Woody Encroachment in Grasslands - Environment And Ecology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Woody Encroachment in Grasslands
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
environment and ecology
📖 Introduction
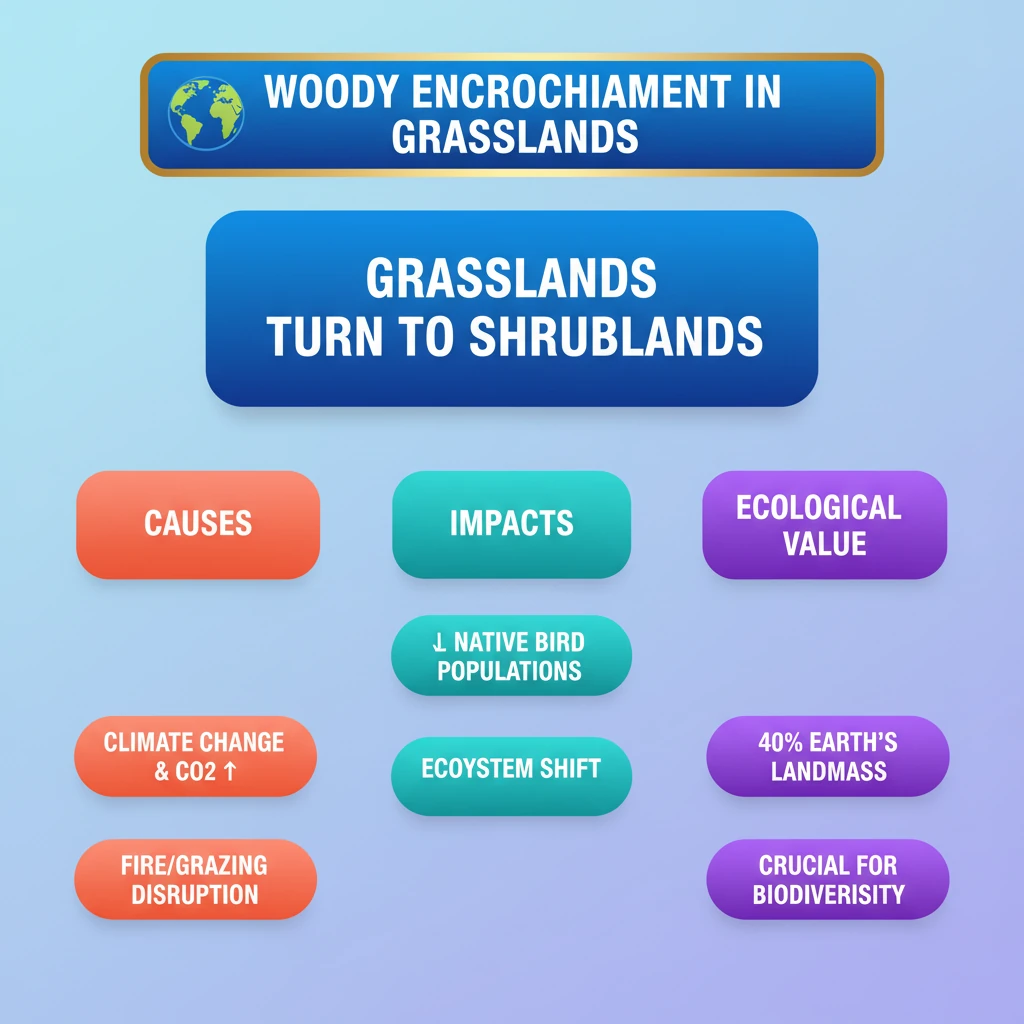
<h4>Introduction to Woody Encroachment</h4><p><strong>Woody encroachment</strong> in grasslands is a critical environmental issue, often overlooked despite its significant impact on biodiversity. While increasing tree cover is generally perceived as beneficial for climate change mitigation and conservation, its unchecked growth in specific ecosystems like grasslands can be detrimental.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>UPSC often tests on environmental paradoxes. Understanding why 'more trees' isn't always good for all ecosystems, especially grasslands, is crucial for <strong>GS Paper III: Environment and Ecology</strong>.</p></div><h4>Recent Study Highlights Concerns</h4><p>A recent study, conducted by researchers from the <strong>Universities of Witwatersrand</strong>, <strong>Cape Town</strong>, and <strong>Oxford</strong>, brought attention to the negative consequences of woody encroachment. Their findings revealed that an increase in tree density in open ecosystems like <strong>savannahs</strong> and <strong>grasslands</strong> has led to a substantial reduction in native grassland bird populations.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Study Finding:</strong> Increased tree cover in open ecosystems like savannahs and grasslands significantly reduces the number of <strong>native grassland birds</strong>.</p></div><h4>Understanding Grasslands and Savannahs</h4><p><strong>Grasslands</strong> and <strong>savannahs</strong> are vital and diverse habitats globally. They are found in both <strong>tropical</strong> and <strong>temperate regions</strong>, collectively covering approximately <strong>40% of the Earth’s landmass</strong>.</p><p>These ecosystems support a rich variety of species. They are home to large herbivores such as <strong>elephants</strong> and <strong>rhinoceroses</strong>, as well as unique grassland birds like <strong>bustards</strong> and <strong>floricans</strong>. Despite their ecological importance, these habitats are currently facing rapid decline due to various threats, including woody encroachment.</p><h4>Defining Woody Encroachment</h4><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Woody encroachment</strong> refers to the gradual process where open habitats, such as grasslands and savannahs, are transformed into areas with a higher density of <strong>trees</strong> and <strong>shrubs</strong>.</p></div><p>This process fundamentally alters the ecosystem structure. It results in the <strong>homogenization of ecosystems</strong>, meaning the diverse grassy understory, which supports unique flora and fauna, is replaced by a more uniform woody cover. This shift reduces habitat diversity and impacts species adapted to open environments.</p><h4>Factors Contributing to Woody Encroachment</h4><p>Several interconnected factors contribute to the phenomenon of woody encroachment:</p><ul><li><strong>Climate Change:</strong> Altered rainfall patterns and increased temperatures can favor woody species over grasses.</li><li><strong>Increased Atmospheric CO2:</strong> Higher levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere can enhance the growth rates of woody plants, giving them a competitive advantage.</li><li><strong>Disruption of Natural Disturbance Regimes:</strong> Historically, natural processes like <strong>grazing</strong> by large herbivores and periodic <strong>fires</strong> played a crucial role in maintaining open grasslands by suppressing woody growth. The disruption or suppression of these regimes allows trees and shrubs to proliferate.</li></ul>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Woody encroachment is the transformation of open grasslands into areas with higher tree/shrub density.
- •It is driven by climate change, increased CO2, and disruption of natural disturbance regimes (grazing, fire).
- •A study revealed it significantly reduces native grassland bird populations.
- •Grasslands and savannahs cover 40% of Earth's landmass and are crucial for diverse species.
- •Increasing tree cover, while generally positive, can be detrimental to specific open ecosystems.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Study by Universities of Witwatersrand, Cape Town, and Oxford (as referenced in the summary)