong>Nitrogen Oxides (NOx)</strong> and <strong>Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)</strong>, react in the presence of sunlight. These reactions are complex and are influenced by temperature, humidity, and atmospheric conditions.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Precursors for GLO Formation:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Nitrogen Oxides (NOx):</strong> Emitted from combustion sources like vehicles, power plants, and industrial boilers.</li><li><strong>Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs):</strong> Released from sources such as vehicle exhaust, industrial processes, chemical solvents, and even natural sources like vegetation.</li></ul></div><h4>Sources and Distribution</h4><p>The primary sources of <strong>NOx</strong> and <strong>VOCs</strong> are human activities. Urban and industrial areas, with high traffic density and industrial output, are particularly susceptible to high concentrations of ground-level ozone, especially during warm, sunny periods.</p><h4>Harmful Effects of Ground Level Ozone</h4><p>GLO has significant adverse impacts on both human health and the environment. It is a major component of <strong>smog</strong> and poses serious risks.</p><ul><li><strong>Human Health:</strong> Causes respiratory problems, exacerbates asthma, reduces lung function, and can lead to premature mortality.</li><li><strong>Vegetation and Ecosystems:</strong> Damages plant tissues, reduces crop yields, affects forest growth, and impacts biodiversity.</li><li><strong>Materials:</strong> Can degrade materials like rubber, plastics, and paints.</li></ul><h4>Government Initiatives and Concern</h4><p>The <strong>Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC)</strong> has highlighted the steps being taken to control <strong>Ground Level Ozone Pollution (GLOP)</strong> in India. This indicates the government's recognition of GLO as a critical environmental and public health issue.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Understanding the distinction between stratospheric and ground-level ozone is crucial. Questions often test this differentiation and the specific impacts of GLO.</p></div>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •Ground Level Ozone (GLO) is a harmful secondary air pollutant, distinct from beneficial stratospheric ozone.
- •GLO forms from precursor pollutants (NOx, VOCs) reacting in sunlight, primarily from human activities.
- •It causes severe respiratory issues, damages crops, and contributes to photochemical smog.
- •The MoEF&CC is actively addressing GLO pollution in India.
- •India's efforts like NCAP and BS-VI norms aim to control GLO precursors.
- •Understanding GLO is crucial for UPSC, especially for environment, health, and agriculture topics.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•National Clean Air Programme (NCAP) documents
•Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) data and guidelines
•World Health Organization (WHO) air quality guidelines
•Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) publications on ozone pollution
•Scientific literature on tropospheric ozone formation and impacts