What are Marine Heat Waves (MHWs)? - Environment And Ecology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

What are Marine Heat Waves (MHWs)?
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
environment and ecology
📖 Introduction
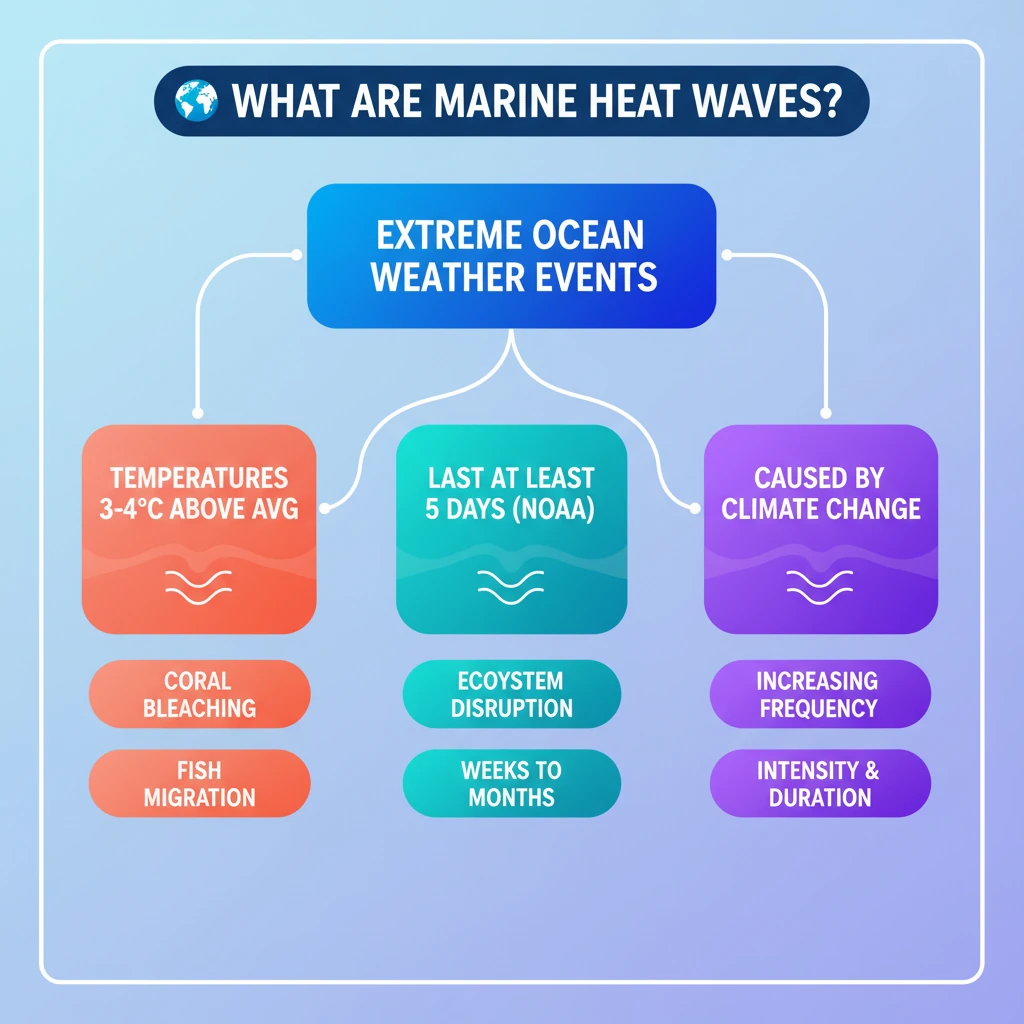
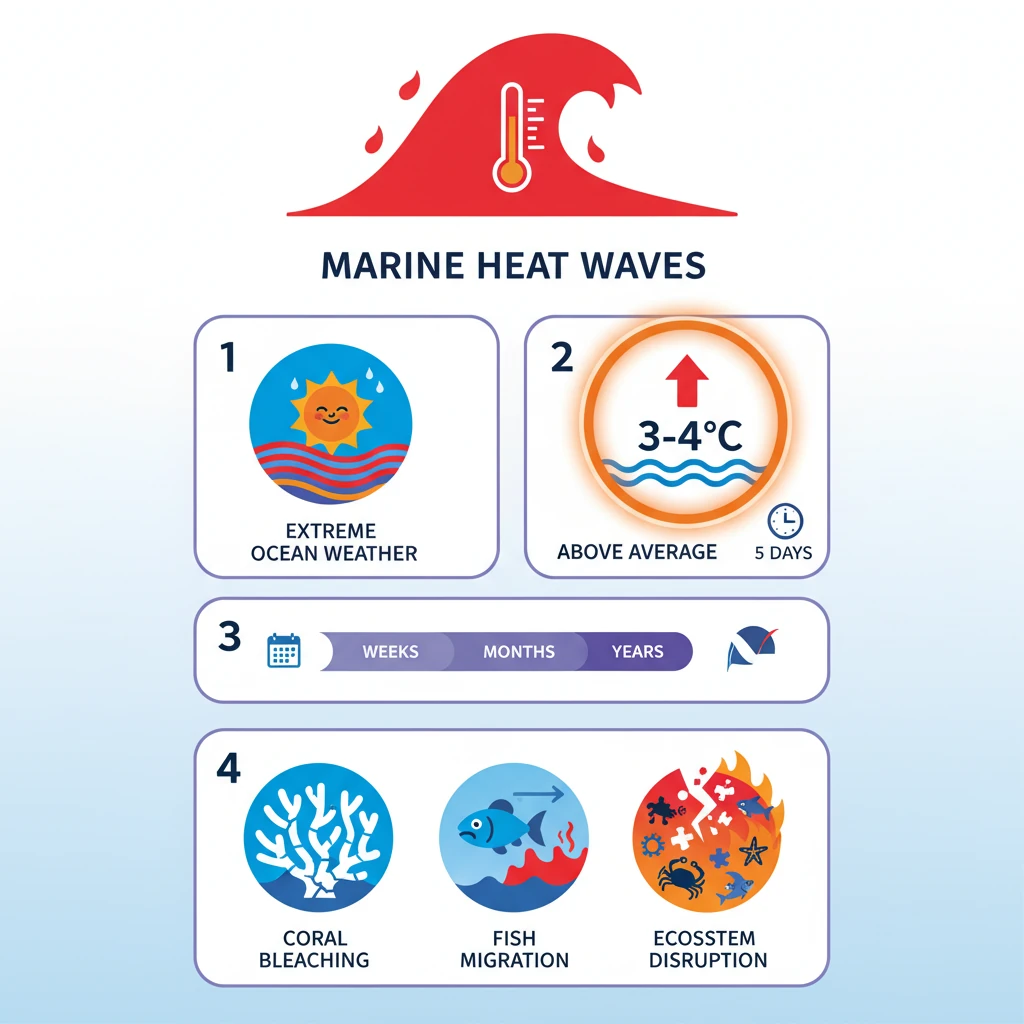
<h4>What are Marine Heat Waves (MHWs)?</h4><p>A <strong>Marine Heat Wave (MHW)</strong> is defined as an <strong>extreme weather event</strong> occurring in the ocean. It signifies a period when sea surface temperatures in a particular region rise significantly above the average.</p><p>Specifically, an MHW is characterized by the <strong>surface temperature</strong> of a sea region increasing to <strong>3 or 4 degree Celsius</strong> above its historical average. This elevated temperature must persist for a minimum duration of <strong>five days</strong> to be classified as an MHW.</p><div class="info-box"><p>According to the <strong>National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)</strong>, the duration of <strong>Marine Heat Waves</strong> can vary greatly. They can last for several <strong>weeks</strong>, extend over multiple <strong>months</strong>, or in some extreme cases, even persist for <strong>years</strong>, causing prolonged impacts on marine ecosystems.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Marine Heat Waves (MHWs) are extreme ocean weather events.
- •Defined by sea surface temperatures 3-4°C above average, lasting at least five days.
- •Can persist for weeks, months, or even years (NOAA data).
- •Cause severe impacts: coral bleaching, fish migration, ecosystem disruption.
- •Frequency, intensity, and duration of MHWs are increasing due to climate change.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) - for definition and duration aspects
•Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) reports - for broader context on MHW trends and impacts