What is the Impact of Rising Unsecured Loans on India’s Economy? - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
What is the Impact of Rising Unsecured Loans on India’s Economy?
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
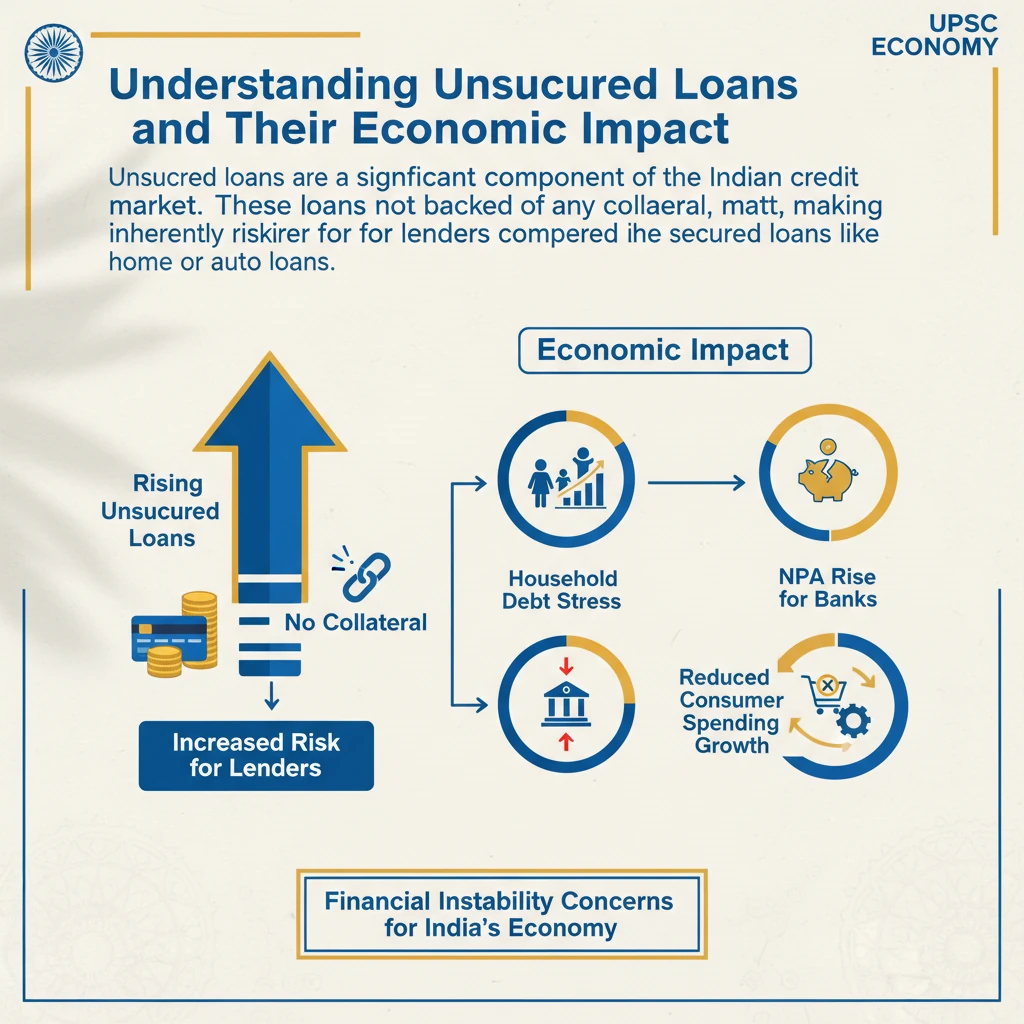
<h4>Understanding Unsecured Loans and Their Economic Impact</h4><p><strong>Unsecured loans</strong> are a significant component of the Indian credit market. These loans are not backed by any collateral, making them inherently riskier for lenders compared to secured loans like home or auto loans.</p><p>The recent surge in such loans has drawn attention from regulators and economists due to potential implications for the nation's financial stability and broader economic health.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>What are Unsecured Loans?</strong></p><ul><li>Loans granted without requiring collateral.</li><li>Examples include <strong>personal loans</strong>, <strong>credit card debt</strong>, and some types of <strong>micro-loans</strong>.</li><li>Lenders assess risk based on the borrower's creditworthiness and income.</li></ul></div><h4>Higher Default Rates and Financial Stress</h4><p>A primary concern with rising unsecured loans is the elevated risk of <strong>defaults</strong>. When borrowers fail to repay these loans, it directly impacts the lenders' asset quality.</p><p>Increased defaults lead to a rise in <strong>Non-Performing Assets (NPAs)</strong> for financial institutions. NPAs are loans where the principal or interest payment has been overdue for a specified period, typically 90 days.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Impact on Financial Institutions:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Banks</strong> and <strong>Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs)</strong> face significant financial strain.</li><li>Higher NPAs erode profitability and capital adequacy.</li><li>This can restrict their ability to lend further, impacting overall credit growth in the economy.</li></ul></div><h4>Inflationary Pressure and Economic Slowdown</h4><p>The consequences of rising unsecured loan defaults extend beyond the financial sector. They can contribute to broader macroeconomic challenges, including <strong>inflationary pressure</strong> and a slowdown in <strong>economic growth</strong>.</p><p>When defaults rise, financial institutions often respond by increasing <strong>interest rates</strong> on new loans to compensate for the higher risk. This makes borrowing more expensive for both consumers and businesses.</p><p>Higher interest rates and reduced access to credit can lead to a decrease in <strong>disposable income</strong> for households and curb <strong>discretionary spending</strong>. Businesses might also defer investment plans.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Macroeconomic Chain Reaction:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Reduced demand</strong> due to lower spending.</li><li>Paradoxically, rising defaults can lead to <strong>cost-push inflation</strong> if businesses pass on higher borrowing costs.</li><li>A combination of reduced spending and higher costs can ultimately lead to a slowdown in <strong>economic growth</strong>.</li></ul></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> This topic is crucial for <strong>GS Paper 3 (Economy)</strong>. Questions can cover financial stability, banking sector issues, inflation, and monetary policy. Understanding the interconnectedness of these factors is key.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
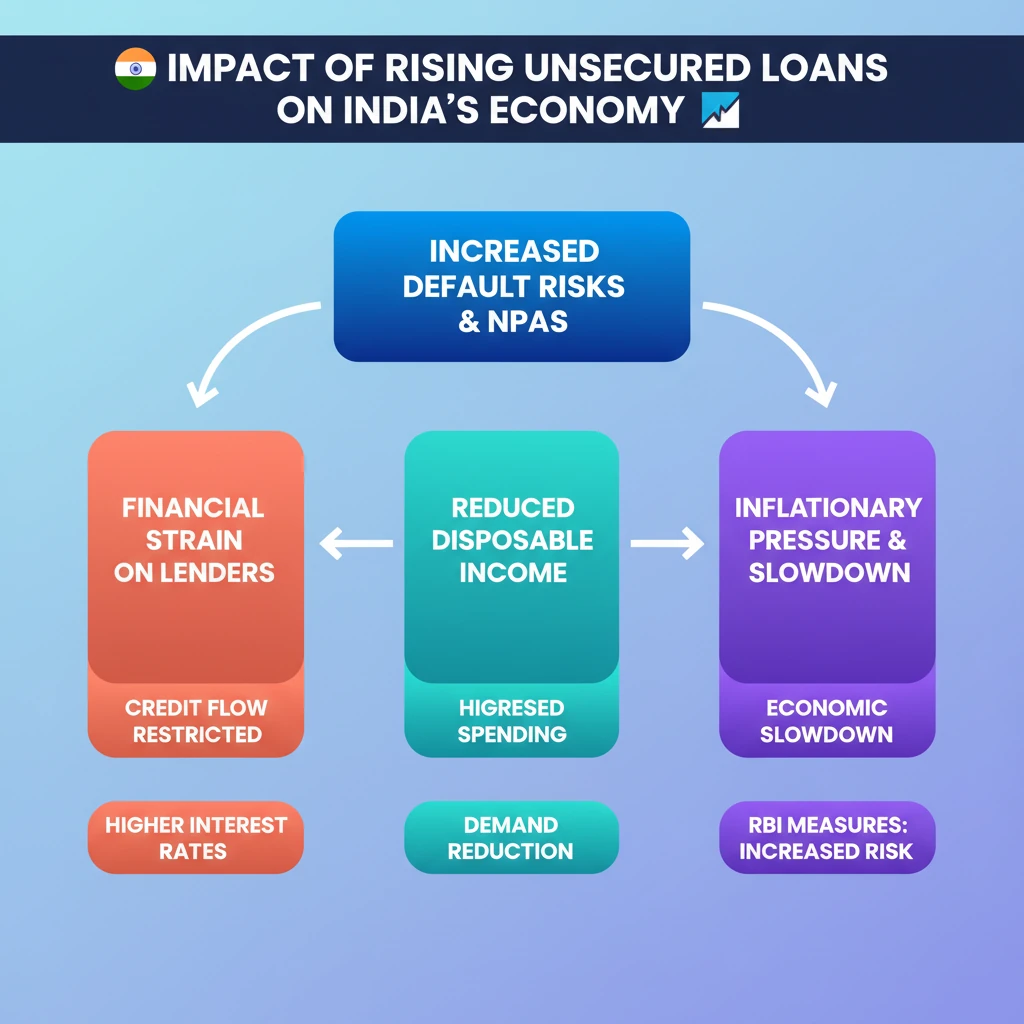
- •Rising unsecured loans increase default risks and Non-Performing Assets (NPAs) for banks and NBFCs.
- •Higher defaults lead to financial strain on lenders, potentially restricting future credit flow.
- •Increased interest rates, often a response to higher risk, reduce disposable income and discretionary spending.
- •This can create inflationary pressure and ultimately slow down overall economic growth.
- •RBI has implemented measures like increased risk weights to moderate the growth of unsecured lending and ensure financial stability.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•RBI Annual Reports and Monetary Policy Statements
•Economic Survey of India (various editions)
•Reports from leading financial dailies (e.g., The Economic Times, Business Standard)
•NITI Aayog policy documents on financial sector