Northeast African Cheetah - Environment And Ecology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Northeast African Cheetah
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
environment and ecology
📖 Introduction
<h4>Introduction to the Northeast African Cheetah</h4><p>The <strong>Northeast African Cheetah</strong> (<em>Acinonyx jubatus soemmeringii</em>) is a distinct subspecies of cheetah primarily found in parts of Northeast Africa. It is recognized for its unique characteristics and plays a vital role in its native ecosystems.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Geographic Range:</strong> Historically found across Sudan, Ethiopia, Eritrea, and Somalia. Its current range is significantly fragmented.</p></div><h4>Key Threats to the Northeast African Cheetah</h4><p>The survival of the <strong>Northeast African Cheetah</strong> is under severe pressure from multiple anthropogenic factors. These threats collectively contribute to its declining population numbers.</p><ul><li><strong>Loss of Natural Prey Species:</strong> A significant threat stems from the depletion of the cheetah's natural food sources. This often results from habitat degradation and competition with human livestock.</li><li><strong>Retaliatory Killing:</strong> Conflict with human populations, particularly livestock owners, leads to retaliatory killings. Cheetahs are often killed when they prey on domestic animals, perceived as a threat to livelihoods.</li><li><strong>Illegal Trade of Fur and Bones:</strong> The <strong>Northeast African Cheetah</strong> is a target for the illegal wildlife trade. Its fur and bones are highly sought after in illicit markets, fueling poaching activities.</li></ul><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Decline in Genetic Diversity:</strong> A critical and growing concern is the significant decline in the <strong>genetic diversity</strong> of the <strong>Northeast African Cheetah</strong> population. This makes the species more vulnerable to diseases and less adaptable to environmental changes.</p></div><p>This genetic erosion is primarily driven by the <strong>illegal trade of cheetah cubs</strong>. These cubs are often smuggled to <strong>Arab countries</strong>, where they are kept as exotic pets, further reducing the breeding pool in the wild.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Understanding the specific threats, especially the link between illegal trade and genetic diversity, is crucial for questions on biodiversity conservation and environmental ethics in <strong>GS Paper 3</strong>.</p></div>
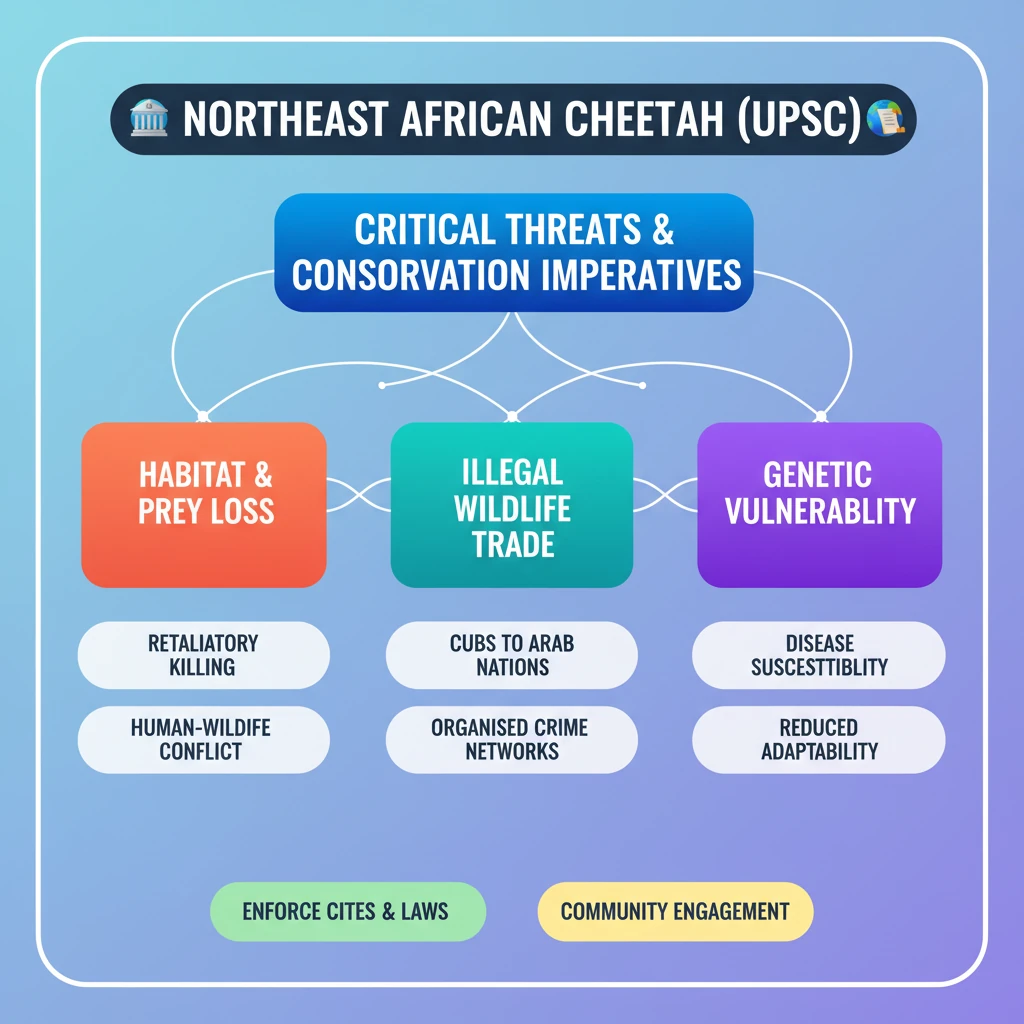
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Northeast African Cheetah faces severe threats including prey loss, retaliatory killing, and illegal trade.
- •Illegal trade of cubs to Arab countries is causing a critical decline in its genetic diversity.
- •Reduced genetic diversity makes the subspecies vulnerable to diseases and less adaptable.
- •Conservation efforts require tackling organized crime, engaging communities, and enforcing international laws like CITES.
- •The issue highlights broader challenges in biodiversity conservation and combating wildlife trafficking.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•IUCN Red List (for cheetah status and threats)
•CITES Official Website (for trade regulations)
•UNODC Reports on Wildlife Crime