What are the Government Initiatives for the Sugar Industry? - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

What are the Government Initiatives for the Sugar Industry?
Medium⏱️ 6 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
<h4>Understanding India's Sugar Industry and the Need for Reforms</h4><p>The <strong>sugar industry</strong> is a vital agro-based sector in India, second only to textiles. It plays a crucial role in the rural economy, impacting millions of farmers involved in <strong>sugarcane cultivation</strong> and workers in sugar mills. Despite its significance, the industry has historically faced numerous challenges, necessitating periodic government intervention and reforms.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The Indian sugar sector is characterized by its cyclical nature, often oscillating between periods of surplus production and scarcity, leading to price volatility and financial distress for stakeholders.</p></div><h4>The Rangarajan Committee (2012): A Landmark Initiative</h4><p>Recognizing the complex issues plaguing the sugar industry, the government established the <strong>Rangarajan Committee</strong> in <strong>2012</strong>. This high-level expert committee was tasked with providing comprehensive recommendations aimed at reforming the sector.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Committee Head:</strong> Dr. C. Rangarajan (former Chairman of the Prime Minister's Economic Advisory Council).</p><p><strong>Year of Establishment:</strong> <strong>2012</strong>.</p><p><strong>Primary Mandate:</strong> To suggest reforms for the <strong>deregulation</strong> and modernization of the sugar industry.</p></div><h4>Objectives and Scope of the Rangarajan Committee</h4><p>The committee's primary objective was to address systemic issues that hindered the industry's efficiency and profitability. This included examining aspects related to pricing, production, distribution, and the overall regulatory framework.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Committees like <strong>Rangarajan Committee</strong> are frequently asked in <strong>GS Paper III (Economy)</strong>, especially their recommendations and impact on specific sectors. Understanding the context of their formation is key.</p></div><p>The recommendations were intended to create a more market-oriented and sustainable environment for sugar production, benefiting both farmers and mill owners, while ensuring consumer access to sugar at reasonable prices.</p>
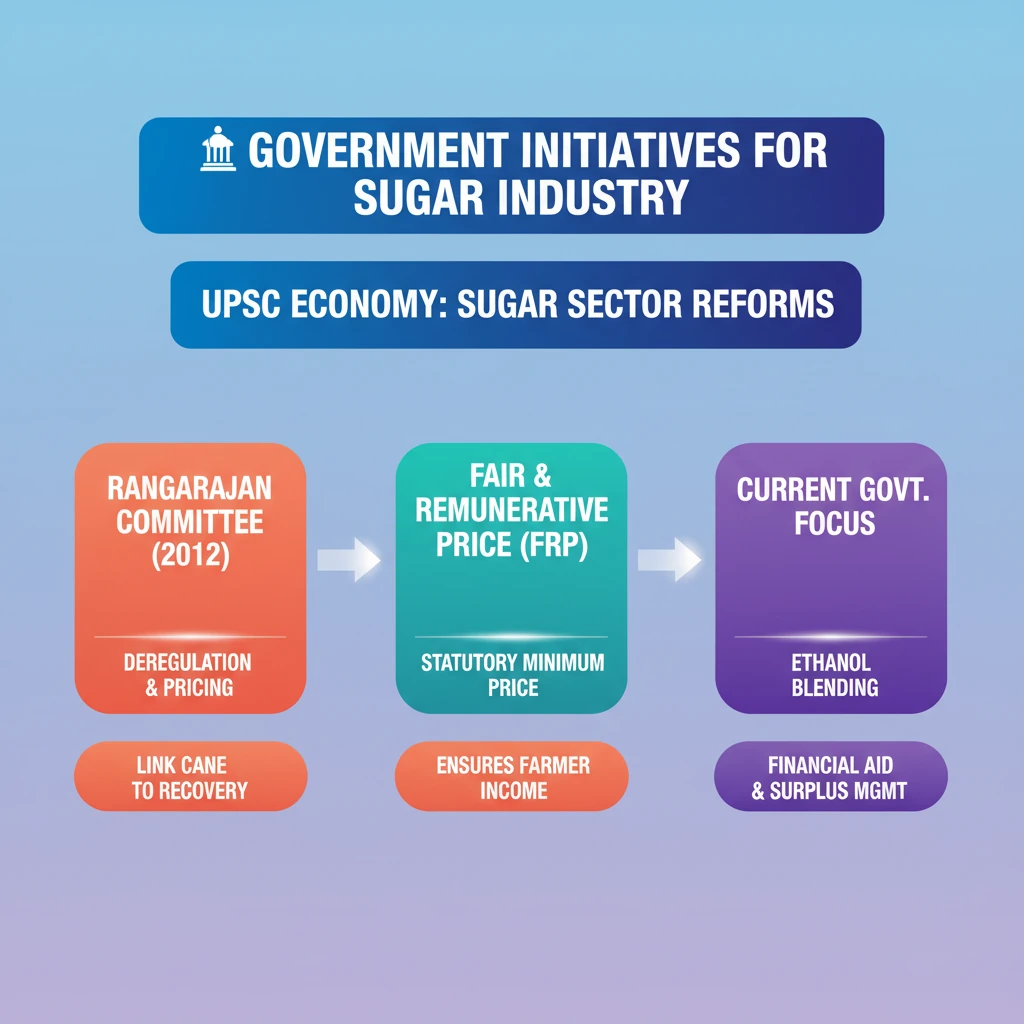
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Rangarajan Committee (2012) was a key initiative for sugar industry reforms.
- •It aimed to deregulate pricing, abolish levy sugar, and link cane prices to sugar recovery.
- •Fair and Remunerative Price (FRP) is a statutory minimum price for sugarcane, ensuring farmer income.
- •The sugar industry faces cyclical production, cane price arrears, and financial distress for mills.
- •Current government focus includes ethanol blending, financial aid to mills, and managing surplus production.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food & Public Distribution, Department of Food & Public Distribution (Official website)
•Press Information Bureau (PIB) releases on sugar industry
•Reports by Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP)