IRDAI: Mandate, Functions, and Regulatory Role in the Insurance Sector - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

IRDAI: Mandate, Functions, and Regulatory Role in the Insurance Sector
Easy⏱️ 6 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
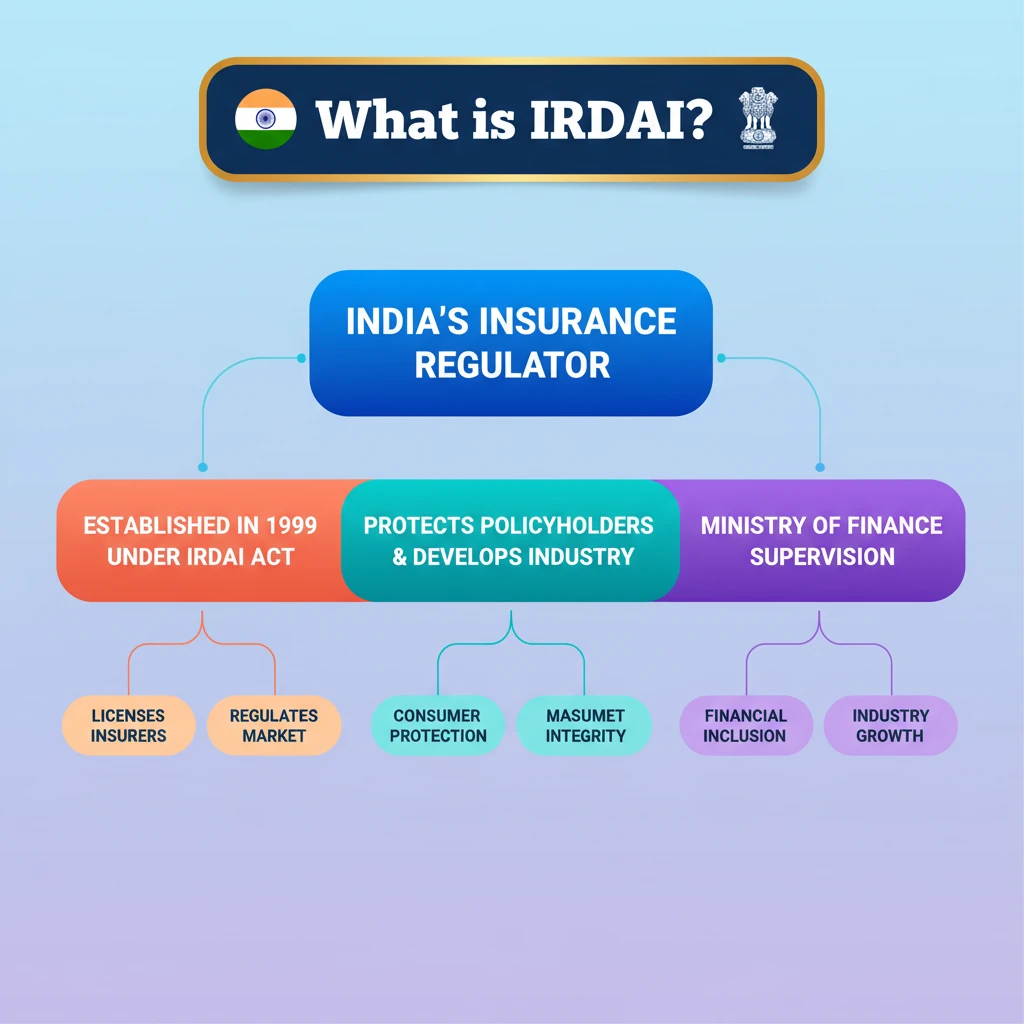
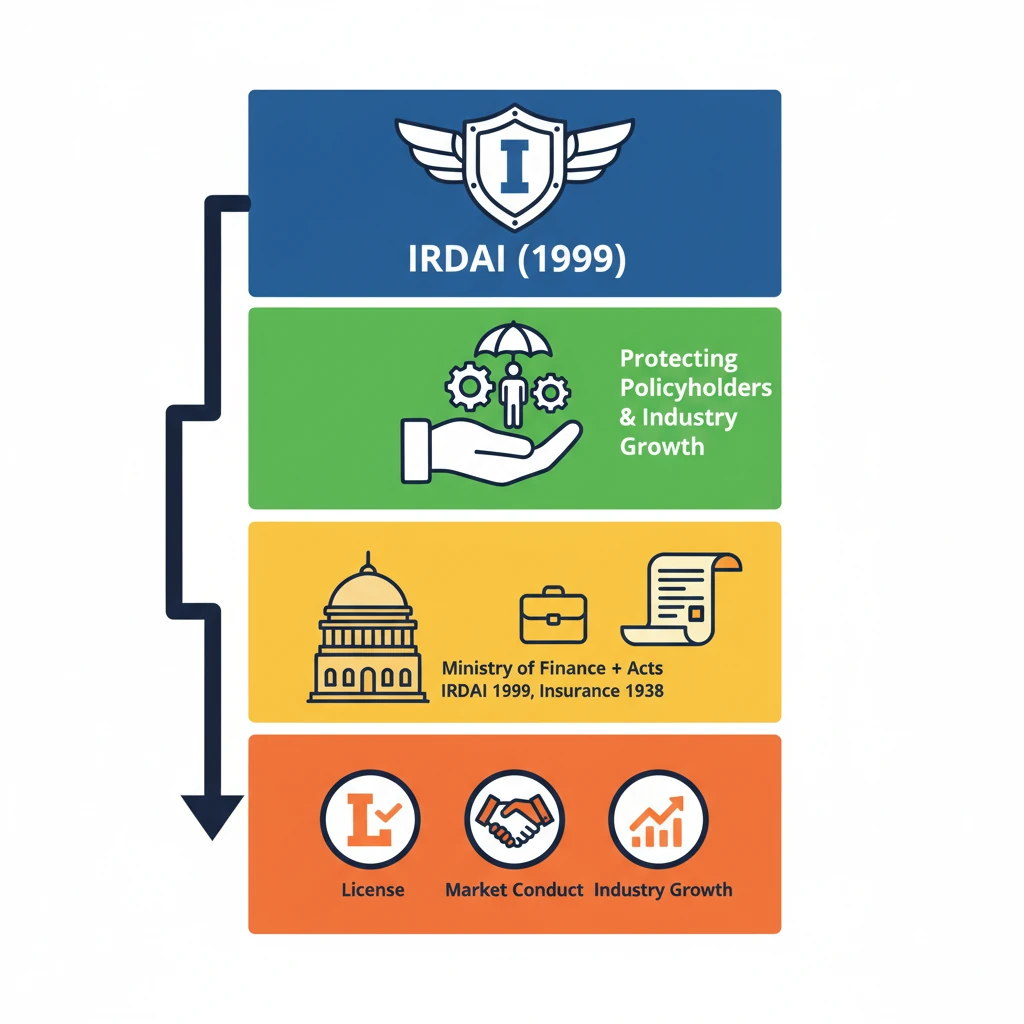
<h4>Introduction to IRDAI</h4><p>The <strong>Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India</strong> (<strong>IRDAI</strong>) is a pivotal institution in India's financial landscape. Established in <strong>1999</strong>, its primary mandate is to safeguard the interests of <strong>insurance policyholders</strong>.</p><p><strong>IRDAI</strong> operates as a <strong>statutory body</strong>, meaning it derives its powers directly from an Act of Parliament. Specifically, it was constituted under the <strong>IRDAI Act, 1999</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Foundation:</strong> <strong>1999</strong><br><strong>Legal Basis:</strong> <strong>IRDAI Act, 1999</strong><br><strong>Jurisdiction:</strong> <strong>Ministry of Finance</strong>, Government of India</p></div><p>Its overarching role involves the comprehensive <strong>regulation</strong> and active <strong>development</strong> of the entire <strong>insurance industry</strong> within India. This includes overseeing all insurance-related activities to ensure fairness and transparency.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Core Functions of IRDAI:</strong><ul><li><strong>Protection of Policyholder Interests:</strong> Ensuring fair practices and timely claim settlements.</li><li><strong>Regulation of the Insurance Sector:</strong> Setting rules for insurers and intermediaries.</li><li><strong>Promotion of Industry Growth:</strong> Facilitating market development and penetration.</li><li><strong>Monitoring Insurance Activities:</strong> Overseeing operations to maintain solvency and ethical conduct.</li></ul></p></div><p>The specific <strong>powers and functions</strong> of the Authority are clearly delineated in both the <strong>IRDAI Act, 1999</strong>, and the older yet still relevant <strong>Insurance Act, 1938</strong>.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>For <strong>UPSC Prelims</strong>, remember <strong>IRDAI's</strong> status as a <strong>statutory body</strong> and its establishment year. For <strong>Mains GS-III</strong>, focus on its role in financial sector regulation and consumer protection.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •IRDAI is India's statutory insurance regulator, established in 1999 under the IRDAI Act.
- •Its primary objective is to protect policyholder interests and develop the insurance industry.
- •It functions under the Ministry of Finance and derives powers from the IRDAI Act, 1999, and Insurance Act, 1938.
- •Key roles include licensing insurers, regulating market conduct, and promoting industry growth.
- •IRDAI ensures market integrity, consumer protection, and contributes to financial inclusion and stability.
🧠 Memory Techniques
98% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•IRDAI Official Website (irdai.gov.in)
•The Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority Act, 1999