Bilateral Currency Swap Agreements: India with Japan & Sri Lanka - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
Bilateral Currency Swap Agreements: India with Japan & Sri Lanka
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
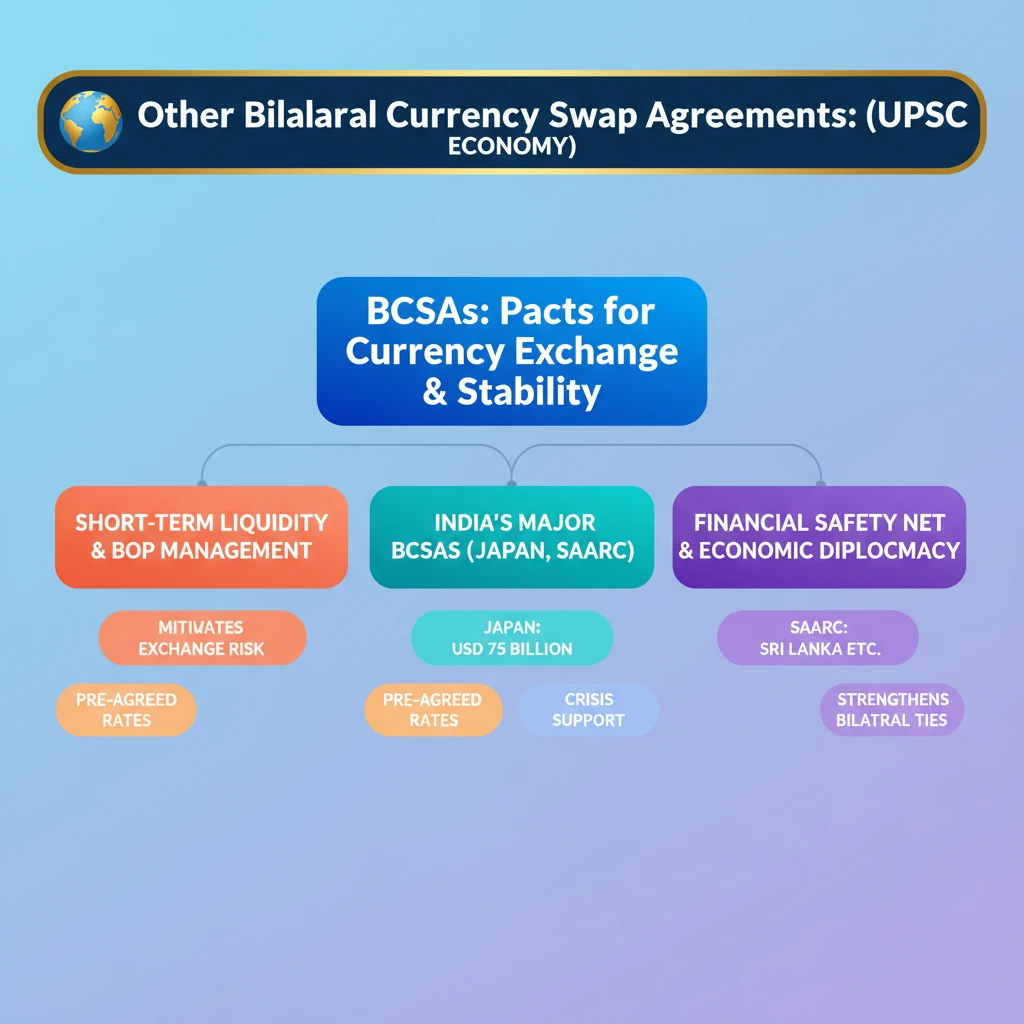
<h4>Understanding Bilateral Currency Swap Agreements</h4><p>A <strong>Bilateral Currency Swap Agreement</strong> (BCSA) is a pact between two countries to exchange their respective currencies at a pre-agreed exchange rate. This arrangement typically involves exchanging a certain amount of currency for a specified period, with an agreement to reverse the transaction at a later date, often at the same exchange rate.</p><p>These agreements are crucial tools for <strong>economic diplomacy</strong> and <strong>financial stability</strong>. They provide a safety net for countries facing short-term liquidity issues or balance of payments crises.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Key Concept:</strong> A currency swap allows a country to borrow foreign currency from another country's central bank without having to tap into international capital markets, which can be costly or difficult during times of stress.</p></div><h4>Purpose and Benefits of BCSAs</h4><p>Bilateral Currency Swap Agreements serve multiple strategic and economic purposes for participating nations.</p><ul><li><strong>Managing Balance of Payments (BoP):</strong> They help countries manage their <strong>Balance of Payments</strong> by providing access to foreign currency liquidity when needed.</li><li><strong>Short-Term Liquidity:</strong> BCSAs offer a ready source of foreign exchange to meet short-term import financing needs or to address sudden capital outflows.</li><li><strong>Reducing Exchange Rate Risk:</strong> By pre-agreeing on exchange rates, they can help mitigate <strong>exchange rate volatility</strong> and risk.</li><li><strong>Strengthening Economic Ties:</strong> These agreements foster closer economic and financial cooperation between signatory countries.</li><li><strong>Crisis Management:</strong> They act as a crucial financial backstop during times of economic distress or global financial crises.</li></ul><h4>India's Bilateral Swap Framework</h4><p>The <strong>Reserve Bank of India (RBI)</strong> has a framework for offering currency swaps to other central banks, particularly those in the <strong>SAARC</strong> (South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation) region and other friendly nations. This framework is part of India's broader strategy to enhance regional financial stability and economic cooperation.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>RBI's Swap Facility:</strong> The RBI's framework allows eligible central banks to draw US Dollar, Euro, or Indian Rupee funds from the RBI, depending on the specific agreement and mutual consent. The facility is typically for a short duration, ranging from <strong>three months to two years</strong>.</p></div><h4>India-Japan Currency Swap Agreement</h4><p>The <strong>India-Japan Currency Swap Agreement</strong> is one of India's most significant bilateral swap arrangements, reflecting the strong economic and strategic partnership between the two nations.</p><p>Initially signed in <strong>2008</strong>, this agreement has been periodically renewed and expanded. It serves as a vital financial safety net for India, providing access to a substantial amount of foreign currency liquidity.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Key Details:</strong> The swap agreement between <strong>India</strong> and <strong>Japan</strong> was significantly enhanced over the years. In <strong>2018</strong>, it was expanded to <strong>USD 75 billion</strong>, making it one of the largest bilateral currency swap agreements globally. This facility can be drawn in <strong>Japanese Yen</strong> or <strong>Indian Rupee</strong>.</p></div><p>The agreement underscores mutual trust and commitment to supporting each other's financial stability, especially during periods of global economic uncertainty.</p><h4>India-Sri Lanka Currency Swap Agreement</h4><p>The <strong>India-Sri Lanka Currency Swap Agreement</strong> is a crucial component of India's efforts to support its neighboring economies, particularly during times of economic hardship.</p><p>This agreement provides <strong>Sri Lanka</strong> with much-needed foreign exchange liquidity, helping it manage its <strong>Balance of Payments</strong> challenges and stabilize its economy.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Recent Developments:</strong> In <strong>2020</strong>, the <strong>Reserve Bank of India</strong> signed a <strong>USD 400 million</strong> currency swap facility with the <strong>Central Bank of Sri Lanka</strong> under the <strong>SAARC Currency Swap Framework</strong>. This was extended multiple times, providing critical support during Sri Lanka's severe economic crisis.</p></div><p>The swap facility demonstrates India's commitment to regional stability and its role as a first responder to the financial needs of its neighbors.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Questions on <strong>Bilateral Currency Swap Agreements</strong> often appear in <strong>GS Paper III (Economy)</strong>, focusing on their role in <strong>forex management</strong>, <strong>international relations</strong>, and <strong>regional cooperation</strong>. Be prepared to discuss their benefits and specific examples like <strong>India-Japan</strong> and <strong>India-Sri Lanka</strong>.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Bilateral Currency Swap Agreements (BCSAs) are pacts between two countries' central banks to exchange currencies at pre-agreed rates.
- •Their primary purpose is to provide short-term foreign currency liquidity, manage Balance of Payments, and mitigate exchange rate risk.
- •India has significant BCSAs, notably with Japan (USD 75 billion) and through the SAARC Currency Swap Framework (e.g., with Sri Lanka).
- •These agreements serve as crucial financial safety nets, especially during global economic uncertainties or crises.
- •BCSAs are key tools for India's economic diplomacy, strengthening bilateral ties and promoting regional financial stability.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Ministry of Finance, Government of India documents.
•Economic Survey of India.
•IMF (International Monetary Fund) publications on currency swap lines.
•News reports from reputable financial media (e.g., The Economic Times, Livemint, Reuters) covering India-Japan and India-Sri Lanka swap agreements.