What are Salt Pan Lands - Environment And Ecology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

What are Salt Pan Lands
Medium⏱️ 4 min read
environment and ecology
📖 Introduction
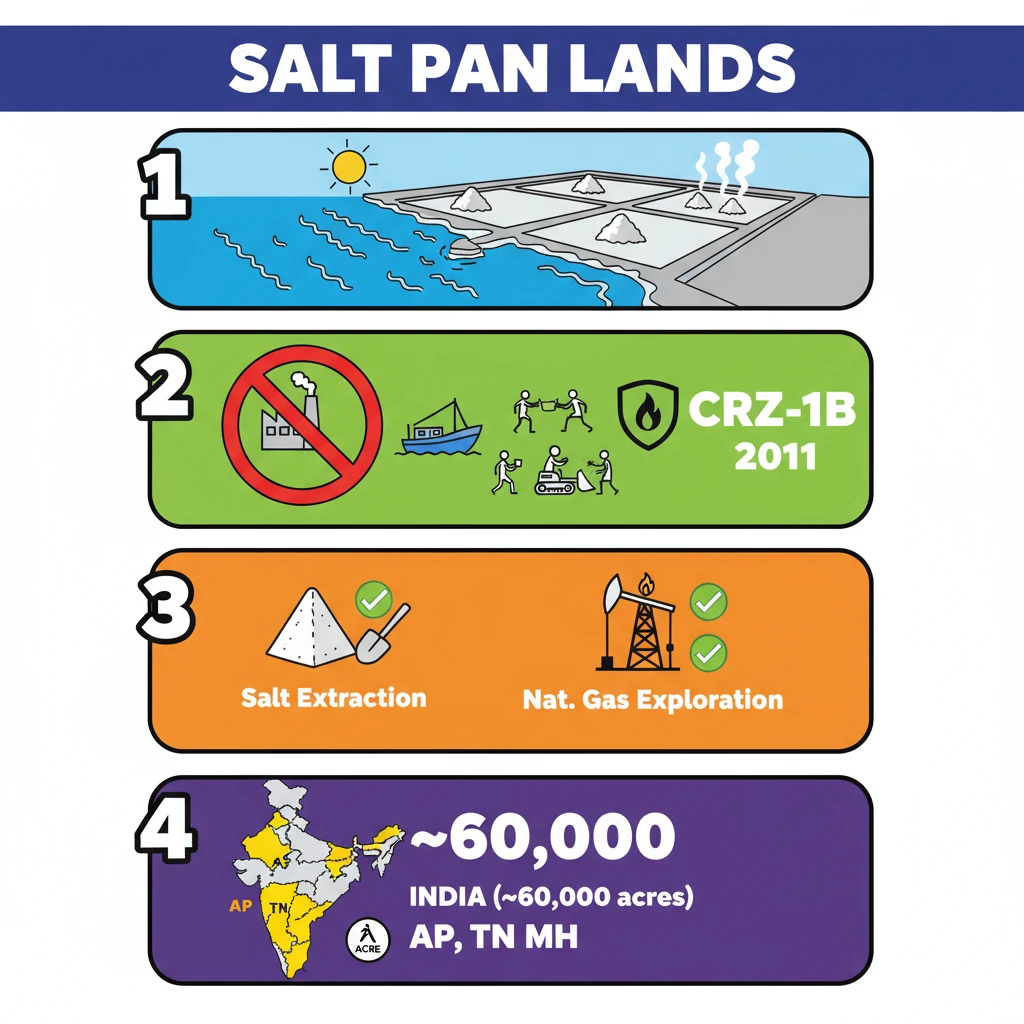
<h4>Introduction to Salt Pan Lands</h4><p><strong>Salt pan lands</strong> are distinct low-lying coastal areas. Here, <strong>seawater</strong> periodically flows in and then recedes or evaporates, leaving behind valuable deposits of <strong>salt and other minerals</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Definition:</strong> <strong>Salt pan lands</strong> are coastal tracts characterized by periodic inundation by seawater, leading to the deposition of salt and minerals upon evaporation.</p></div><p>This natural process is not merely geological; it plays a fundamental role in maintaining the delicate balance of <strong>coastal ecosystems</strong>. They are crucial habitats for various flora and fauna adapted to saline conditions.</p><h4>Protection Status and Regulations</h4><p>Recognizing their ecological sensitivity, <strong>salt pan lands</strong> are afforded special protection under Indian environmental law. The <strong>Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ) Notification of 2011</strong> specifically addresses these areas.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>CRZ Classification:</strong> Under the <strong>CRZ Notification of 2011</strong>, <strong>salt pan lands</strong> are classified under <strong>CRZ-1B</strong>. This designation signifies them as highly ecologically sensitive areas.</p></div><p>The <strong>CRZ-1B</strong> classification imposes significant restrictions on economic activities within these zones. The primary goal is to preserve their ecological integrity and prevent degradation.</p><ul><li><strong>Restricted Activities:</strong> Most economic development activities are strictly prohibited.</li><li><strong>Permitted Activities:</strong> Only specific activities like <strong>salt extraction</strong> and <strong>natural gas exploration</strong> are allowed, provided they adhere to stringent environmental norms.</li></ul><h4>Salt Pan Lands in India</h4><p>India possesses a significant expanse of <strong>salt pan lands</strong>, crucial for both ecological balance and traditional salt production. These lands are distributed across several coastal states.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>National Overview:</strong> Approximately <strong>60,000 acres</strong> of <strong>salt pan lands</strong> have been identified across India.</p></div><p>These lands are vital for local economies and provide unique ecosystems. Their distribution highlights the extensive coastline of India.</p><ul><li><strong>Major States:</strong> States with significant <strong>salt pan lands</strong> include <strong>Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Odisha, Gujarat,</strong> and <strong>Karnataka</strong>.</li></ul><p>Specific regions hold larger concentrations of these lands, indicating their regional importance.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>State-wise Distribution (Acreage):</strong><ul><li><strong>Andhra Pradesh:</strong> Largest expanse with <strong>20,716 acres</strong>.</li><li><strong>Tamil Nadu:</strong> Second largest with <strong>17,095 acres</strong>.</li><li><strong>Maharashtra:</strong> Significant area with <strong>12,662 acres</strong>.</li></ul></p></div><p>In urban centers like <strong>Mumbai</strong>, these lands face unique challenges due to developmental pressures.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Mumbai Specifics:</strong> A total of <strong>5,378 acres</strong> have been designated as <strong>salt pan lands</strong> within the city limits of <strong>Mumbai</strong>.</p></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Questions on <strong>CRZ classifications</strong>, particularly <strong>CRZ-1B</strong>, and the ecological/economic significance of <strong>salt pan lands</strong> are common in <strong>GS Paper III (Environment & Ecology)</strong>. Be prepared to discuss their conservation challenges.</p></div>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •Salt pan lands are low-lying coastal areas where seawater evaporates, leaving salt and minerals.
- •They are classified as CRZ-1B under the CRZ Notification of 2011, restricting most economic activities.
- •Salt extraction and natural gas exploration are the only permitted activities.
- •India has ~60,000 acres of salt pan lands, with Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, and Maharashtra having the largest shares.
- •They play a critical role in coastal ecosystem balance, biodiversity, and flood mitigation.
- •Face significant conservation challenges due to urban development pressures.
🧠 Memory Techniques
98% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ) Notification, 2011 (Official Document)
•Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) publications on CRZ