What is the National Green Tribunal? - Environment And Ecology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
What is the National Green Tribunal?
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
environment and ecology
📖 Introduction
<h4>Introduction to NGT</h4><p>The <strong>National Green Tribunal (NGT)</strong> is a specialized judicial body established in India. Its primary objective is to ensure the effective and expeditious disposal of cases relating to <strong>environmental protection</strong> and the <strong>conservation of forests</strong> and other <strong>natural resources</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The NGT plays a crucial role in providing <strong>environmental justice</strong> and helping reduce the burden on higher courts regarding environmental disputes.</p></div><h4>Establishment and Mandate</h4><p>The NGT was formally established in <strong>2010</strong>. This was done under the provisions of the <strong>National Green Tribunal Act, 2010</strong>, an Act of the Parliament of India.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Establishment:</strong> 2010<br><strong>Enabling Legislation:</strong> National Green Tribunal Act, 2010</p></div><p>Its core mandate is to facilitate the <strong>swift and efficient resolution</strong> of cases. This includes matters pertaining to environmental protection, the conservation of forests, and the preservation of India's vital natural resources.</p><h4>Composition of the Tribunal</h4><p>The Tribunal is headed by a <strong>Chairperson</strong>. This individual is appointed by the <strong>Central Government</strong> in consultation with the <strong>Chief Justice of India (CJI)</strong>, ensuring judicial independence and expertise.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Head:</strong> Chairperson<br><strong>Appointment:</strong> Central Government in consultation with CJI</p></div><p>The Chairperson presides over the <strong>Principal Bench</strong> of the NGT. In addition to the Chairperson, the Tribunal comprises a specified number of <strong>judicial members</strong> and <strong>expert members</strong>.</p><ul><li>The Act mandates a minimum of <strong>10 judicial members</strong> and <strong>10 expert members</strong>.</li><li>The maximum strength can go up to <strong>20 judicial members</strong> and <strong>20 expert members</strong>.</li></ul><div class='key-point-box'><p>The presence of <strong>expert members</strong> is a unique feature, allowing for technically sound decisions on complex environmental issues.</p></div><h4>Scope of Jurisdiction</h4><p>The NGT's jurisdiction is broad, encompassing various aspects of environmental governance. It is empowered to enforce <strong>environmental legal rights</strong> of individuals and communities.</p><p>Furthermore, the Tribunal can grant <strong>relief and compensation</strong> for damages caused to individuals and property due to environmental harm. This includes restitution for victims of pollution and environmental degradation.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Key Areas:</strong><br>1. Enforcement of environmental rights<br>2. Granting relief and compensation for damages<br>3. Addressing environmental protection and conservation matters</p></div><h4>Types of Jurisdiction</h4><p>The NGT exercises both <strong>original</strong> and <strong>appellate jurisdiction</strong>, making it a powerful body for environmental adjudication.</p><ul><li><strong>Original Jurisdiction:</strong> This allows individuals or organizations to directly file applications before the NGT for environmental disputes.</li><li><strong>Appellate Jurisdiction:</strong> The NGT also has the authority to hear appeals against certain orders or decisions made by other environmental authorities or courts, functioning as an appellate tribunal.</li></ul><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>Understanding the dual nature of <strong>original and appellate jurisdiction</strong> is crucial for UPSC. It highlights the NGT's comprehensive role in environmental justice.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
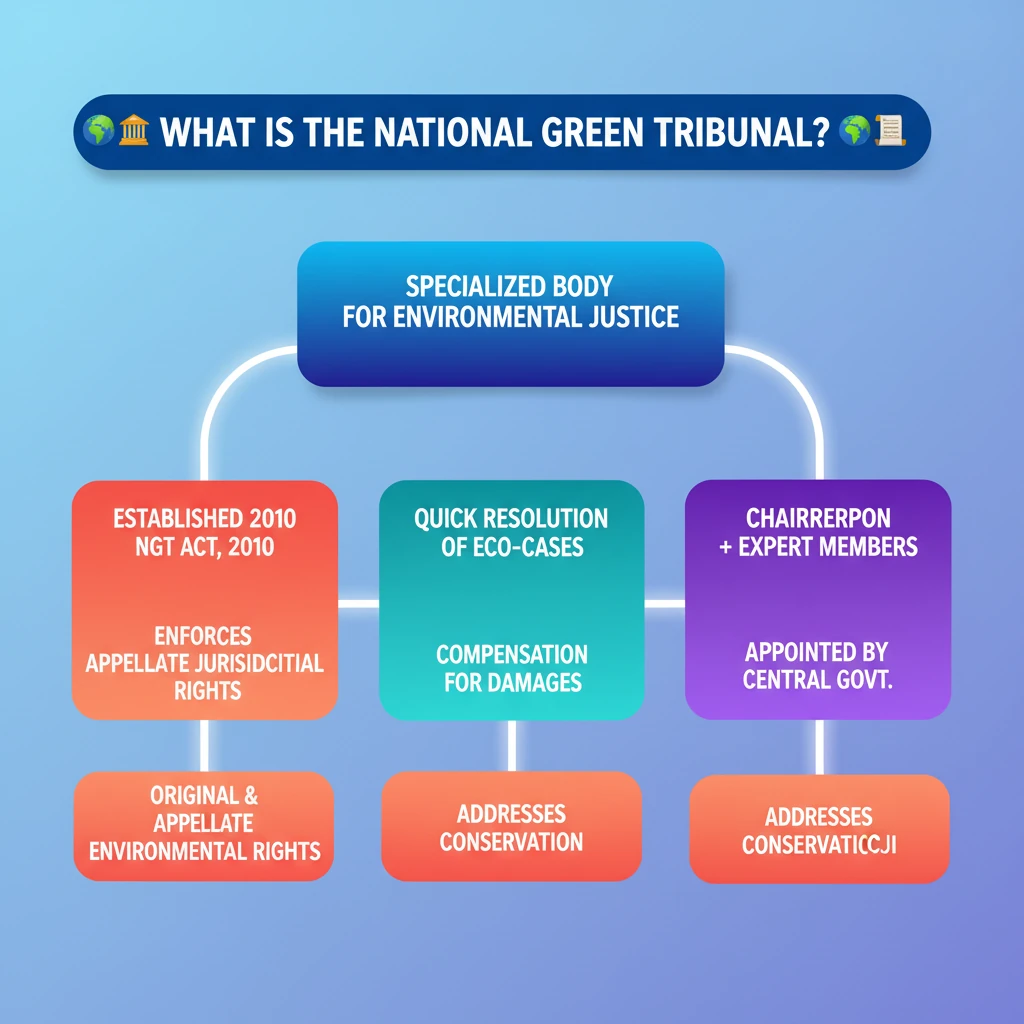
- •NGT established in 2010 under the National Green Tribunal Act, 2010.
- •Specialized body for swift and efficient resolution of environmental cases.
- •Headed by a Chairperson (appointed by Central Govt. in consultation with CJI) with judicial and expert members.
- •Possesses both original and appellate jurisdiction for environmental matters.
- •Enforces environmental rights, grants compensation for damages, and addresses conservation.
- •Crucial for environmental justice and sustainable development in India.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Official website of the National Green Tribunal (www.greentribunal.gov.in)
•Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) publications
•Reports on environmental law and governance in India