Forest Advisory Committee (FAC) - Environment And Ecology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Forest Advisory Committee (FAC)
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
environment and ecology
📖 Introduction
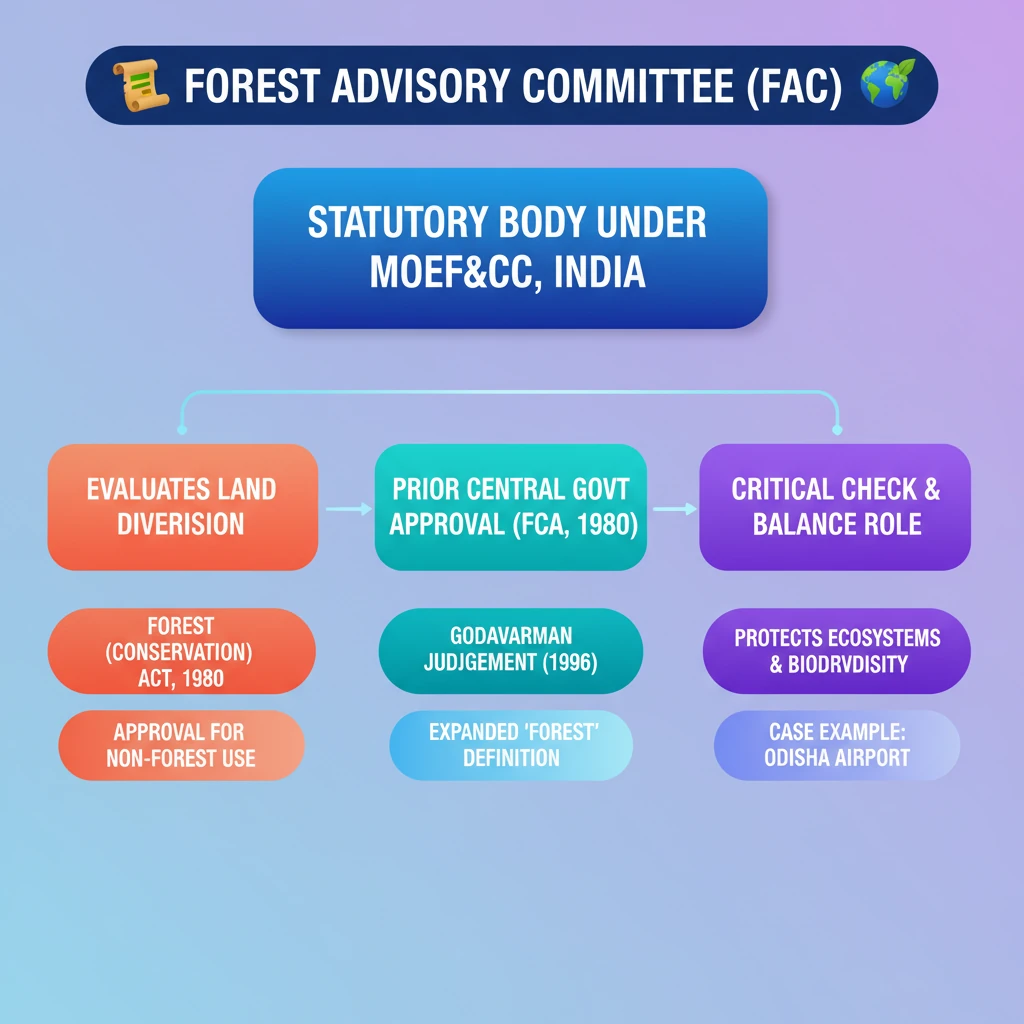
<h4>Why in News?</h4><p>Recently, the <strong>Forest Advisory Committee (FAC)</strong> of the <strong>Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change (MoEF&CC)</strong> issued a reprimand to the <strong>Odisha government</strong>.</p><p>The reprimand was for constructing walls on forest land without prior approval. This land is designated for the proposed <strong>Shree Jagannath International Airport</strong> in <strong>Puri</strong>.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'>This incident highlights the critical role of the <strong>FAC</strong> in ensuring compliance with environmental regulations, particularly the <strong>Forest (Conservation) Act, 1980</strong>.</div><h4>What is the Forest Advisory Committee (FAC)?</h4><p>The <strong>Forest Advisory Committee (FAC)</strong> is a <strong>statutory body</strong> established under the provisions of the <strong>Forest (Conservation) Act, 1980</strong>.</p><p>It operates under the administrative control of the <strong>Ministry of Environment, Forests & Climate Change (MoEF&CC)</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><ul><li><strong>Nature:</strong> Statutory body</li><li><strong>Parent Act:</strong> Forest (Conservation) Act, 1980</li><li><strong>Ministry:</strong> Ministry of Environment, Forests & Climate Change (MoEF&CC)</li></ul></div><p>The primary function of the <strong>FAC</strong> is to evaluate industrial or developmental projects that necessitate the <strong>diversion of forest land</strong> for non-forest activities.</p><p>The committee holds the authority to either approve or reject such projects. It can also grant approval with specific conditions attached to mitigate environmental impact.</p><p>In the recent <strong>Odisha case</strong>, satellite imagery revealed that the agency involved had already commenced wall construction without awaiting the necessary approval from the <strong>FAC</strong>, demonstrating a clear violation of protocol.</p><div class='key-point-box'>The <strong>FAC's</strong> approval is mandatory for any project involving the diversion of forest land, underscoring its role as a gatekeeper for forest conservation.</div><h4>What is the Forest Conservation Act, 1980?</h4><p>The <strong>Forest Conservation Act (FCA) of 1980</strong> was enacted with the objective of streamlining forest-related laws and regulating various activities impacting forest ecosystems.</p><p>Its key aims include controlling <strong>deforestation</strong>, overseeing the transportation of <strong>forest products</strong>, and levying duties on timber and other forest produce.</p><div class='info-box'><ul><li><strong>Enactment Year:</strong> 1980</li><li><strong>Primary Goal:</strong> Regulate deforestation and forest land diversion.</li><li><strong>Key Requirement:</strong> Prior Central Government approval for non-forest use of forest land.</li></ul></div><p>A crucial provision of this <strong>Act</strong> mandates that prior approval from the <strong>Central Government</strong> is essential before any forest land can be diverted for <strong>non-forest purposes</strong>.</p><p>Initially, the <strong>FCA 1980</strong> primarily applied to lands recognized as forests under the <strong>Indian Forest Act, 1927</strong>, or those recorded as forest land in State records since <strong>1980</strong>.</p><h4>Supreme Court's Interpretation: Godavarman Judgement, 1996</h4><p>A landmark ruling by the <strong>Supreme Court</strong> in the <strong>T.N. Godavarman Thirumulpad vs Union of India case</strong> in <strong>1996</strong> significantly broadened the scope of forest protection.</p><p>This judgement, often referred to as the <strong>Godavarman judgement</strong>, mandated the protection of all forests, irrespective of their official classification or ownership status.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'>The <strong>Godavarman judgement</strong> is a pivotal legal precedent for environmental law in India, extending the protective ambit of the <strong>FCA 1980</strong> to 'deemed forests' and unrecorded forest areas.</div><div class='key-point-box'>This ruling ensured that the definition of "forest" for the purpose of the <strong>FCA 1980</strong> is not limited to legally notified forests but includes any area that fits the dictionary meaning of a forest.</div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •FAC is a statutory body under MoEF&CC, established by the Forest (Conservation) Act, 1980.
- •Its primary role is to evaluate and approve proposals for diverting forest land for non-forest purposes.
- •The Forest (Conservation) Act, 1980, mandates prior Central Government approval for such diversions.
- •The Godavarman Judgement (1996) significantly expanded the definition of 'forest' to include all areas resembling forests, regardless of classification.
- •FAC acts as a critical check and balance in development projects impacting forest ecosystems, as seen in the Odisha airport case.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content