Forms of Acid Rain/Deposition - Environment And Ecology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
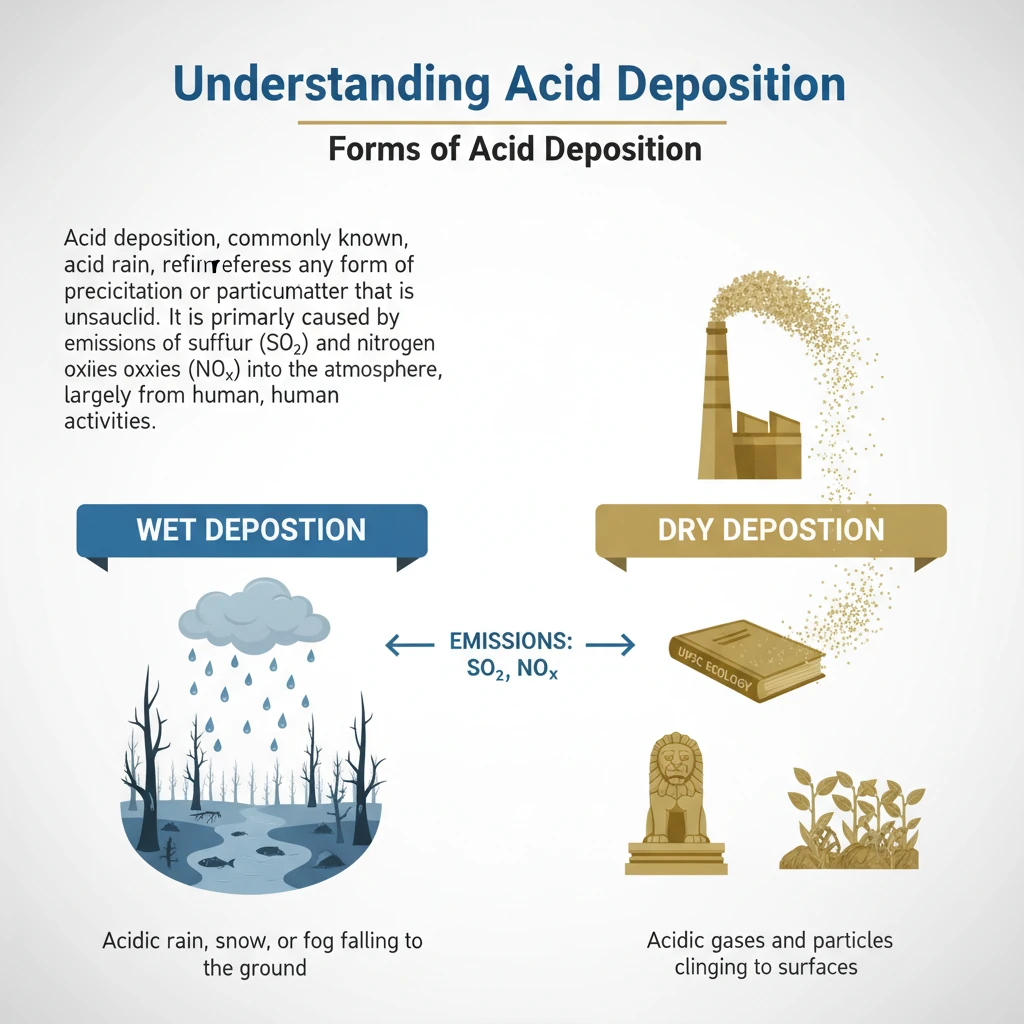
Forms of Acid Rain/Deposition
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
environment and ecology
📖 Introduction
<h4>Understanding Acid Deposition</h4><p><strong>Acid deposition</strong>, commonly known as <strong>acid rain</strong>, refers to any form of precipitation or particulate matter that is unusually acidic.</p><p>It is primarily caused by emissions of <strong>sulfur dioxide (SO₂)</strong> and <strong>nitrogen oxides (NOₓ)</strong> into the atmosphere, largely from human activities.</p><h4>Forms of Acid Deposition</h4><p>Acid deposition occurs in two primary forms: <strong>wet deposition</strong> and <strong>dry deposition</strong>. Both forms contribute significantly to environmental degradation.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>Understanding these distinct forms is crucial for comprehending the full scope of acid rain's environmental and health impacts.</p></div><h4>Wet Deposition</h4><p><strong>Wet deposition</strong> occurs when acidic compounds are dissolved or suspended in atmospheric moisture and then fall to the Earth's surface.</p><div class='info-box'><p>This form includes <strong>rain</strong>, <strong>snow</strong>, <strong>fog</strong>, and <strong>hail</strong> that have become acidic due to the presence of <strong>sulfuric acid</strong> and <strong>nitric acid</strong>.</p></div><p>These acids are formed in the atmosphere from the reaction of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides with water, oxygen, and other chemicals.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>UPSC often asks about the specific forms of precipitation involved in <strong>wet deposition</strong>. Remember it's not just rain, but also snow, fog, and hail!</p></div><h4>Dry Deposition</h4><p><strong>Dry deposition</strong> refers to the direct deposition of acidic particles and gases from the atmosphere onto surfaces without the involvement of moisture.</p><div class='info-box'><p>This includes <strong>acidic particles</strong> (like sulfates and nitrates) and <strong>acidic gases</strong> (such as <strong>sulfur dioxide</strong> and <strong>nitrogen oxides</strong>) settling directly on surfaces.</p></div><p>These acidic substances can deposit on various surfaces, including <strong>water bodies</strong>, <strong>vegetation</strong>, and <strong>buildings</strong>.</p><p>The particles and gases may deposit quickly or react further during atmospheric transport to form larger particles that can be harmful to <strong>human health</strong>.</p><h4>Combined Impact</h4><p>Both <strong>wet</strong> and <strong>dry deposition</strong> contribute to the overall phenomenon of acid rain, leading to widespread environmental degradation.</p><p>The effects range from acidification of lakes and soil to damage to forests, crops, and man-made infrastructure.</p>
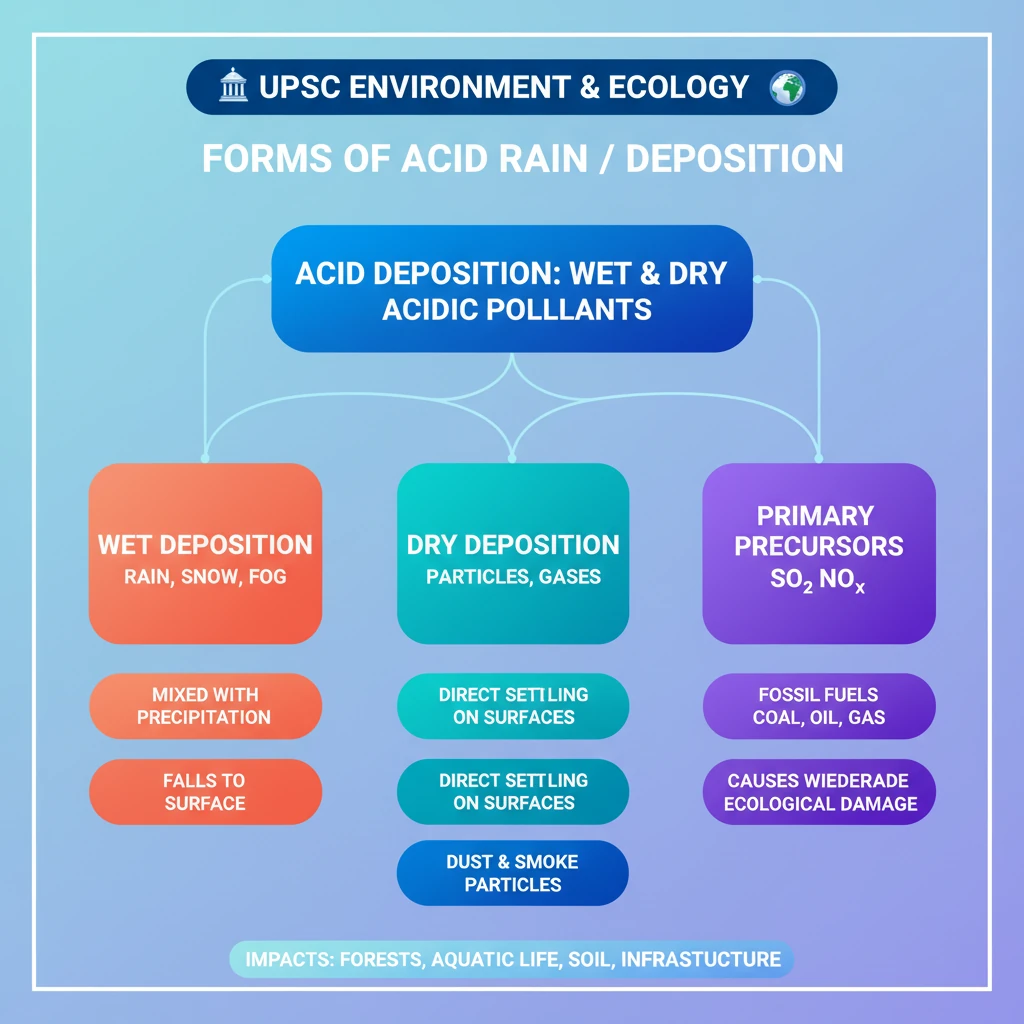
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Acid deposition (acid rain) includes both wet and dry forms of acidic pollutants.
- •Wet deposition involves acidic compounds mixed with rain, snow, fog, or hail.
- •Dry deposition is the direct settling of acidic particles and gases on surfaces.
- •Primary precursors are sulfur dioxide (SO₂) and nitrogen oxides (NOₓ), mainly from burning fossil fuels.
- •Acid rain causes widespread environmental damage to forests, aquatic ecosystems, soil, and infrastructure.
- •Mitigation involves emission controls, renewable energy transition, and international cooperation.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•NCERT Class 11/12 Environmental Chemistry
•United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) resources on Acid Rain
•United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) reports on Air Pollution
•Britannica - Acid Rain