National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD)
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
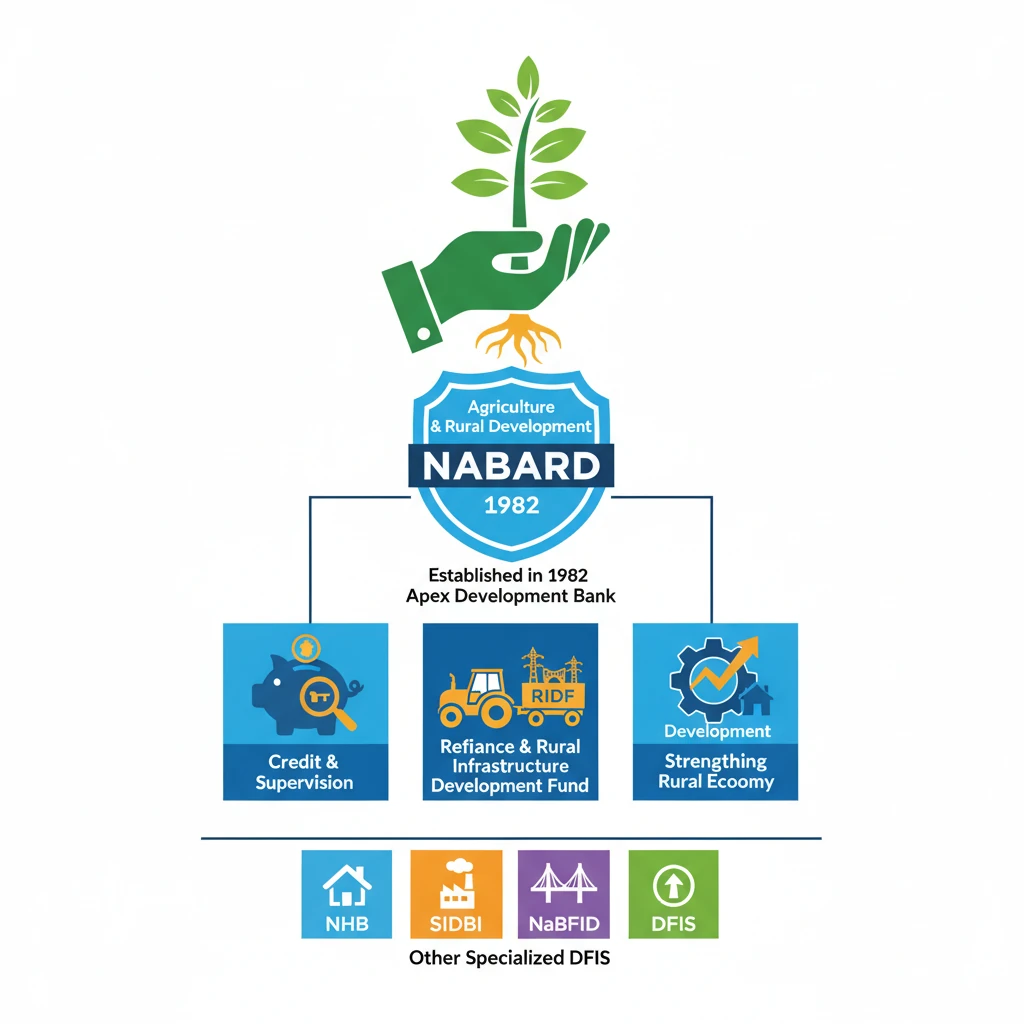
<h4>Introduction to NABARD</h4><p>The <strong>National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD)</strong> is an apex development financial institution in India. It was established with the primary objective of facilitating credit flow for promoting and developing agriculture, small-scale industries, cottage and village industries, handicrafts, and other allied economic activities in rural areas. NABARD plays a crucial role in fostering sustainable and equitable rural prosperity.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Key Role:</strong> NABARD serves as an <strong>apex regulatory body</strong> for overall regulation and licensing of regional rural banks and cooperative banks in India.</p></div><h4>Genesis and Mandate</h4><p>NABARD was established on <strong>July 12, 1982</strong>, based on the recommendations of the <strong>B. Sivaraman Committee (Committee to Review the Arrangements for Institutional Credit for Agriculture and Rural Development - CRAFICARD)</strong>. It took over the agricultural credit functions of the <strong>Reserve Bank of India (RBI)</strong> and the refinance functions of the erstwhile <strong>Agricultural Refinance and Development Corporation (ARDC)</strong> and the <strong>Rural Planning and Credit Cell (RPCC)</strong> of RBI.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Establishment Details:</strong><ul><li><strong>Date of Establishment:</strong> July 12, 1982</li><li><strong>Act:</strong> National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development Act, 1981</li><li><strong>Initial Capital:</strong> ₹100 crore (fully subscribed by Government of India and RBI)</li><li><strong>Current Ownership:</strong> Wholly owned by the <strong>Government of India</strong> since 2017.</li></ul></p></div><h4>Core Functions of NABARD</h4><p>NABARD performs a wide range of functions, broadly categorized into three areas: <strong>Credit Functions</strong>, <strong>Developmental Functions</strong>, and <strong>Supervisory Functions</strong>. These functions are aimed at strengthening the rural credit delivery system and promoting integrated rural development.</p><ul><li><strong>Refinance Facilities:</strong> Provides refinance to various financial institutions that extend credit for agriculture and rural development. This ensures liquidity for these institutions.</li><li><strong>Rural Infrastructure Development:</strong> Manages funds like the <strong>Rural Infrastructure Development Fund (RIDF)</strong> to finance infrastructure projects in rural areas.</li><li><strong>Institutional Development:</strong> Works towards strengthening the rural credit institutions, including cooperative banks and Regional Rural Banks (RRBs), through training, capacity building, and policy formulation.</li><li><strong>Supervision:</strong> Exercises supervisory powers over cooperative banks and RRBs to ensure their sound functioning and adherence to prudential norms.</li><li><strong>Research and Development:</strong> Undertakes research and studies related to agriculture and rural development to inform policy and strategy.</li></ul><h4>Other Specialized Financial Institutions in India</h4><p>Apart from NABARD, India has several other specialized financial institutions, each catering to specific sectors or developmental needs. These institutions play a crucial role in the country's economic development by providing targeted financial support and regulatory oversight.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>National Housing Bank (NHB):</strong> An apex financial institution for housing. It was established in <strong>1988</strong> under the <strong>National Housing Bank Act, 1987</strong>, to promote a sound, healthy, viable, and efficient housing finance system in the country and to regulate the activities of housing finance companies.</p></div><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI):</strong> Established in <strong>1990</strong> under an Act of the Indian Parliament, SIDBI is the principal financial institution for the promotion, financing, and development of the <strong>Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME)</strong> sector. It also coordinates the functions of institutions engaged in similar activities.</p></div><div class='info-box'><p><strong>National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development (NaBFID):</strong> Constituted in <strong>2021</strong> under the <strong>NaBFID Act, 2021</strong>, as a Development Financial Institution (DFI). Its primary objective is to finance infrastructure projects, both greenfield and brownfield, and to catalyze investment in the infrastructure sector in India.</p></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Relevance:</strong> Understanding the roles of <strong>NABARD, NHB, SIDBI, and NaBFID</strong> is vital for <strong>GS Paper III (Indian Economy)</strong>. Questions often relate to their mandates, functions, and impact on specific sectors like agriculture, housing, MSMEs, and infrastructure. Differentiate their specific areas of focus.</p></div>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •NABARD is India's apex development bank for agriculture and rural development, established in 1982.
- •It provides refinance, promotes rural infrastructure (RIDF), and supervises rural credit institutions.
- •Key functions include credit, development, and supervision, aimed at strengthening rural economy.
- •NHB, SIDBI, and NaBFID are other specialized DFIs for housing, MSMEs, and infrastructure respectively.
- •NABARD plays a vital role in financial inclusion, supporting SHGs, FPOs, and climate-resilient agriculture.
🧠 Memory Techniques
98% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Reserve Bank of India (RBI) Publications
•Economic Survey of India
•Ministry of Finance, Government of India Documents