Legislative Amendments: The Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957 - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Legislative Amendments: The Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
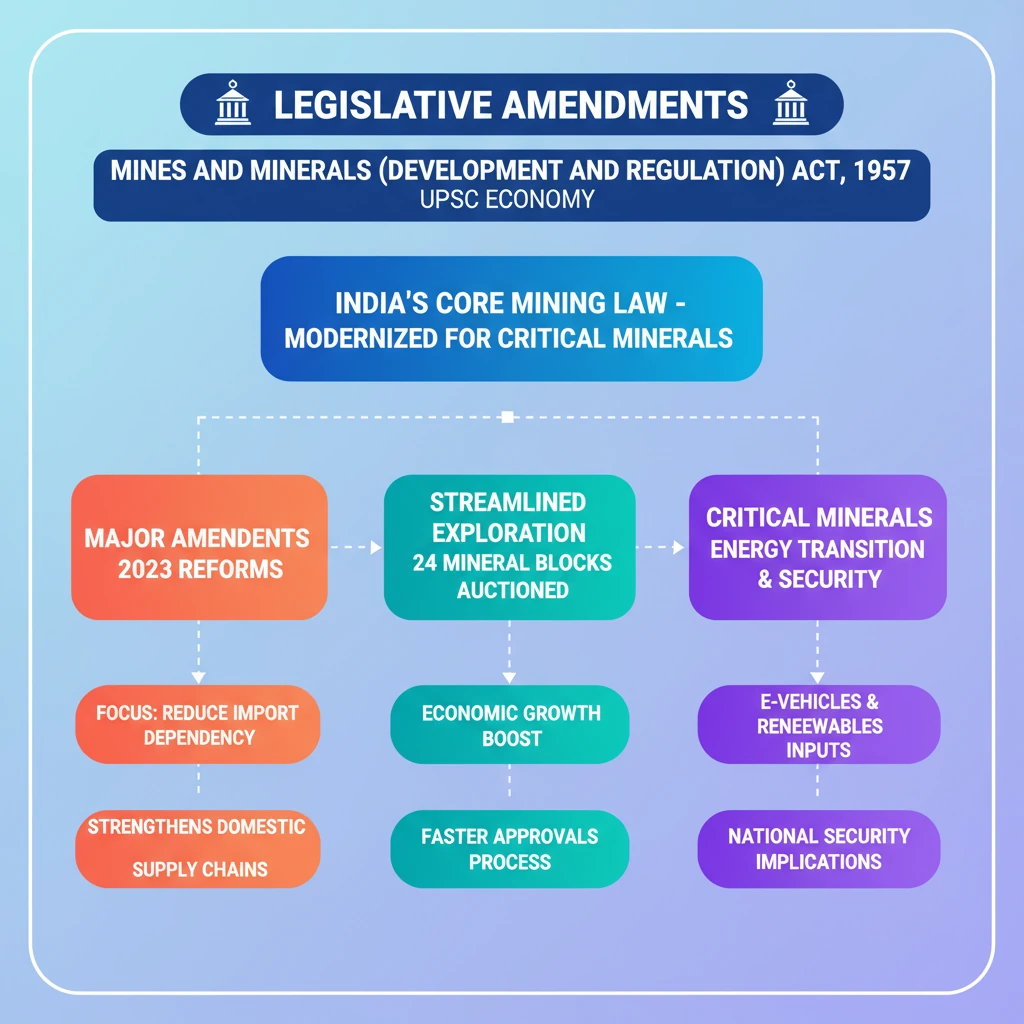
<h4>The Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957</h4><p>The <strong>Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957 (MMDR Act)</strong> is the principal legislation governing the mining sector in India. It aims to provide for the development and regulation of mines and minerals under the control of the Union.</p><p>This Act lays down the framework for granting <strong>mining leases</strong> and <strong>prospecting licenses</strong>, ensuring systematic development of mineral resources while safeguarding environmental and social concerns.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Act Name:</strong> The Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957</p><p><strong>Primary Objective:</strong> Regulation of mines and mineral development in India.</p></div><h4>The 2023 Amendment and its Rationale</h4><p>In <strong>2023</strong>, significant legislative amendments were introduced to the <strong>MMDR Act, 1957</strong>. These changes were primarily aimed at boosting the exploration and extraction of <strong>critical minerals</strong> within the country.</p><p>The amendment seeks to <strong>streamline critical mineral exploration</strong> by simplifying processes and encouraging private sector participation. This move is crucial for India's strategic independence and economic growth.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Critical Minerals:</strong> These are essential for modern technologies, economic development, and national security. They often have high supply chain risks due to geographical concentration of production.</p></div><h4>Impact: Auction of Strategic Mineral Blocks</h4><p>A direct outcome of the <strong>2023 amendments</strong> has been the facilitation of the <strong>auction of strategic mineral blocks</strong>. This initiative aims to unlock India's mineral potential and reduce reliance on imports.</p><p>Specifically, the amendments led to the auction of <strong>24 strategic mineral blocks</strong>. These blocks contain minerals vital for sectors like renewable energy, electric vehicles, and defence manufacturing.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Outcome of Amendment:</strong> Auction of <strong>24 strategic mineral blocks</strong>.</p><p><strong>Purpose:</strong> Enhance domestic supply, reduce import dependency, and secure raw materials for future industries.</p></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Understand the distinction between 'critical' and 'strategic' minerals. The <strong>MMDR Act amendments</strong> are a key policy tool for India's energy transition and self-reliance goals. Questions can link to GS-3 (Economy, Infrastructure) and GS-2 (Governance, Policy).</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •The MMDR Act, 1957, is India's core mining legislation.
- •Major amendments in 2023 aimed to streamline critical mineral exploration.
- •The amendments led to the auction of 24 strategic mineral blocks.
- •Focus on critical minerals is vital for India's energy transition, economic growth, and national security.
- •These reforms reduce import dependency and strengthen domestic supply chains for key industries.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Press Information Bureau (PIB) releases, Ministry of Mines, Government of India
•Annual Reports of the Ministry of Mines, Government of India