Need of Reforms in Tea Industry - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Need of Reforms in Tea Industry
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
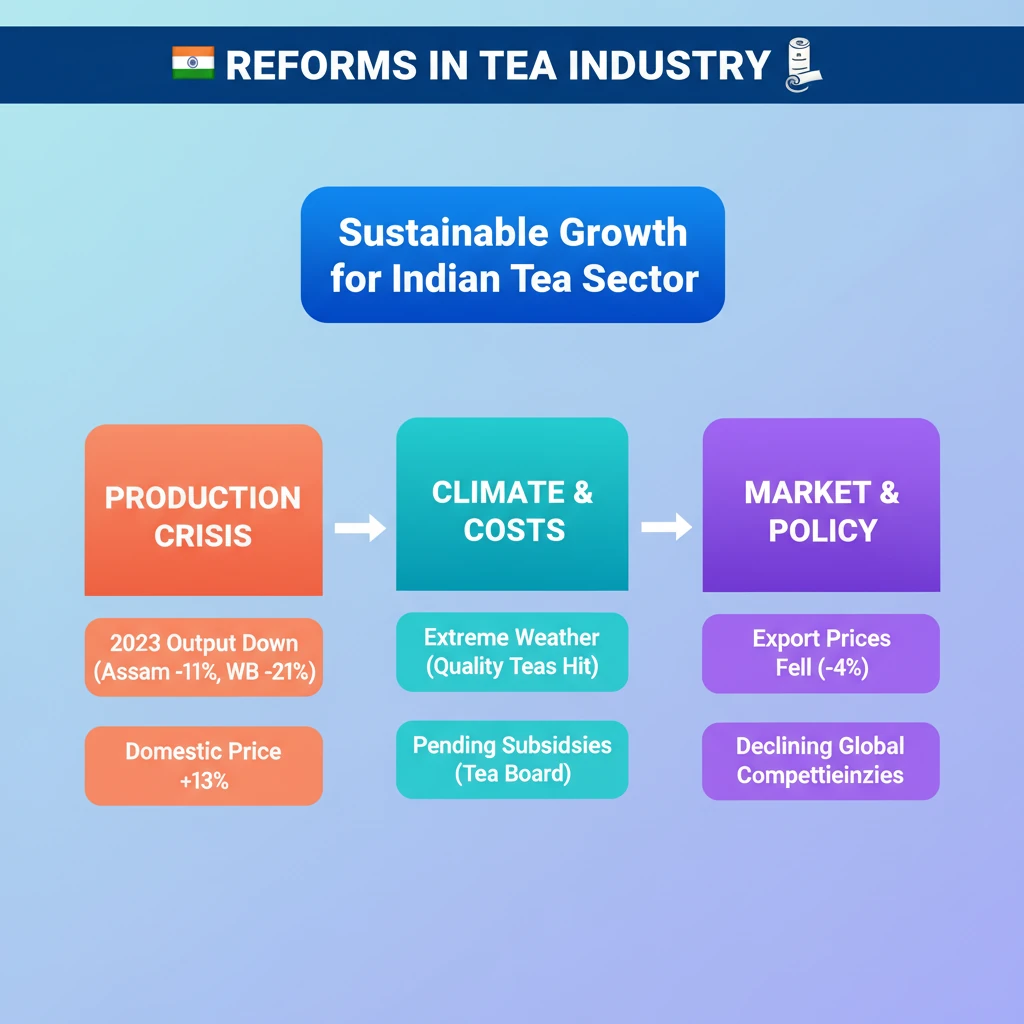
<h4>Introduction to the Need for Reforms</h4><p>The <strong>Indian Tea Industry</strong> is currently facing significant challenges, necessitating urgent reforms. A notable <strong>price increase</strong> of approximately <strong>13%</strong> for <strong>Assam</strong> and <strong>West Bengal</strong> teas has been observed.</p><p>This surge in prices is directly attributed to a substantial <strong>drop in tea production</strong> in <strong>2024</strong>. The industry's sustainability is at risk, highlighting the critical need for strategic interventions.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Key Challenge:</strong> The primary driver for reform is the imperative to ensure <strong>sustainable development</strong> in the face of declining production and market pressures.</p></div><h4>Current State of the Indian Tea Industry</h4><p>The Indian tea sector, a significant contributor to the agricultural economy, is grappling with multiple issues. Recent trends indicate a concerning downturn in key performance indicators.</p><p>These challenges collectively impact the profitability and long-term viability of tea plantations and associated livelihoods.</p><h4>Recent Production and Price Trends</h4><p><strong>Tea production</strong> witnessed a significant decline in <strong>2023</strong>. <strong>West Bengal</strong> experienced a drop of around <strong>21%</strong>, while <strong>Assam</strong> saw an <strong>11%</strong> reduction.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Impact of Production Drop:</strong> This decrease directly led to a <strong>13% increase</strong> in <strong>domestic tea prices</strong>, affecting consumers and indicating supply-side stress.</p></div><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Root Cause:</strong> <strong>Extreme weather events</strong> and broader <strong>climate change</strong> impacts are identified as major contributors to these production losses, threatening future harvests.</p></div><h4>Impact on Premium Products</h4><p>The crop losses predominantly affected the <strong>first and second shower of monsoon</strong> teas. These are traditionally considered the <strong>best quality teas</strong> of the year, commanding premium prices.</p><p>The loss of these high-value products severely impacts the industry's overall <strong>profitability</strong> and <strong>cash flows</strong>, especially for smaller growers and estates.</p><h4>Challenges in the Export Market</h4><p>Despite domestic price increases, the <strong>export market</strong> for Indian tea has shown a discouraging trend. <strong>Export prices</strong> have fallen by <strong>4%</strong> this year, indicating a loss of competitiveness.</p><p>This decline in export value further strains the financial health of the industry, which relies on international markets for a significant portion of its revenue.</p><h4>Financial Burden: Pending Subsidies</h4><p>The industry is facing additional financial pressure due to <strong>pending subsidies</strong> from the <strong>Tea Board</strong>. These subsidies are crucial for <strong>developmental work</strong> carried out by estates in recent years.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Financial Strain:</strong> The non-receipt of these due funds has exacerbated the <strong>financial burden</strong> on tea growers, particularly during a period of reduced production and profitability.</p></div><h4>Global Tea Landscape</h4><p>Understanding India's position requires a look at global statistics. The <strong>global tea market</strong> is substantial, with significant production and consumption figures.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Global Tea Statistics (2022):</strong><ul><li><strong>Total Global Production:</strong> 6,478 million kg</li><li><strong>Global Tea Consumption:</strong> 6,209 million kg</li></ul></p></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Questions on the <strong>Tea Industry</strong> often link to <strong>agricultural policy</strong>, <strong>climate change impacts</strong> on crops, <strong>international trade</strong>, and the role of <strong>commodity boards</strong> like the <strong>Tea Board of India</strong>. Be prepared to discuss challenges and potential solutions.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Indian tea production dropped significantly in 2023 (Assam -11%, WB -21%), leading to a 13% domestic price rise.
- •Extreme weather and climate change are primary causes of production loss, particularly for premium first/second flush teas.
- •Export prices fell by 4%, indicating declining global competitiveness.
- •Pending subsidies from the Tea Board are adding to the financial burden on the industry.
- •Reforms are crucial for the sustainable development and long-term viability of the Indian tea sector.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•General knowledge of Indian economy and agriculture