What is Energy Security? - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

What is Energy Security?
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
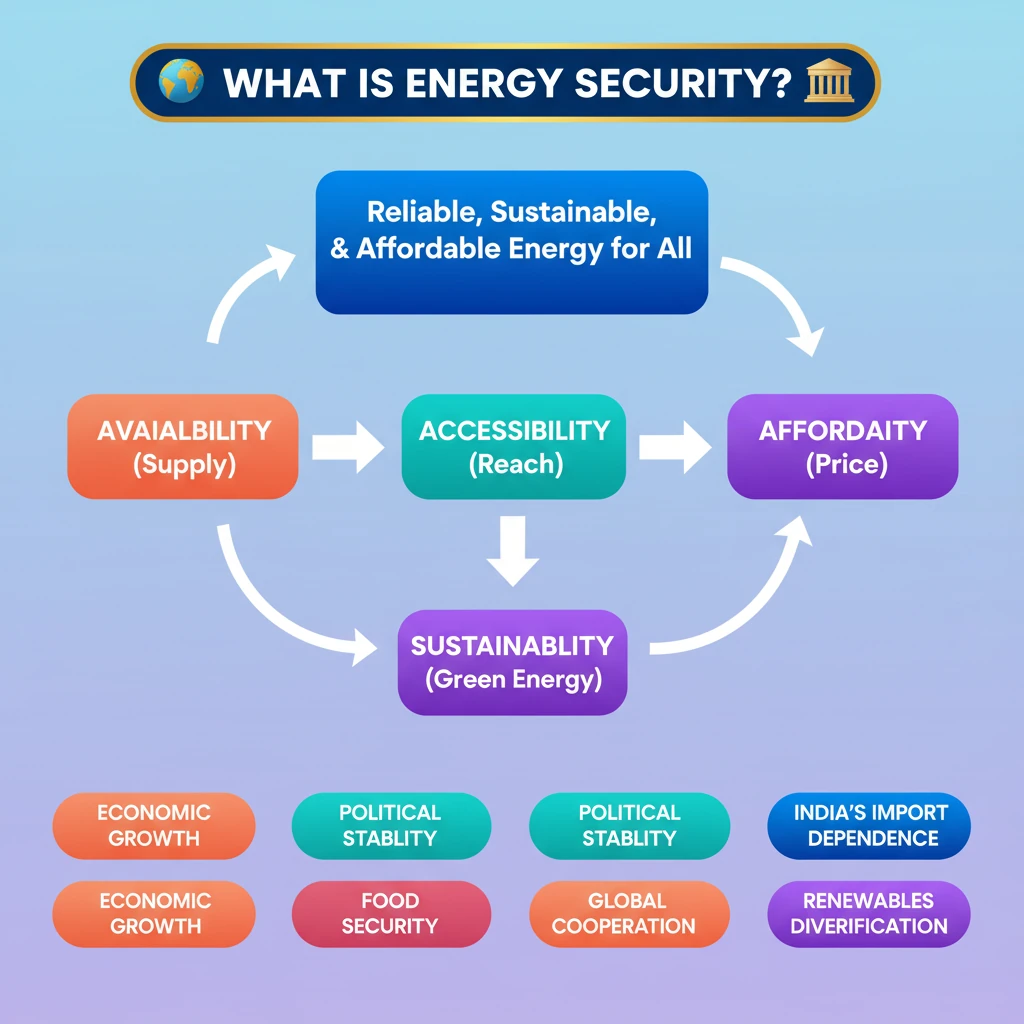
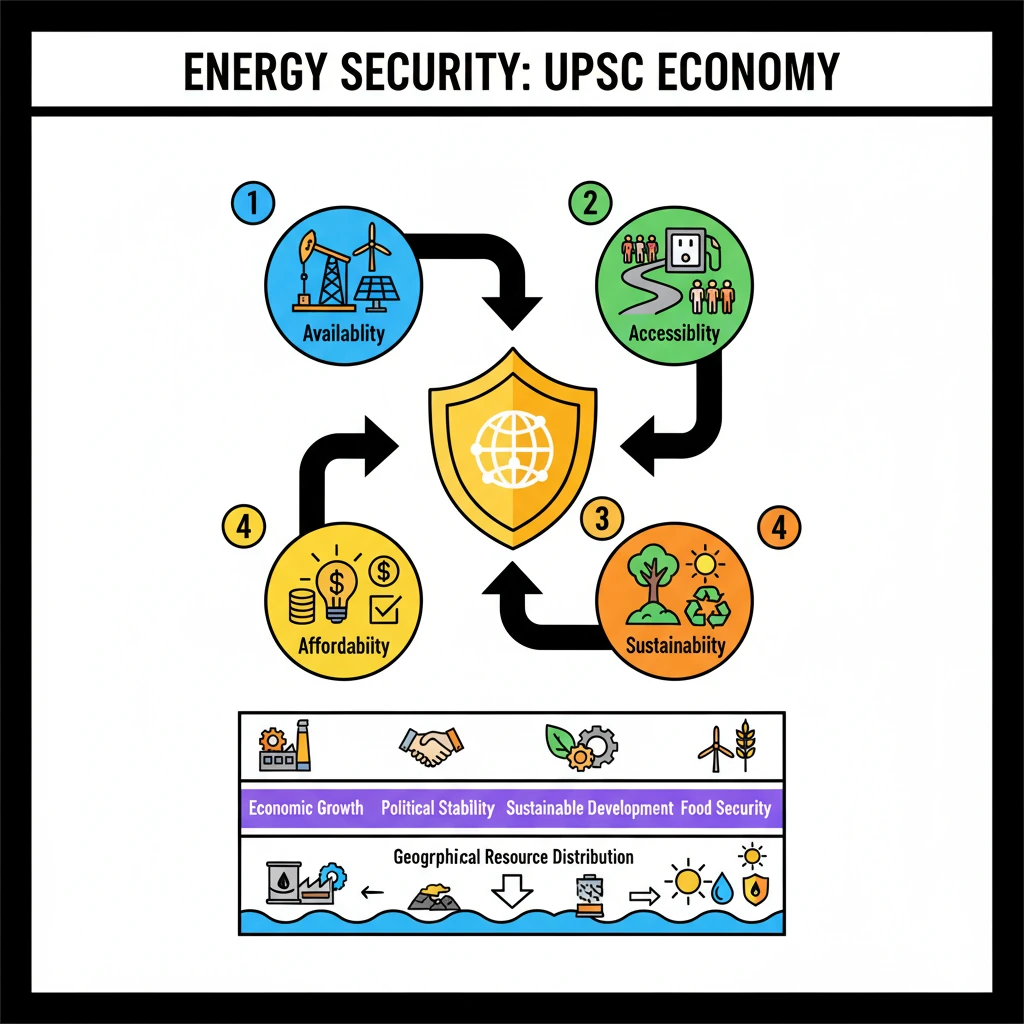
<h4>Understanding Energy Security: A Core Concept</h4><p><strong>Energy security</strong> refers to the ability of a nation to maintain a <strong>reliable</strong>, <strong>sustainable</strong>, and <strong>affordable energy system</strong>.</p><p>This system must be capable of meeting the diverse energy needs of its <strong>individuals</strong>, various <strong>industries</strong>, and the <strong>government</strong> consistently.</p><h4>Key Components of Energy Security: The 4 A's</h4><p>Energy security is typically understood through four interconnected components, often referred to as the <strong>'4 A's'</strong>:</p><ul><li><strong>Availability</strong>: Ensuring a reliable and sufficient energy supply from diverse sources to meet current and future demand.</li><li><strong>Accessibility</strong>: Developing robust infrastructure to deliver energy to all regions and populations, including remote areas.</li><li><strong>Affordability</strong>: Maintaining stable and cost-effective energy prices for both consumers and industrial sectors.</li><li><strong>Sustainability</strong>: Promoting clean and efficient energy use, along with the transition to renewable sources, for long-term environmental balance.</li></ul><div class='key-point-box'><p>The <strong>4 A's</strong>—<strong>Availability</strong>, <strong>Accessibility</strong>, <strong>Affordability</strong>, and <strong>Sustainability</strong>—are crucial for a holistic approach to energy security.</p></div><h4>The Multifaceted Importance of Energy Security</h4><p>Achieving energy security is paramount for a nation's overall well-being and progress. It directly impacts several critical sectors and national objectives.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>It is essential for meeting <strong>daily energy demands</strong> and supporting vital sectors such as <strong>agriculture</strong> and <strong>manufacturing</strong>.</p></div><ul><li><strong>Economic Growth</strong>: A stable energy supply fuels <strong>industrial growth</strong>, enhances <strong>productivity</strong>, and drives overall economic development.</li><li><strong>Political Stability</strong>: Preventing energy shortages helps mitigate potential social unrest and contributes to national <strong>political stability</strong>.</li><li><strong>Sustainable Development</strong>: Focus on clean energy ensures environmental protection and facilitates long-term <strong>sustainable development</strong> goals.</li><li><strong>Food Security</strong>: Energy is indispensable for modern <strong>agriculture</strong>, impacting <strong>food production</strong>, efficient <strong>distribution</strong>, and stable <strong>food prices</strong>.</li></ul><h4>Factors Influencing Energy Security</h4><p>Various factors, both natural and geopolitical, significantly impact a nation's energy security posture.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Physical Factors</strong>: Regions naturally rich in <strong>fossil fuels</strong> (like oil and natural gas) often possess inherent advantages in energy security.</p><p>Conversely, nations lacking significant domestic energy reserves face considerable challenges and greater dependence on external sources, leading to potential <strong>scarcity issues</strong>.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Energy security ensures reliable, sustainable, and affordable energy for all national needs.
- •Its four core components are Availability, Accessibility, Affordability, and Sustainability (the 4 A's).
- •Energy security is crucial for economic growth, political stability, sustainable development, and food security.
- •Factors like geographical resource distribution significantly impact a nation's energy security.
- •India faces challenges due to high import dependence but is actively diversifying its energy mix with renewables and international cooperation.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas, Government of India reports
•International Energy Agency (IEA) reports
•NITI Aayog publications on India's energy sector
•Press Information Bureau (PIB) releases on government schemes