Status of India’s Renewable Energy - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Status of India’s Renewable Energy
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
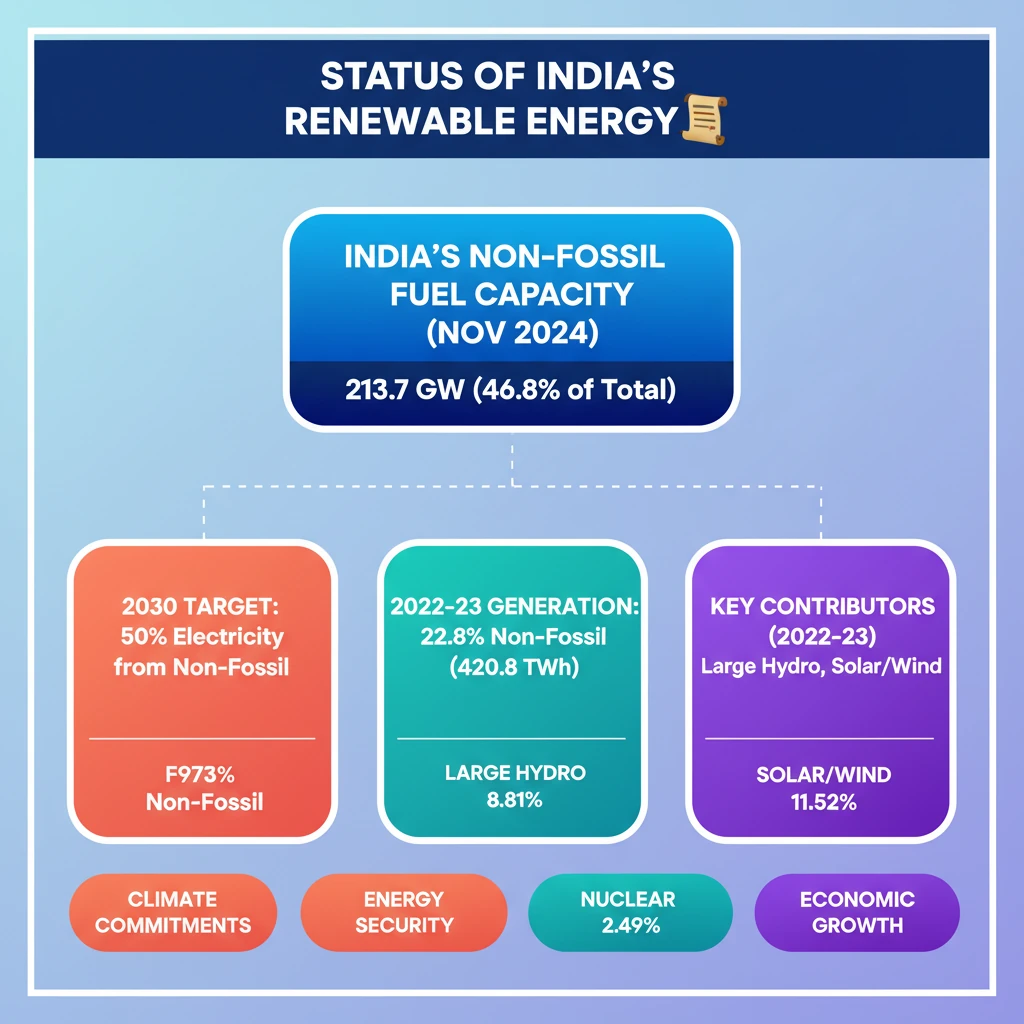
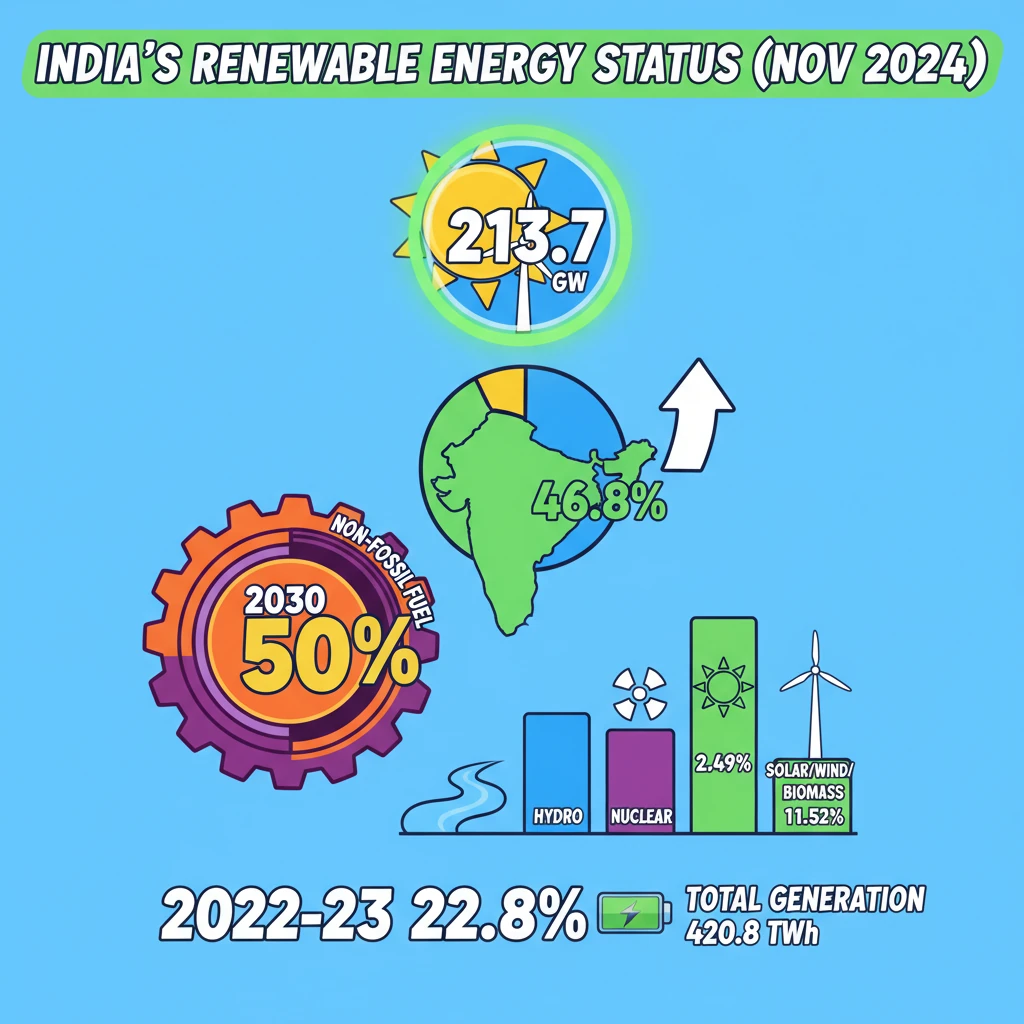
<h4>India's Renewable Energy Status: An Overview</h4><p>India is making significant strides in its transition towards a sustainable energy future. The nation's commitment to reducing its carbon footprint is evident in its rapidly expanding <strong>renewable energy capacity</strong> and ambitious future targets.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The shift towards <strong>non-fossil fuel sources</strong> is a cornerstone of India's energy policy, aiming to bolster energy security and meet international climate commitments.</p></div><h4>Current Installed Capacity from Non-Fossil Fuels</h4><p>As of <strong>November 2024</strong>, India's total installed electricity capacity from <strong>non-fossil fuel sources</strong> stands at an impressive <strong>213,701 MW</strong>. This represents a substantial portion of the country's overall power generation infrastructure.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Key Data:</strong><ul><li><strong>Installed Non-Fossil Fuel Capacity:</strong> 213,701 MW</li><li><strong>Share of Total Electricity Capacity:</strong> 46.8%</li></ul></p></div><h4>Future Targets for Electricity Generation</h4><p>India has set an ambitious target to further increase its reliance on clean energy. The goal is to ensure that <strong>50% of its electricity generation</strong> originates from <strong>non-fossil fuel sources by 2030</strong>.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>This target is crucial for understanding India's commitments under the <strong>Paris Agreement</strong> and its broader climate action strategy. UPSC often asks about such national targets and their implications.</p></div><h4>Progress in Non-Fossil Fuel Generation (2022-23)</h4><p>In the fiscal year <strong>2022-23</strong>, the contribution from <strong>non-fossil fuel sources</strong> to India's total electricity generation was significant. A total of <strong>420.8 thousand GWh</strong> was generated from these sources.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Generation Share (2022-23):</strong><ul><li><strong>Total Non-Fossil Fuel Generation:</strong> 420.8 thousand GWh</li><li><strong>Contribution to Total Generation:</strong> 22.8%</li></ul></p></div><h4>Component-wise Contribution to Non-Fossil Fuel Generation</h4><p>The <strong>non-fossil fuel generation mix</strong> comprises various sources, each playing a vital role in India's energy landscape. <strong>Solar</strong>, <strong>Wind</strong>, and <strong>Biomass</strong> collectively form a significant portion, alongside <strong>Large Hydro</strong> and <strong>Nuclear Power</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Breakdown of Non-Fossil Fuel Generation (2022-23):</strong><ul><li><strong>Large Hydro:</strong> 8.81%</li><li><strong>Nuclear:</strong> 2.49%</li><li><strong>Solar, Wind, Biomass (combined):</strong> 11.52%</li></ul></p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •As of November 2024, India's non-fossil fuel capacity is 213,701 MW, comprising 46.8% of total electricity capacity.
- •India aims for 50% of its electricity generation from non-fossil fuels by 2030.
- •In 2022-23, non-fossil fuels contributed 22.8% to total generation (420.8 thousand GWh).
- •Large Hydro (8.81%), Nuclear (2.49%), and Solar/Wind/Biomass (11.52%) are key contributors to non-fossil fuel generation.
- •India's renewable energy push is crucial for climate commitments, energy security, and economic growth.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Ministry of Power, Government of India (for installed capacity data)
•Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE), Government of India (for policy and generation data)