What are the Reasons for High Plastic Pollution in India? - Environment And Ecology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
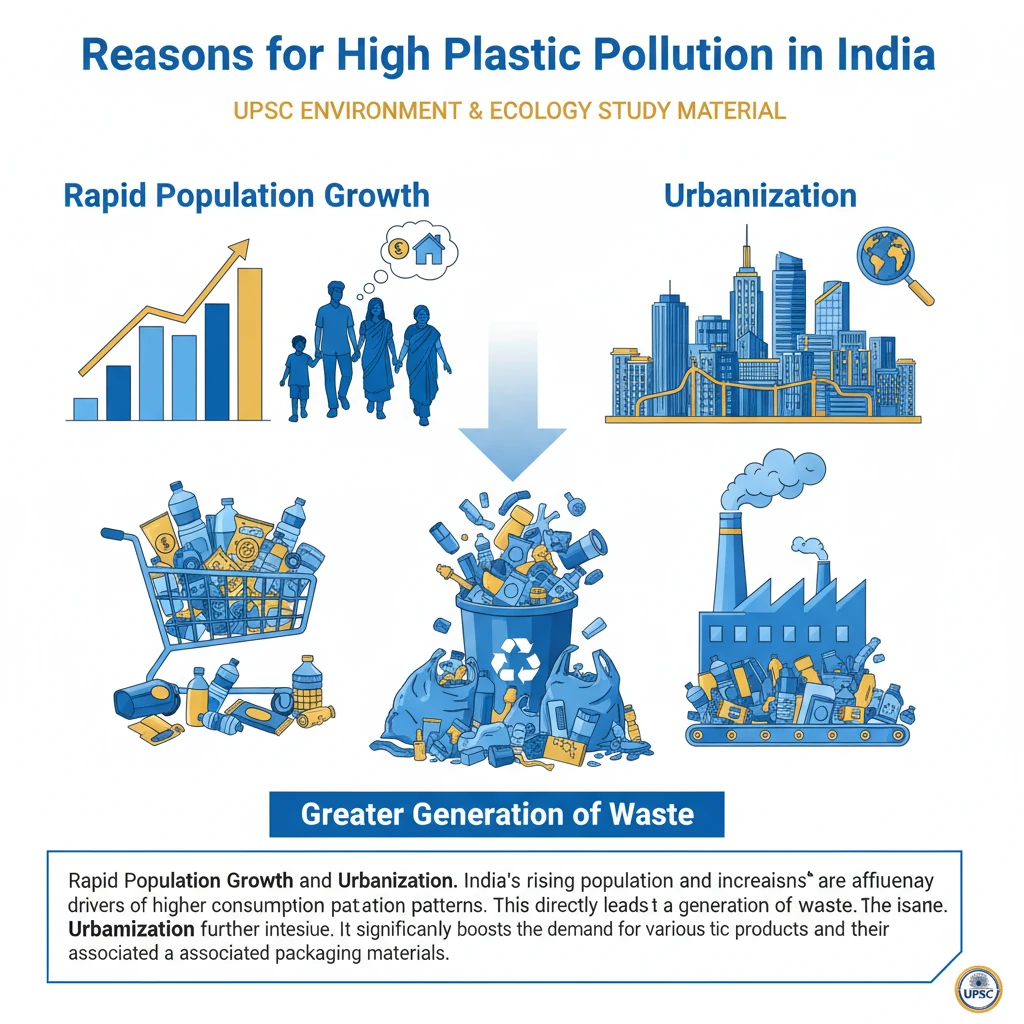
What are the Reasons for High Plastic Pollution in India?
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
environment and ecology
📖 Introduction
<h4>Rapid Population Growth and Urbanization</h4><p>India’s <strong>rising population</strong> and increasing <strong>affluence</strong> are primary drivers of higher consumption patterns. This directly leads to a greater generation of <strong>waste</strong>.</p><p><strong>Urbanization</strong> further intensifies the issue. It significantly boosts the demand for various <strong>plastic products</strong> and their associated <strong>packaging materials</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><strong>Key Impact:</strong> More people and urban living equate to higher per capita plastic use and waste output.</div><h4>Inadequate Waste Management Infrastructure</h4><p>India faces a severe challenge with its <strong>waste management infrastructure</strong>, which is largely insufficient. It cannot effectively handle the immense volumes of <strong>municipal solid waste</strong> generated daily.</p><p>The country has a disproportionately high number of <strong>uncontrolled dumping sites</strong>. These far outnumber scientifically engineered <strong>sanitary landfills</strong>.</p><p>This imbalance reflects critical deficiencies in proper <strong>waste disposal facilities</strong> and the widespread adoption of effective <strong>waste management practices</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><strong>Core Problem:</strong> Lack of proper infrastructure leads to accumulation and environmental leakage of plastic waste.</div><h4>Discrepancies in Waste Collection Data</h4><p>Official statistics often present an inflated picture of <strong>waste collection efficiency</strong> in India. The reported collection rate is frequently cited as high as <strong>95%</strong>.</p><p>However, independent research and ground-level assessments reveal a significant disparity. The actual <strong>waste collection rate</strong> is estimated to be around <strong>81%</strong>.</p><p>This substantial gap indicates a major shortfall in the operational efficiency of <strong>waste collection mechanisms</strong> across the country, contributing to uncollected plastic waste.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Be critical of official data; always look for independent assessments to present a balanced view in answers.</div><h4>Open Burning of Waste</h4><p>A significant quantity of plastic waste in India is disposed of through <strong>open burning</strong>. Approximately <strong>5.8 million tons</strong> of plastic waste are burned annually.</p><p>This practice severely exacerbates <strong>air pollution</strong> and releases a range of <strong>toxic pollutants</strong> into the atmosphere. These include dioxins and furans.</p><p>Such emissions pose grave <strong>health risks</strong> to communities, leading to respiratory illnesses and other chronic conditions, alongside causing substantial <strong>environmental degradation</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><strong>Annual Plastic Waste Burned:</strong> Approximately <strong>5.8 million tons</strong>.</div>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •India's high plastic pollution is driven by rapid population growth, urbanization, and increased consumption.
- •Inadequate waste management infrastructure, including a lack of sanitary landfills, is a major contributing factor.
- •Official waste collection rates are often overstated, masking significant operational inefficiencies.
- •Open burning of approximately 5.8 million tons of plastic annually exacerbates air pollution and health risks.
- •Policy efforts like PWM Rules and EPR are in place, but effective implementation and public participation are crucial.
- •Transitioning to a circular economy and promoting alternatives are key to long-term solutions.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) reports
•Various academic studies and environmental reports on plastic waste management in India