What are the Government Initiatives in the Manufacturing Sector in India? - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
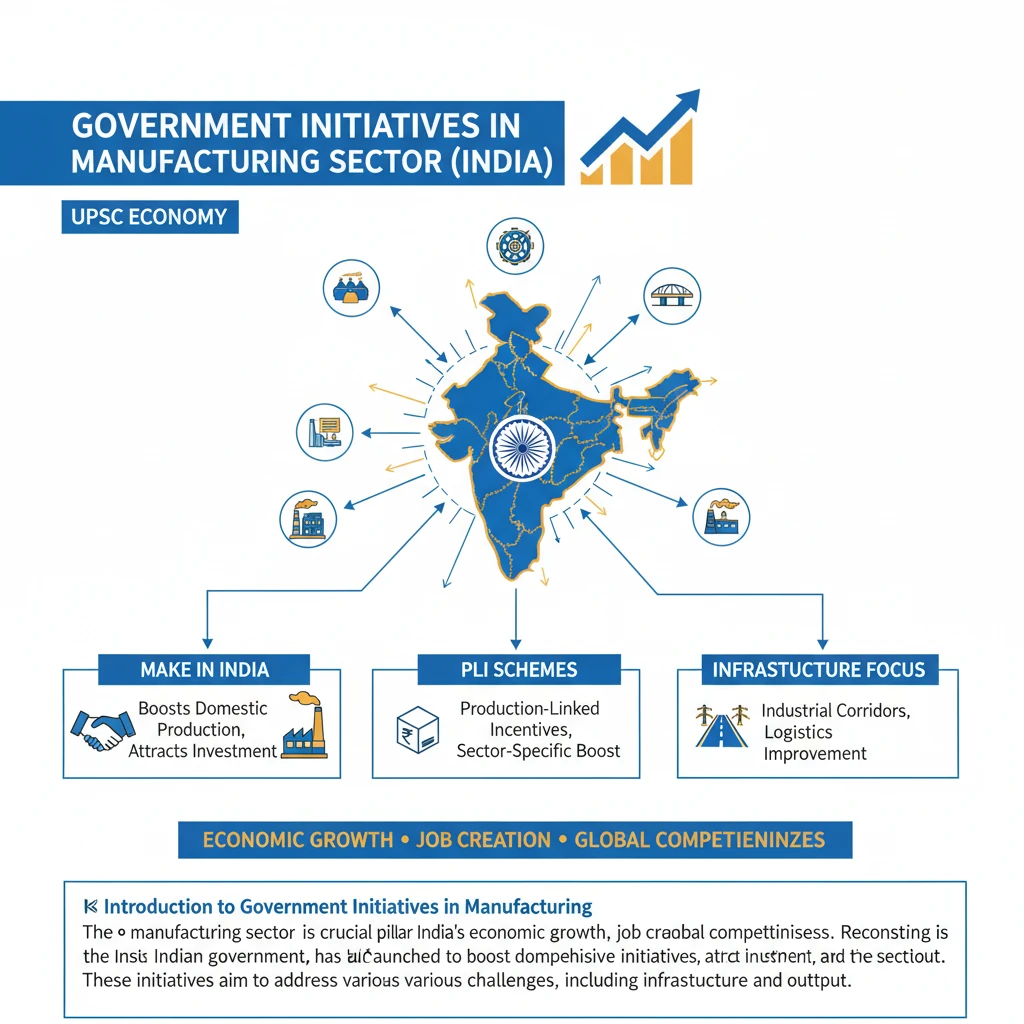
What are the Government Initiatives in the Manufacturing Sector in India?
Medium⏱️ 10 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
<h4>Introduction to Government Initiatives in Manufacturing</h4><p>The <strong>manufacturing sector</strong> is a crucial pillar for India's economic growth, job creation, and global competitiveness. Recognising its importance, the Indian government has launched a series of comprehensive initiatives to boost domestic production, attract investment, and enhance the sector's overall efficiency and output.</p><p>These initiatives aim to address various challenges, including infrastructure bottlenecks, ease of doing business, access to finance, and technological advancements. The goal is to transform India into a global manufacturing hub and achieve self-reliance.</p><h4>Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme</h4><p>The <strong>Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme</strong> is a flagship initiative designed to boost domestic manufacturing and reduce import dependence. It offers incentives to companies for incremental sales from products manufactured in India.</p><div class="info-box"><p><strong>Aim:</strong> To make Indian manufacturers globally competitive, attract investment in key sectors, create employment opportunities, and enhance exports.</p></div><div class="key-point-box"><p><strong>Coverage:</strong> The scheme covers 14 key sectors, including automobiles and auto components, electronics and IT hardware, pharmaceuticals, telecom and networking products, textiles, and food products.</p></div><h4>PM Gati Shakti - National Master Plan</h4><p>The <strong>PM Gati Shakti - National Master Plan</strong> is a transformative approach for integrated planning and coordinated implementation of infrastructure connectivity projects. It brings together 16 ministries under one digital platform.</p><div class="info-box"><p><strong>Objective:</strong> To break departmental silos and ensure holistic planning for multi-modal connectivity, reducing logistics costs and improving project execution efficiency.</p></div><div class="key-point-box"><p><strong>Impact:</strong> Better infrastructure directly supports the manufacturing sector by improving supply chain efficiency, reducing transit times, and lowering operational costs for industries.</p></div><h4>Bharatmala and Sagarmala Projects</h4><p>The <strong>Bharatmala Pariyojana</strong> focuses on optimising the efficiency of freight and passenger movement across India by bridging critical infrastructure gaps. It involves developing economic corridors, inter-corridors, feeder routes, and coastal and border roads.</p><p>The <strong>Sagarmala Programme</strong> aims to promote port-led development by enhancing port capacity, improving connectivity to ports, and promoting coastal community development. It integrates ports, inland waterways, and coastal shipping.</p><div class="key-point-box"><p><strong>Synergy:</strong> Both projects significantly enhance logistics and connectivity, which are vital for raw material procurement and finished goods distribution for manufacturers.</p></div><h4>Start-up India Initiative</h4><p>The <strong>Start-up India</strong> initiative aims to foster a culture of innovation and entrepreneurship in the country. It provides a supportive ecosystem for startups, including simplified regulations, funding support, and incubation facilities.</p><div class="info-box"><p><strong>Support:</strong> This initiative encourages manufacturing innovation, particularly in areas like advanced materials, robotics, and sustainable production technologies, through new ventures.</p></div><h4>Make in India 2.0</h4><p><strong>Make in India 2.0</strong> is an updated version of the original initiative, focusing on 27 key sectors to boost domestic manufacturing. It aims to increase the manufacturing sector's share of GDP and create millions of jobs.</p><div class="key-point-box"><p><strong>Focus Areas:</strong> It emphasises ease of doing business, attracting foreign investment, skill development, and building world-class manufacturing infrastructure.</p></div><h4>Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan (Self-Reliant India Campaign)</h4><p>The <strong>Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan</strong> is a vision to make India a self-reliant nation, especially in critical sectors. It encompasses economic stimulus packages and structural reforms across various domains.</p><div class="info-box"><p><strong>Pillars:</strong> It stands on five pillars: economy, infrastructure, system, demography, and demand. It strongly advocates for local manufacturing and consumption.</p></div><h4>Special Economic Zones (SEZs)</h4><p><strong>Special Economic Zones (SEZs)</strong> are designated areas in India that offer a more liberal and business-friendly environment to promote exports. They provide fiscal incentives, simplified procedures, and world-class infrastructure.</p><div class="key-point-box"><p><strong>Benefits:</strong> SEZs attract foreign and domestic investment in manufacturing, facilitating export-oriented production and creating employment opportunities.</p></div><h4>Liberalised Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Policy</h4><p>India has progressively liberalised its <strong>Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) policy</strong> across various sectors, allowing for higher foreign equity participation through automatic routes in most manufacturing industries.</p><div class="info-box"><p><strong>Impact:</strong> This liberalisation attracts global capital, technology, and best practices, leading to increased production capacity, technological upgrades, and integration into global supply chains.</p></div><h4>MSME Innovative Scheme</h4><p>The <strong>MSME Innovative Scheme</strong> (Incubation, Design, and IPR) aims to promote and support innovation in the Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSME) sector. It encourages MSMEs to develop new products, processes, and services.</p><div class="key-point-box"><p><strong>Components:</strong> It includes sub-schemes for incubation, design expertise, and facilitating intellectual property rights (IPR) protection, thereby boosting manufacturing competitiveness.</p></div><h4>Ease of Doing Business Reforms</h4><p>The government has implemented significant reforms to improve India's ranking in the <strong>Ease of Doing Business</strong> index. These include simplifying regulations, reducing compliance burdens, and streamlining various processes for businesses.</p><div class="info-box"><p><strong>Measures:</strong> Reforms cover areas like starting a business, dealing with construction permits, getting electricity, registering property, paying taxes, and enforcing contracts, making India more attractive for manufacturers.</p></div><h4>Goods and Services Tax (GST) and Corporate Tax Reduction</h4><p>The introduction of the <strong>Goods and Services Tax (GST)</strong> has unified India into a common market, eliminating cascading taxes and simplifying the indirect tax structure. This has reduced logistics costs and improved supply chain efficiency for manufacturers.</p><p>Furthermore, the government has significantly reduced the <strong>corporate tax rate</strong> for new domestic manufacturing companies to 15% (from 22% for existing companies), making India a more attractive investment destination for manufacturers.</p><div class="exam-tip-box"><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Understanding the synergy between these initiatives is key. For example, <strong>PM Gati Shakti</strong> complements <strong>PLI</strong> by providing the necessary infrastructure for enhanced production, while <strong>Ease of Doing Business</strong> and <strong>GST</strong> create a conducive environment for all.</p></div>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •Government initiatives aim to boost India's manufacturing sector for economic growth and job creation.
- •Key schemes include PLI for sector-specific incentives, PM Gati Shakti for integrated infrastructure, and Make in India 2.0 for overall promotion.
- •Bharatmala and Sagarmala enhance logistics and connectivity, crucial for manufacturing supply chains.
- •Ease of Doing Business, GST, and reduced corporate tax create a favorable investment climate.
- •Atmanirbhar Bharat and liberalised FDI policies support self-reliance and global integration simultaneously.
- •MSME Innovative Scheme and Start-up India foster innovation and entrepreneurship within the sector.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•NITI Aayog reports and press releases (PM Gati Shakti, Atmanirbhar Bharat)
•Press Information Bureau (PIB) releases on various government schemes
•Reserve Bank of India (RBI) publications on FDI policy
•Ministry of Finance (GST, Corporate Tax reforms)