Agriculture and Food Management - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Agriculture and Food Management
Medium⏱️ 12 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
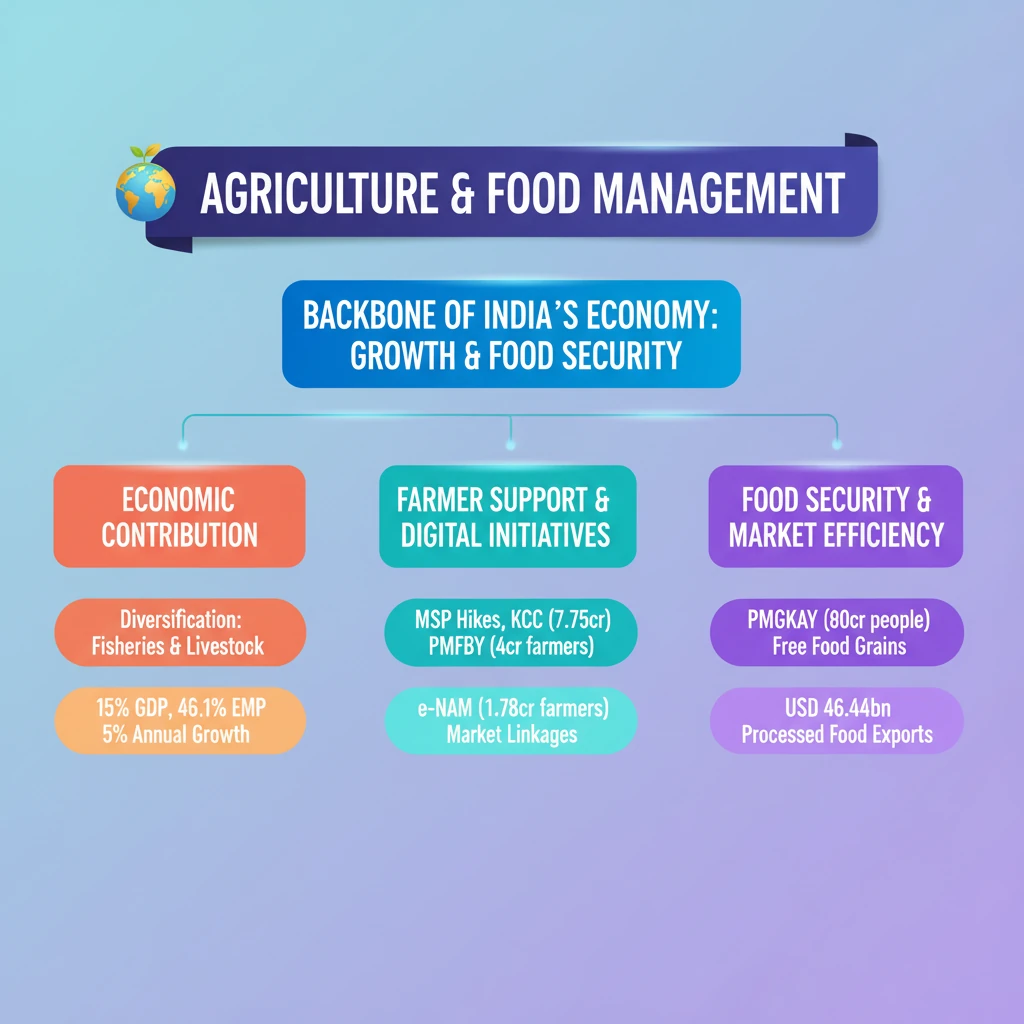
<h4>Broader Economic Context</h4><p>India's economy has shown diverse growth across sectors. The <strong>tourism sector</strong> experienced a significant rebound, contributing <strong>5% to GDP</strong> in <strong>FY23</strong>. This highlights its crucial role in economic recovery and job creation.</p><p>The <strong>real estate market</strong> also demonstrated robust performance, with sales reaching an <strong>11-year high</strong> in the first half of <strong>FY25</strong>. This indicates strong consumer confidence and investment in the housing sector.</p><p>Furthermore, the <strong>telecom sector</strong> continues its impressive trajectory, boasting <strong>1.18 billion subscribers</strong>. India leads globally in <strong>mobile data consumption</strong>, underscoring the digital transformation underway.</p><h4>Agriculture Sector Overview</h4><p>The <strong>agriculture sector</strong> remains a cornerstone of the Indian economy. It contributed <strong>15% to India's GDP</strong> in <strong>FY23</strong> and employs a substantial portion of the workforce, specifically <strong>46.1% of the population</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Agriculture Sector Growth:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>GDP Contribution (FY23):</strong> 15%</li><li><strong>Employment:</strong> 46.1% of population</li><li><strong>Annual Growth (FY17-FY23):</strong> 5%</li></ul></div><p>This sector has demonstrated a consistent <strong>annual growth of 5%</strong> between <strong>FY17 and FY23</strong>, showcasing its resilience and importance to national economic stability.</p><h4>Agricultural Production Trends</h4><p><strong>Kharif foodgrain production</strong> reached <strong>1,647 LMT</strong> in <strong>2024</strong>, marking an increase of <strong>89.37 LMT year-on-year</strong>. This reflects efforts to boost agricultural output and ensure food security.</p><p>Beyond traditional farming, sectors like <strong>fisheries</strong> and <strong>livestock</strong> are experiencing accelerated growth. <strong>Fisheries production</strong> stands at <strong>184 LMT</strong>, while the <strong>livestock sector</strong> recorded a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of <strong>12.99%</strong>, outpacing traditional farming segments.</p><h4>Farmer Support and Welfare Initiatives</h4><p>The government has implemented several measures to ensure farmer profitability and welfare. The <strong>Minimum Support Price (MSP)</strong> for key crops like <strong>Arhar</strong> and <strong>Bajra</strong> was significantly increased by <strong>59%</strong> and <strong>77%</strong> respectively in <strong>FY25</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Irrigation Coverage:</strong> Approximately <strong>55% of India’s net sown area is irrigated</strong>. However, a significant challenge remains as <strong>two-thirds of farmland faces severe drought risks</strong>.</p></div><p>The <strong>Kisan Credit Card (KCC)</strong> scheme facilitates access to credit for farmers, with <strong>7.75 crore accounts</strong> active. This scheme is vital for providing timely and adequate credit support.</p><p>The <strong>PM Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY)</strong>, a crop insurance scheme, has seen widespread adoption. In <strong>FY24</strong>, <strong>4 crore farmers</strong> were enrolled, covering <strong>600 LMT hectares</strong> of land, providing crucial financial protection against crop losses.</p><p>The <strong>e-NAM platform</strong> (National Agriculture Market) has been instrumental in improving price discovery for farmers. As of <strong>October 2024</strong>, it has linked <strong>1.78 crore farmers</strong> and <strong>2.62 lakh traders</strong>, creating a unified national market for agricultural commodities.</p><h4>Food Security and Processing</h4><p><strong>Food security</strong> remains a top priority. The <strong>Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana (PMGKAY)</strong> provides free food grains to <strong>80 crore people</strong>, ensuring access to basic sustenance for vulnerable populations.</p><p>The <strong>processed food sector</strong> is a significant contributor to India's exports. Processed food exports reached <strong>USD 46.44 billion</strong> in <strong>FY23</strong>, accounting for a <strong>23.4% share in agri-food exports</strong> and <strong>11.7% of India’s total exports</strong>.</p><h4>Climate and Environment Initiatives</h4><p>India's commitment to climate adaptation is evident in its increased spending. <strong>Climate adaptation spending</strong> rose from <strong>3.7% to 5.6% of GDP</strong> between <strong>FY16 and FY22</strong>.</p><p>The <strong>Lifestyle for the Environment (LiFE) initiative</strong> promotes sustainable living practices. This initiative has the potential to generate global savings of <strong>USD 400 billion by 2030</strong> through reduced consumption and lower prices, emphasizing mindful utilization of resources.</p><h4>Renewable Energy and Emissions Reduction</h4><p>India is making strides in its renewable energy targets. <strong>46.8% of India’s power capacity</strong> is now from <strong>non-fossil fuel sources</strong>, nearing the target of <strong>50% by 2030</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Forest Carbon Sink:</strong> India's forest cover has contributed significantly to carbon sequestration, with an increase of <strong>2.29 billion tonnes of CO2</strong> between <strong>2005 and 2023</strong>.</p></div><h4>Climate Finance and International Cooperation</h4><p>International cooperation on climate finance is crucial. The <strong>Conference of Parties (COP 29)</strong> called for securing adequate climate funds, highlighting a gap between the <strong>USD 300 billion annual goal</strong> and the estimated <strong>USD 5.1 to 6.8 trillion needed by 2030</strong>.</p><p>Domestically, India issued <strong>Sovereign Green Bonds</strong> worth <strong>USD 20,000 crore</strong> in <strong>FY24</strong>. These bonds are specifically designed to fund green projects, demonstrating India's commitment to sustainable development financing.</p><h4>Sustainable Development and Resilience</h4><p>The <strong>Mangrove Initiative for Shoreline Habitats & Tangible Incomes (MISHTI)</strong> is a key program focused on ecological restoration. It aims at restoring <strong>22,560 hectares of mangroves</strong> across <strong>9 states and Union Territories</strong>, protecting coastal ecosystems and livelihoods.</p><p><strong>Water conservation</strong> efforts are being bolstered through <strong>AMRUT 2.0</strong>, under which <strong>3,078 water body rejuvenation projects</strong> have been approved. This initiative is critical for enhancing water security and urban resilience.</p><p>The <strong>PM Surya Ghar Yojana</strong> promotes rooftop solar installations, with <strong>7 lakh rooftop solar systems</strong> already installed. The ambitious goal is to reach <strong>1 crore households</strong>, significantly boosting renewable energy adoption at the household level.</p><h4>Energy Security and Transition</h4><p><strong>Coal</strong> remains India’s primary energy source, with <strong>65,290 MW of supercritical coal plants</strong> deployed to ensure efficiency and reduce emissions from thermal power generation.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>Balanced Energy Transition:</strong> India is pursuing a balanced energy transition strategy. While coal remains dominant, there is a strong focus on expanding <strong>nuclear, hydrogen, and bioenergy programs</strong> to diversify the energy mix and achieve long-term sustainability.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Agriculture is vital to India's economy, contributing 15% to GDP and employing 46.1% of the population, with 5% annual growth.
- •Diversification in agriculture is evident, with fisheries and livestock outpacing traditional farming.
- •Government support for farmers includes MSP hikes (Arhar, Bajra), KCC (7.75 crore accounts), and PMFBY (4 crore farmers, 600 LMT hectares covered).
- •Digital platforms like e-NAM (1.78 crore farmers, 2.62 lakh traders) enhance market efficiency and price discovery.
- •Food security is addressed by PMGKAY, providing free food grains to 80 crore people, and processed food exports reached USD 46.44 billion.
- •India's climate commitment is strong: 5.6% of GDP for adaptation, 46.8% non-fossil power capacity, and initiatives like LiFE, MISHTI, AMRUT 2.0, and PM Surya Ghar.
- •Energy transition balances coal (65,290 MW supercritical plants) with expansion in nuclear, hydrogen, and bioenergy programs.
🧠 Memory Techniques

98% Verified Content