What is Blockchain Technology? - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
What is Blockchain Technology?
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
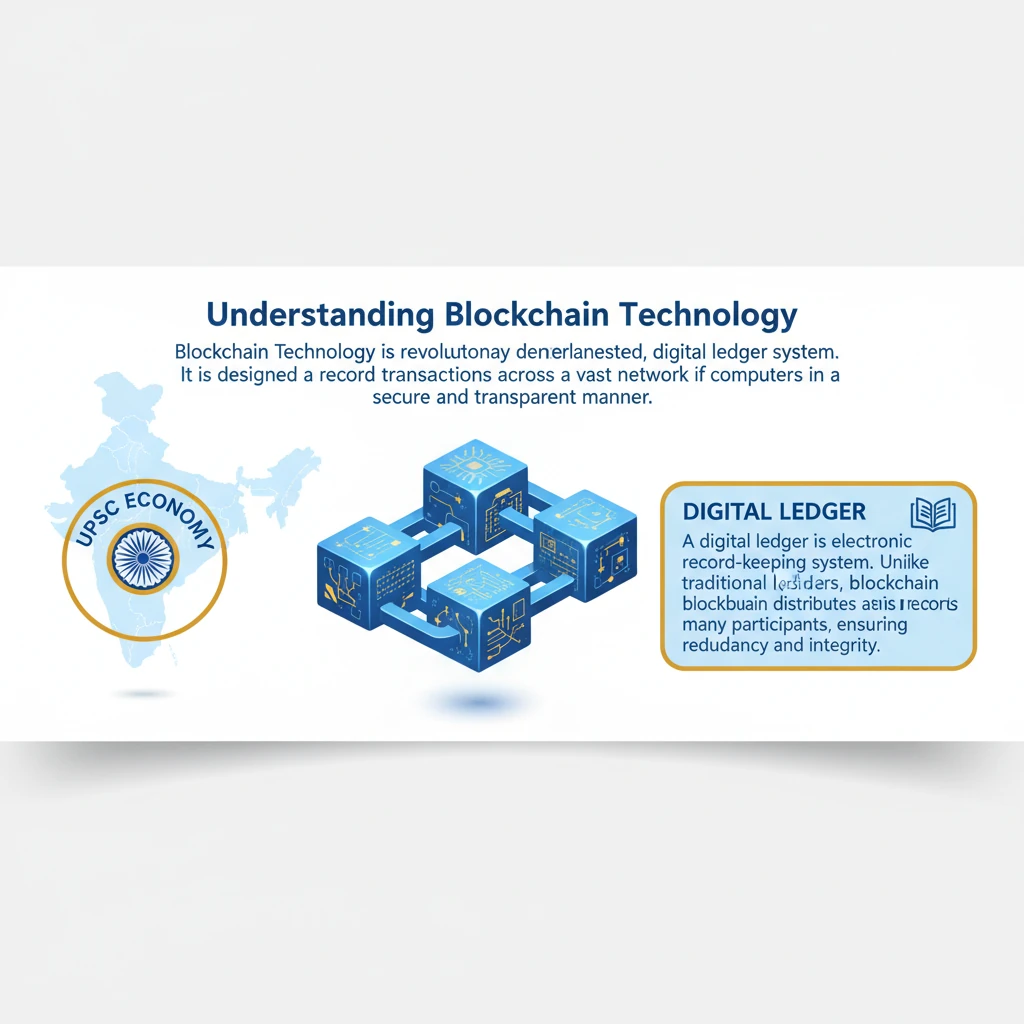
<h4>Understanding Blockchain Technology</h4><p><strong>Blockchain Technology</strong> is a revolutionary <strong>decentralised, digital ledger</strong> system. It is designed to record transactions across a vast network of computers in a secure and transparent manner.</p><div class='info-box'><p>A <strong>digital ledger</strong> is an electronic record-keeping system. Unlike traditional ledgers, blockchain distributes this record across many participants, ensuring redundancy and integrity.</p></div><h4>How Blockchain Works: Blocks and Transactions</h4><p>The fundamental unit of a blockchain is a <strong>block</strong>. Each block contains a collection of verified transactions, along with a timestamp and a cryptographic hash of the previous block.</p><p>When a new transaction occurs, it is first verified by the network participants. Once validated, it is added to a new block, which is then cryptographically appended to the existing chain of blocks.</p><p>Crucially, a record of this new block and its transactions is added to <strong>every participant's ledger</strong> within the network. This creates a distributed and redundant record, making it highly resilient.</p><h4>Decentralisation, Security, and Transparency</h4><p>The <strong>decentralised nature</strong> of blockchain technology is its core strength. It means no single central authority controls the ledger, eliminating a single point of failure or control.</p><p>This architecture ensures that once a transaction is recorded in a block and added to the chain, it becomes extremely difficult to alter or delete. Any attempt to tamper would require changing the record on a majority of the network's computers simultaneously, which is practically impossible.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>This inherent design provides a high degree of <strong>security</strong> and <strong>transparency</strong>, making blockchain resistant to fraud and unauthorised modifications. All participants can view the ledger, ensuring accountability.</p></div><h4>Applications Beyond Cryptocurrencies</h4><p>While <strong>Blockchain</strong> is famously the underlying technology for <strong>cryptocurrencies</strong> such as <strong>Bitcoin</strong>, its potential applications extend far beyond digital currencies.</p><p>Its ability to create immutable and transparent records makes it valuable in various sectors where trust and verifiable records are paramount.</p><p>For instance, <strong>financial institutions</strong> have been actively exploring and implementing blockchain for secure and transparent transaction processing. This helps in reducing fraud, streamlining operations, and lowering operational costs significantly.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>UPSC often asks about the broader applications of emerging technologies. Beyond cryptocurrencies, consider blockchain's use in supply chain management, healthcare, voting systems, and intellectual property rights for <strong>GS Paper III</strong>.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
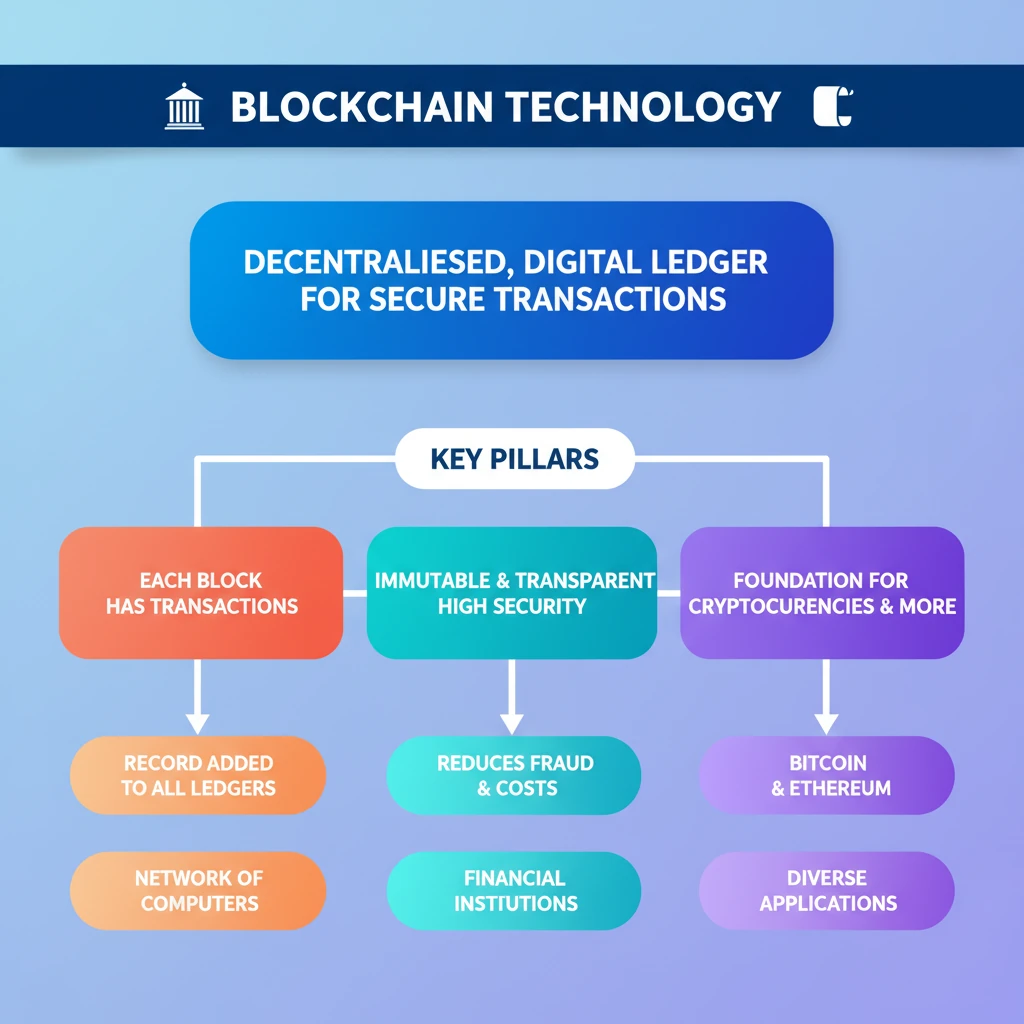
- •Blockchain is a decentralised, digital ledger recording transactions across a network of computers.
- •Each block contains multiple transactions, and a record is added to every participant's ledger.
- •Its decentralised nature ensures transactions are immutable, providing high security and transparency.
- •Blockchain is the foundation for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin but has diverse applications.
- •Financial institutions use blockchain for secure transaction processing, reducing fraud and operational costs.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Bitcoin Whitepaper by Satoshi Nakamoto
•IBM Blockchain documentation
•Reserve Bank of India (RBI) reports on Digital Currency
•Academic papers on Distributed Ledger Technology