Medium-Term Outlooks - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Medium-Term Outlooks
Medium⏱️ 12 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
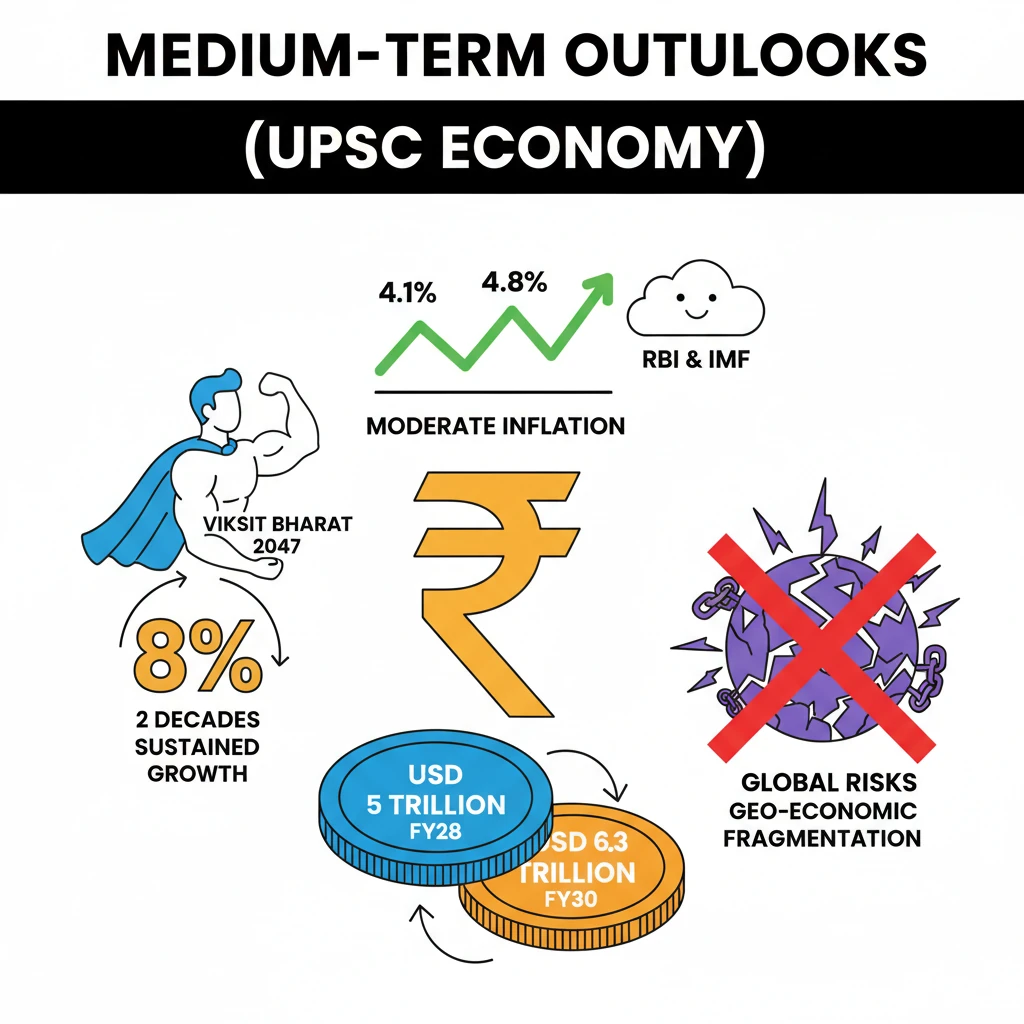
<h4>Inflation Projections and Economic Stability</h4><p>The <strong>Reserve Bank of India (RBI)</strong> has revised its inflation forecast for <strong>FY25</strong> to <strong>4.8%</strong>, up from a previous estimate of 4.5%. For <strong>FY26</strong>, the RBI anticipates inflation to moderate to <strong>4.2%</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The <strong>International Monetary Fund (IMF)</strong> provides a slightly different outlook, projecting <strong>4.4%</strong> inflation for <strong>FY25</strong> and <strong>4.1%</strong> for <strong>FY26</strong>. These forecasts assume stable economic conditions.</p></div><p>India's economic stability has shown improvement, with the <strong>rupee</strong> projected to depreciate mildly at only <strong>0.5% per year</strong>. This indicates a stronger economic footing compared to previous decades.</p><h4>Medium-Term Economic Growth Outlook</h4><p>The <strong>IMF</strong> projects India to achieve significant economic milestones in the coming years. India is expected to become a <strong>USD 5 trillion economy</strong> by <strong>FY28</strong>.</p><p>Furthermore, the <strong>IMF</strong> forecasts India's economy to reach <strong>USD 6.3 trillion</strong> by <strong>FY30</strong>. This growth is underpinned by an anticipated nominal <strong>GDP growth rate</strong> of <strong>10.2%</strong> between <strong>FY25 and FY30</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>To realize its ambitious goal of <strong>Viksit Bharat 2047</strong>, India needs to sustain an annual economic growth rate of <strong>8%</strong> for the next two decades. The <strong>IMF</strong> forecasts India's real <strong>GDP growth</strong> at <strong>6.5% annually</strong> from <strong>FY26 to FY30</strong>.</p></div><p>The <strong>Current Account Deficit (CAD)</strong> is expected to see a moderate increase, projected to rise to <strong>2.2% of GDP</strong> by <strong>FY30</strong>.</p><h4>Global Challenges and Risks</h4><p>Despite strong domestic projections, the global landscape presents several challenges. <strong>Geo-economic fragmentation</strong> poses a significant risk to global supply chains and investment flows.</p><p>Increased <strong>trade restrictions</strong> worldwide can impede India's export potential and integration into global value chains. <strong>China’s dominance</strong> in manufacturing and energy transition sectors also presents competitive pressures and supply chain vulnerabilities for India.</p><h4>Investment and Infrastructure Boost</h4><p><strong>Capital expenditure (Capex)</strong> has been a major driver of growth, demonstrating a robust <strong>38.8% Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR)</strong> from <strong>FY20 to FY24</strong>.</p><p>The government has launched several key initiatives to further boost infrastructure. These include the <strong>National Infrastructure Pipeline</strong> and the <strong>National Monetisation Pipeline</strong>, designed to channel significant investments into infrastructure development.</p><h4>Key Infrastructure Developments</h4><p>Significant progress has been made across various infrastructure sectors:</p><ul><li><strong>Road Connectivity:</strong> National Highway construction under <strong>Bharatmala</strong> reached <strong>6,215 km</strong>.</li><li><strong>Railways:</strong> <strong>2031 km</strong> of railway network commissioned between <strong>April and November 2024</strong>. <strong>17 new Vande Bharat trains</strong> have been introduced, enhancing modern rail travel.</li><li><strong>Aviation:</strong> <strong>619 UDAN air routes</strong> have been operationalized under the <strong>Regional Connectivity Scheme</strong>, improving air access to remote areas.</li><li><strong>Ports:</strong> Port capacity has grown under the <strong>Sagarmala</strong> program, with projects like the <strong>Jawaharlal Nehru Port</strong> contributing to enhanced maritime trade capabilities.</li></ul><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Energy Sector:</strong> India's total installed power capacity reached <strong>456.4 GW</strong>. Notably, <strong>renewable energy</strong> accounts for a substantial <strong>209.4 GW</strong>, representing a <strong>47% share</strong> of the total capacity.</p></div><p><strong>Digital Connectivity:</strong> <strong>5G services</strong> now cover <strong>779 districts</strong> across the country. The <strong>BharatNet</strong> project has expanded optical fiber connectivity to <strong>2.14 lakh Gram Panchayats</strong>, bridging the digital divide.</p><h4>Rural and Urban Development Initiatives</h4><p>Government schemes have significantly impacted rural and urban living standards:</p><ul><li><strong>Housing:</strong> The <strong>Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY)</strong> has sanctioned <strong>1.18 crore houses</strong>, providing affordable housing solutions.</li><li><strong>Water Supply:</strong> The <strong>Jal Jeevan Mission</strong> has successfully provided tap water connections to <strong>15.3 crore households</strong>, covering <strong>75.1%</strong> of rural households.</li><li><strong>Electrification:</strong> <strong>18,374 villages</strong> have been electrified, and <strong>2.9 crore households</strong> connected under schemes like <strong>Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Gram Jyoti Yojana (DDUGJY)</strong> and <strong>SAUBHAGYA</strong>.</li><li><strong>Sanitation:</strong> Under <strong>Swachh Bharat Mission (Phase II)</strong>, <strong>1.92 lakh villages</strong> were declared <strong>ODF Plus</strong> in 2024, contributing to a total of <strong>3.64 lakh ODF Plus villages</strong> by 2024.</li></ul><h4>Space Assets and Future Missions</h4><p>India currently operates <strong>56 active space assets</strong>, showcasing its growing capabilities in space technology. The <strong>Space Vision 2047</strong> aims for ambitious future missions.</p><p>These future missions include the human spaceflight program <strong>Gaganyaan</strong> and advanced lunar exploration with <strong>Chandrayaan-4</strong>, highlighting India's long-term strategic vision in space.</p><h4>Industrial Growth and Manufacturing Prowess</h4><p>The <strong>industrial sector</strong> is projected to grow by <strong>6.2%</strong> in <strong>FY25</strong>, according to first advance estimates. This growth is primarily driven by robust performance in the <strong>electricity</strong> and <strong>construction</strong> sectors.</p><p>The government is actively promoting <strong>Smart Manufacturing</strong> and <strong>Industry 4.0</strong> initiatives. Support is provided for establishing <strong>SAMARTH Udyog centres</strong> to foster technological adoption and innovation in manufacturing.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Key Sectoral Growth:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Steel production</strong> saw an <strong>8.3% increase</strong> from <strong>April to November FY24</strong>.</li><li><strong>Electronics output</strong> reached <strong>₹8.9 lakh crore</strong>.</li><li><strong>98% of smartphones</strong> are now made domestically, significantly reducing India's dependence on imports.</li></ul></div><p>According to the <strong>WIPO Report 2022</strong>, India ranks <strong>sixth</strong> among the top 10 patent filing offices globally. Resident filings accounted for over half (<strong>55.5%</strong>) of all submissions, a first for the country.</p><h4>MSME Sector Contributions</h4><p>The <strong>MSME sector</strong> is a vital employer, providing livelihoods to <strong>23.24 crore people</strong>. Formalization efforts have seen <strong>2.35 crore businesses</strong> registered under <strong>Udyam Assist</strong>.</p><p>To provide crucial equity funding and support scaling up for promising MSMEs, the government launched the <strong>Self-Reliant India Fund</strong>. This initiative aims to strengthen the backbone of India's economy.</p>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •RBI and IMF project moderate inflation (4.1-4.8%) for FY25-FY26, indicating economic stability.
- •India is projected to become a USD 5 trillion economy by FY28 and USD 6.3 trillion by FY30.
- •Achieving Viksit Bharat 2047 requires sustained 8% annual growth for two decades.
- •Global challenges like geo-economic fragmentation pose risks to India's outlook.
- •Robust Capex growth (38.8% CAGR) and infrastructure projects (NIP, Bharatmala, Sagarmala) are key growth drivers.
- •Significant progress in rural/urban development (PMAY, Jal Jeevan Mission, ODF Plus) and digital/space sectors.
- •Manufacturing sector showing strong growth, with increased domestic production (e.g., smartphones) and patent filings.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Reserve Bank of India (RBI) Monetary Policy Reports
•International Monetary Fund (IMF) World Economic Outlook reports
•Ministry of Finance, Government of India - Economic Survey
•Press Information Bureau (PIB) releases on government schemes