Central Bank Digital Currency - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Central Bank Digital Currency
Easy⏱️ 7 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
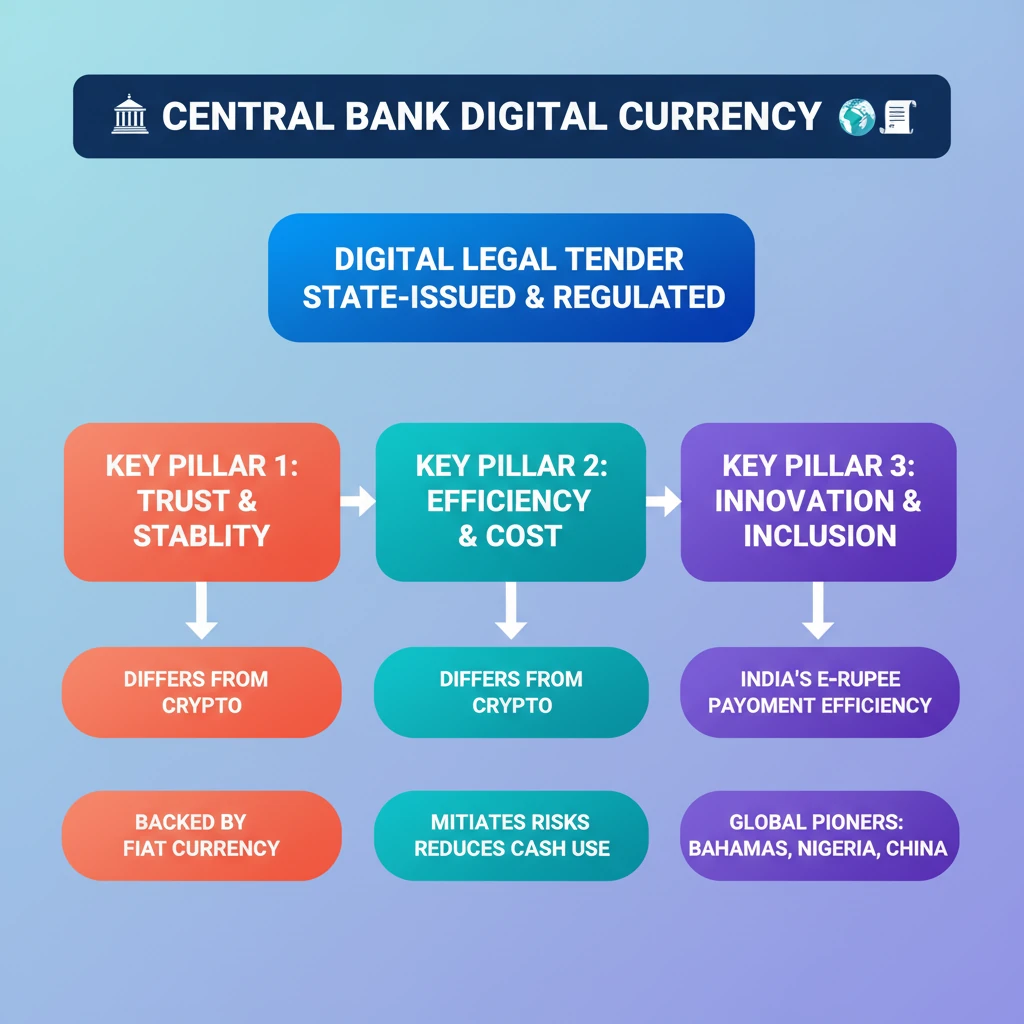
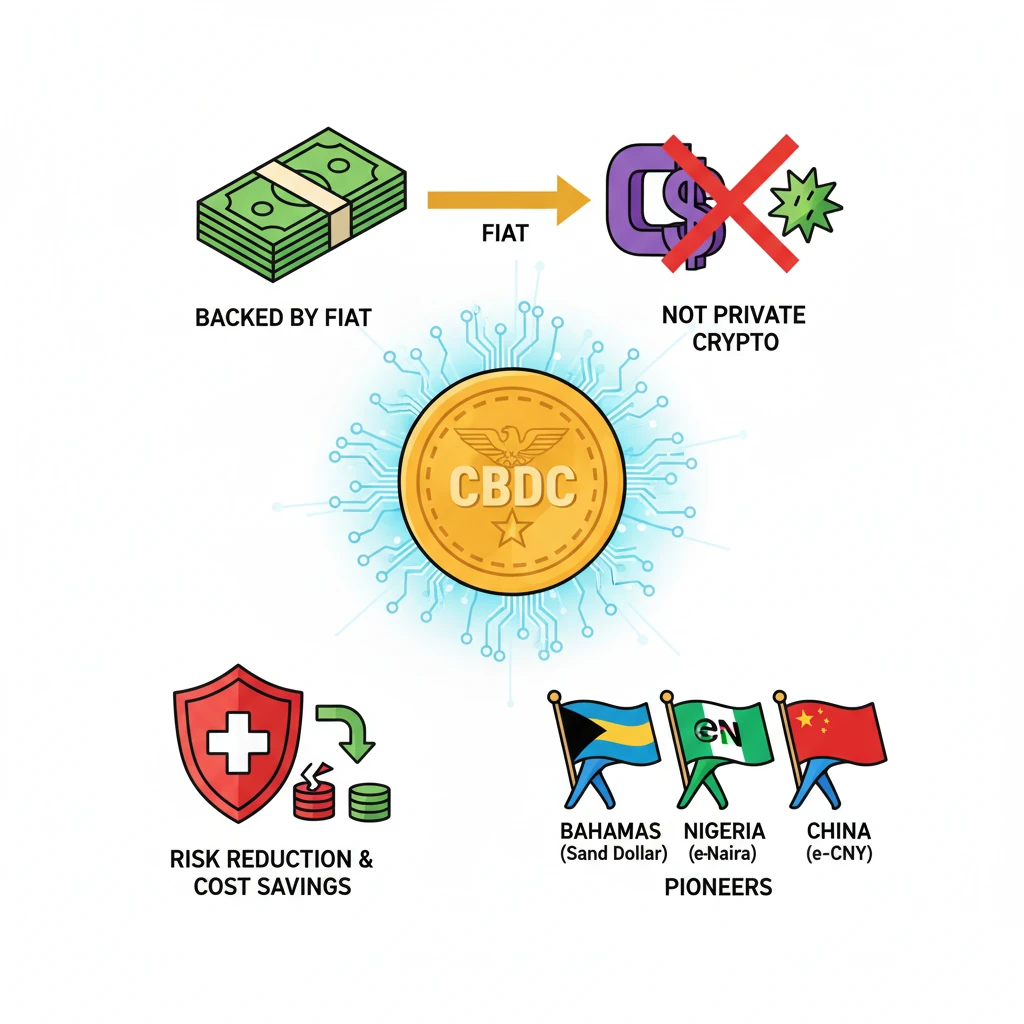
<h4>Introduction to Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC)</h4><p>The <strong>Reserve Bank of India (RBI)</strong> Governor has highlighted the innovative features under development for <strong>India's Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC)</strong>, also known as the <strong>e-rupee</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>A <strong>Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC)</strong> represents a <strong>legal tender</strong> issued by a <strong>central bank</strong>, but in a digital format. It aims to offer the benefits of digital payments while retaining the stability and trust associated with traditional <strong>fiat currency</strong>.</p></div><h4>What is a Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC)?</h4><div class='info-box'><p>A <strong>CBDC</strong> is essentially a <strong>legal tender</strong> issued by a <strong>central bank</strong> in a digital form. It is distinct from private cryptocurrencies due to its backing by the central bank, which ensures its stability and public trust.</p></div><p>It functions identically to a <strong>fiat currency</strong> and is fully exchangeable on a one-to-one basis with its physical counterpart. This means one <strong>e-rupee</strong> would be equivalent to one physical <strong>Indian Rupee</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p>A <strong>fiat currency</strong> is defined as a national currency that is not pegged to the price of a physical commodity, such as <strong>gold</strong> or <strong>silver</strong>. Its value is derived from government decree and public trust.</p></div><p>While the concept of <strong>CBDCs</strong> was inspired by the emergence of cryptocurrencies like <strong>Bitcoin</strong>, they differ significantly. <strong>CBDCs</strong> are issued by the state and possess <strong>legal tender</strong> status, unlike decentralized virtual currencies and crypto assets.</p><h4>Objectives of CBDC</h4><p>The primary objective behind the introduction of <strong>CBDCs</strong> is multifaceted, focusing on efficiency and risk mitigation within the financial system.</p><ul><li>To <strong>mitigate risks</strong> associated with the handling and management of physical currency.</li><li>To <strong>trim costs</strong> involved in the printing, storage, distribution, and security of banknotes and coins.</li><li>To enhance the efficiency and security of payment systems.</li></ul><h4>Global Trends in CBDC Adoption</h4><p>Several countries have already taken significant steps towards launching or piloting their own <strong>CBDCs</strong>, showcasing a global shift towards digital sovereign currencies.</p><div class='info-box'><ul><li><strong>Bahamas</strong>: The first economy globally to launch a nationwide <strong>CBDC</strong>, named <strong>Sand Dollar</strong>, in <strong>2020</strong>.</li><li><strong>Nigeria</strong>: Rolled out its own digital currency, the <strong>eNaira</strong>, also in <strong>2020</strong>.</li><li><strong>China</strong>: Became the world's first major economy to pilot a digital currency, the <strong>e-CNY</strong>, in <strong>April 2020</strong>.</li></ul></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>For <strong>UPSC Prelims</strong>, remember the first countries to launch/pilot <strong>CBDCs</strong> and their respective names. The year <strong>2020</strong> is a significant common factor for early adoption.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •CBDC is a digital legal tender issued by a central bank, backed by fiat currency.
- •It differs from private cryptocurrencies by being state-issued and having legal tender status.
- •Key objectives include mitigating risks and reducing costs of physical currency.
- •Bahamas (Sand Dollar), Nigeria (eNaira), and China (e-CNY) are pioneers in CBDC adoption.
- •India's e-rupee aims for innovation, financial inclusion, and payment efficiency.
🧠 Memory Techniques
98% Verified Content