Crocodile Conservation Project: Implementation & Achievements - Environment And Ecology | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Crocodile Conservation Project: Implementation & Achievements
Medium⏱️ 5 min read
environment and ecology
📖 Introduction
<h4>Project Initiation and Support</h4><p>The <strong>Crocodile Conservation Project</strong> was launched with crucial assistance from international organizations. This collaborative effort aimed to bolster crocodile populations across India.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The project received support from the <strong>United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)</strong> and the <strong>Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO)</strong>. These partnerships provided essential technical and financial backing.</p></div><h4>Key Conservation Sanctuaries</h4><p>Several protected areas were identified and strengthened to serve as vital habitats for different crocodile species. These sanctuaries play a pivotal role in the species' recovery.</p><ul><li><strong>Bhitarkanika National Park</strong> (<strong>Odisha</strong>): This sanctuary is renowned for its successful conservation of <strong>saltwater crocodiles</strong>. It provides an ideal estuarine environment for their breeding and growth.</li><li><strong>National Chambal Sanctuary</strong> (spanning <strong>Madhya Pradesh</strong>, <strong>Rajasthan</strong>, and <strong>Uttar Pradesh</strong>): This extensive riverine sanctuary is critical for the protection of <strong>gharials</strong>, a critically endangered crocodile species.</li></ul><h4>Project Achievements and Adaptations</h4><p>Since its inception, the project has demonstrated significant success, particularly in the recovery of certain crocodile populations. This success has led to adaptive management strategies.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The <strong>saltwater crocodile</strong> population has shown a steady and encouraging rise since the launch of the <strong>Crocodile Conservation Project</strong> in <strong>1975</strong>. This marks a major achievement in wildlife conservation.</p></div><p>Due to the achieved population saturation, the active crocodile breeding program within the park was discontinued in <strong>2024</strong>. This decision reflects the success of initial conservation efforts.</p><p>However, the collection of eggs continues annually. These eggs are subsequently bred, primarily for educational and tourism purposes, showcasing the species to the public.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>Remember the specific species-sanctuary pairings (<strong>saltwater crocodile</strong> with <strong>Bhitarkanika</strong>, <strong>gharials</strong> with <strong>Chambal</strong>) as these are common factual questions in <strong>UPSC Prelims</strong>.</p></div>
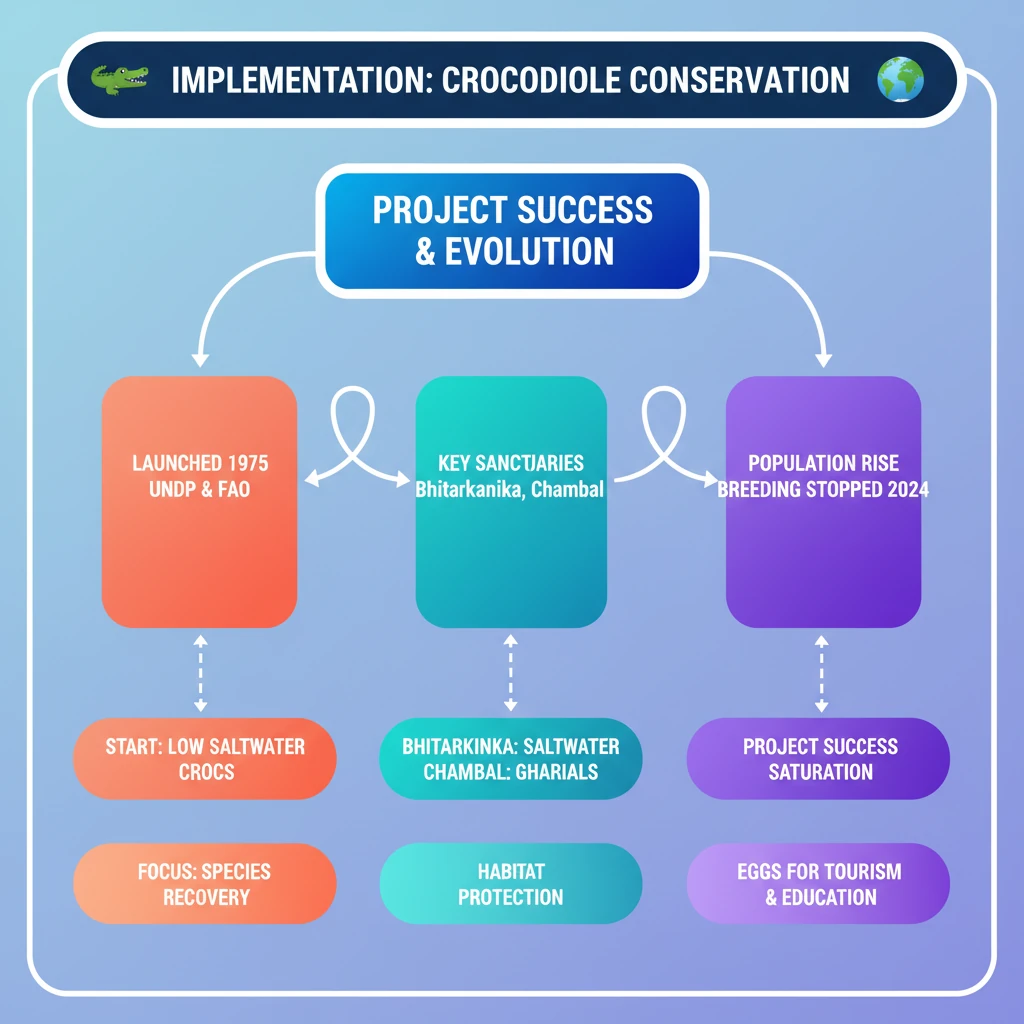
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Crocodile Conservation Project launched in 1975 with UNDP and FAO support.
- •Key sanctuaries: Bhitarkanika (saltwater crocodiles) and National Chambal (gharials).
- •Saltwater crocodile population has significantly risen since 1975.
- •Breeding program stopped in 2024 due to population saturation, showing project success.
- •Eggs still collected annually for tourist breeding, linking conservation to education/tourism.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•General knowledge about Indian wildlife conservation projects