What is LNG and SSLNG? - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

What is LNG and SSLNG?
Medium⏱️ 6 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
<h4>What is Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG)?</h4><p><strong>Liquefied natural gas (LNG)</strong> is a crucial form of <strong>natural gas</strong> that has been processed for efficient storage and transportation. This transformation involves cooling the gas to an extremely low temperature.</p><p>The primary purpose of converting <strong>natural gas</strong> into its liquid state is to significantly reduce its volume, making it more practical to move across vast distances, particularly via specialized vessels.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Key Specification:</strong> <strong>LNG</strong> is created by cooling <strong>natural gas</strong> to approximately <strong>-260°F (-162°C)</strong>, at which point it becomes a liquid.</p></div><h4>Importance of Natural Gas in Energy Transition</h4><p><strong>Natural gas</strong> stands out as a cleaner and more economical alternative to conventional <strong>hydrocarbons</strong> such as <strong>coal and oil</strong>.</p><p>Its environmental benefits, including lower carbon emissions when burned, make it a pivotal fuel in India's strategic transition towards more sustainable and <strong>greener energy sources</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Strategic Role:</strong> <strong>Natural gas</strong> is considered a bridge fuel in the global shift from high-carbon fossil fuels to renewable energy, offering a relatively cleaner option during this transition.</p></div><h4>Composition of Natural Gas</h4><p>The chemical makeup of <strong>natural gas</strong> is predominantly composed of a single hydrocarbon.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Primary Component:</strong> <strong>Methane</strong> is the main constituent of <strong>natural gas</strong>, typically comprising <strong>70-90%</strong> of its total composition.</p></div><h4>Understanding Small-Scale LNG (SSLNG)</h4><p>While this content primarily details <strong>Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG)</strong> in its general form, the concept of <strong>Small-Scale LNG (SSLNG)</strong> is also relevant.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>SSLNG Definition:</strong> <strong>SSLNG</strong> generally refers to the production, storage, and distribution of <strong>LNG</strong> in smaller volumes, often tailored for specific regional demands, industrial uses, or as fuel for smaller vessels and vehicles. The detailed scope of <strong>SSLNG</strong> was not provided in the source material.</p></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Questions on <strong>LNG</strong> often revolve around India's energy security, environmental policies, and infrastructure development. Understanding the 'why' behind liquefaction and its role in the energy mix is crucial for Mains answers.</p></div>
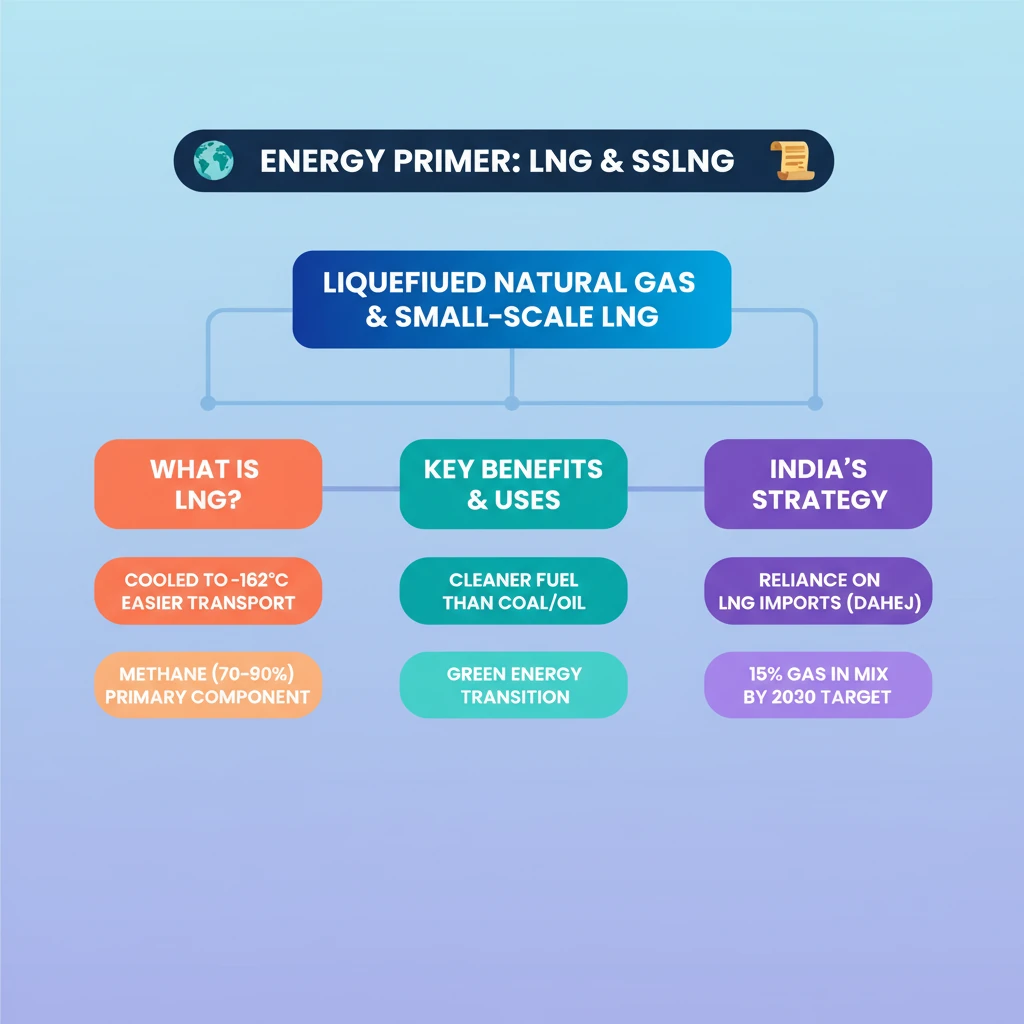
💡 Key Takeaways
- •LNG is natural gas cooled to -162°C for easier storage and transport.
- •It's a cleaner, more economical alternative to coal/oil, crucial for India's green energy transition.
- •Methane is the primary component (70-90%) of natural gas.
- •India heavily relies on LNG imports, with terminals like Dahej being vital infrastructure.
- •The government aims to increase natural gas's share in India's energy mix to 15% by 2030.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas, Government of India reports
•Petronet LNG Limited official website
•International Energy Agency (IEA) publications