Debt Sustainability and Exchange Rate Management - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Debt Sustainability and Exchange Rate Management
Medium⏱️ 9 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
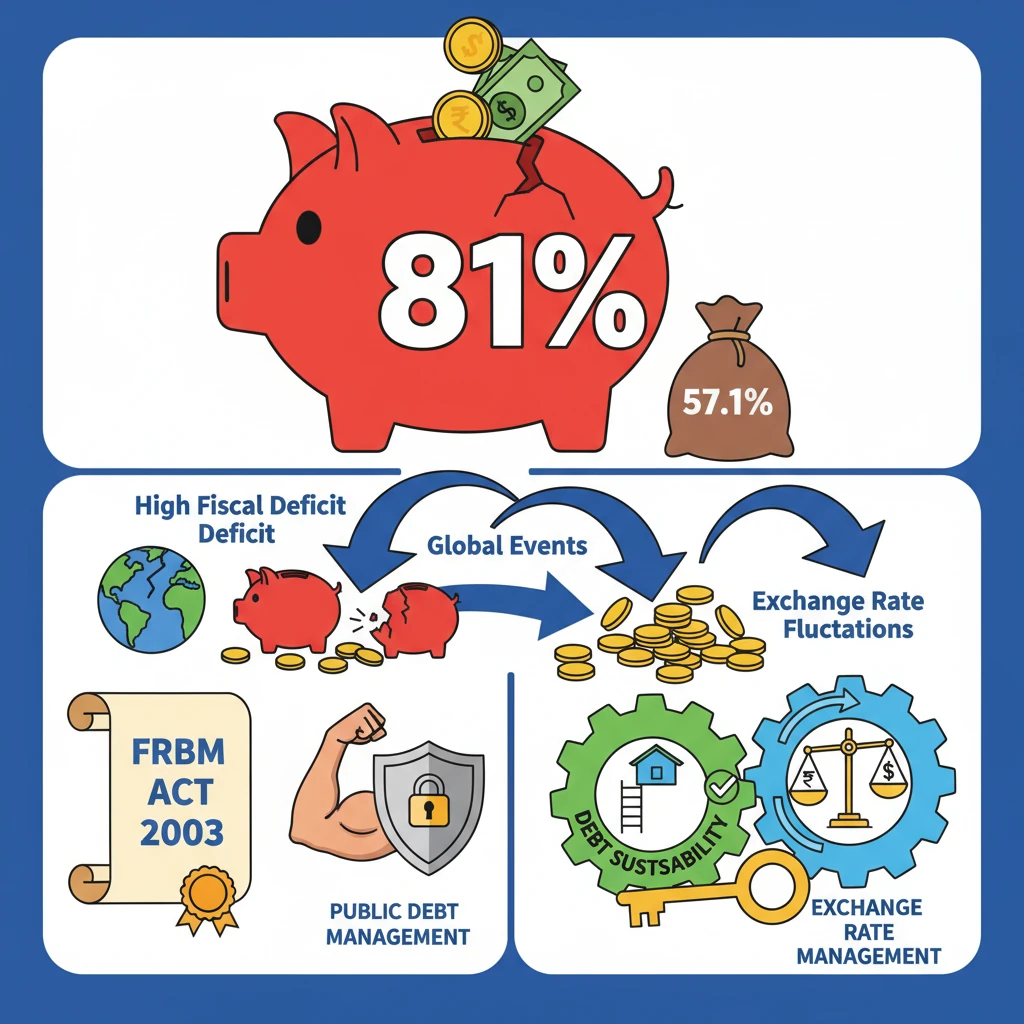
<h4>Introduction to Debt Sustainability and Exchange Rate Management</h4><p>The <strong>International Monetary Fund (IMF)</strong> recently released its annual <strong>Article IV consultation report</strong> on <strong>India</strong>.</p><p>This report provides a comprehensive assessment of India's economic health, including critical areas like <strong>debt sustainability</strong> and <strong>exchange rate management</strong>.</p><h4>India's Current Debt Scenario</h4><p>Understanding <strong>India's debt landscape</strong> is crucial for evaluating its economic stability and future growth prospects.</p><p>Both the <strong>Central Government</strong> and <strong>State Governments</strong> contribute significantly to the overall public debt burden.</p><div class='info-box'><ul><li><strong>Central Government's debt</strong>: Approximately <strong>₹155.6 trillion</strong> by <strong>March 2023</strong>.</li><li>This figure represented about <strong>57.1% of India's GDP</strong> at that time.</li><li><strong>State Governments' debt</strong>: Accounted for roughly <strong>28% of GDP</strong>.</li><li><strong>Overall Public Debt-to-GDP Ratio</strong>: Stood at <strong>81% in 2022-23</strong>, as reported by the <strong>Finance Ministry</strong>.</li></ul></div><h4>Factors Contributing to India's Rising Debt Levels</h4><p>Several interconnected factors contribute to the upward trend in <strong>India's public debt</strong>. These factors highlight both internal structural issues and external influences.</p><div class='key-point-box'><ul><li><strong>High Fiscal Deficit</strong>: A persistent imbalance where <strong>government expenditure exceeds its revenue</strong>. This deficit is primarily financed through <strong>borrowing</strong>.</li><li><strong>High Expenditure Commitments</strong>: Significant spending on welfare schemes, infrastructure projects, subsidies, and defense can strain public finances.</li><li><strong>Slow Revenue Growth</strong>: Insufficient growth in tax and non-tax revenues limits the government's ability to fund its commitments without resorting to debt.</li><li><strong>Global Geopolitical Events</strong>: External shocks like wars, pandemics, or commodity price spikes can necessitate increased government spending or reduce revenue, leading to higher borrowing.</li><li><strong>Informal Economy and Tax Leakage</strong>: A large informal sector and issues like tax evasion can reduce the overall tax base, impacting revenue collection.</li><li><strong>Guarantees and Contingencies</strong>: Government guarantees to public sector undertakings or other entities can turn into actual liabilities if the guaranteed party defaults, adding to debt.</li><li><strong>Exchange Rate Fluctuations</strong>: A depreciation of the domestic currency can increase the local currency value of foreign currency denominated debt, making it more expensive to service.</li></ul></div><h4>Legislative Framework for Debt Management</h4><p>To ensure fiscal discipline and manage debt sustainably, <strong>India</strong> has enacted specific legislation.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The primary legal framework is the <strong>Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management Act, 2003 (FRBM Act)</strong>.</p><p>This Act aims to introduce transparency and accountability in India's fiscal management and set targets for reducing fiscal deficit and public debt.</p></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight</strong>: Understanding the provisions and amendments of the <strong>FRBM Act</strong> is crucial for Mains <strong>GS Paper III (Economy)</strong> questions on fiscal policy and public finance.</p></div>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •India's public debt-to-GDP ratio stood at 81% in 2022-23, with Central Government debt at 57.1% of GDP by March 2023.
- •High fiscal deficit, global events, and exchange rate fluctuations are key drivers of rising debt levels.
- •The FRBM Act, 2003, is India's primary legislation for fiscal discipline and public debt management.
- •Debt sustainability ensures a nation can meet its financial obligations without economic distress, while exchange rate management stabilizes currency value.
- •The IMF's Article IV consultation provides an external assessment and recommendations for India's macroeconomic policies.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•International Monetary Fund (IMF) Article IV Consultation Report on India
•Ministry of Finance, Government of India