What are Key Facts About Rubber? - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

What are Key Facts About Rubber?
Easy⏱️ 8 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
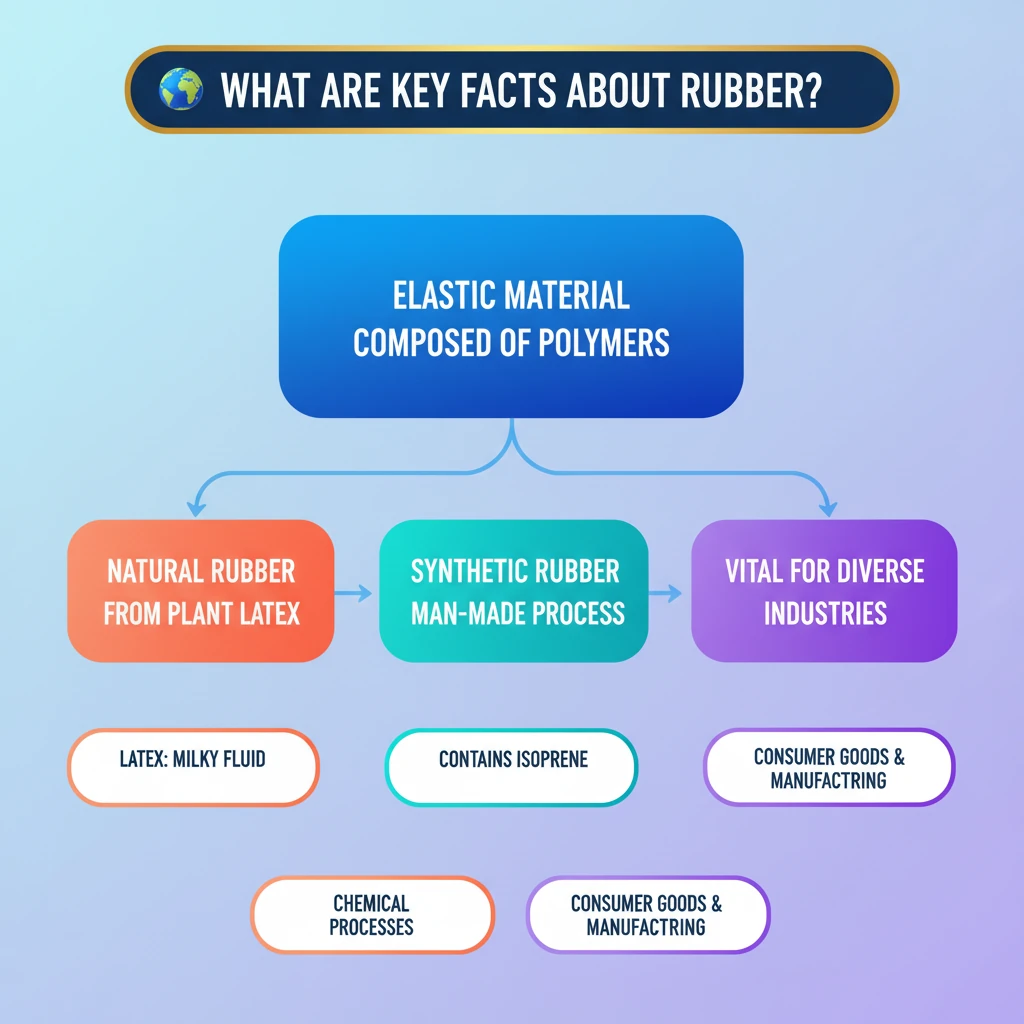
<h4>Introduction to Rubber</h4><p><strong>Rubber</strong> is a remarkable <strong>elastic material</strong> known for its unique property of deforming under an external force and then quickly regaining its original shape once the force is removed. This characteristic makes it indispensable in countless applications.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Key Property:</strong> <strong>Elasticity</strong> - ability to return to original shape after deformation.</p></div><h4>Composition of Rubber</h4><p>Rubber, whether <strong>natural</strong> or <strong>synthetic</strong>, is fundamentally composed of <strong>polymers</strong>. These are large molecules made up of repeating smaller units. The primary building block for rubber polymers is the organic compound <strong>isoprene</strong>, along with other associated organic compounds.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Polymers of Isoprene:</strong> The core chemical structure of rubber relies on long chains of <strong>isoprene</strong> units.</p></div><h4>Types of Rubber</h4><p>Rubber is broadly categorized into two main types based on its origin and production method: <strong>Natural Rubber</strong> and <strong>Synthetic Rubber</strong>. Both types serve critical roles in various industries globally.</p><h4>Natural Rubber: Origin and Characteristics</h4><p><strong>Natural Rubber</strong> is a biopolymer produced directly from plants. It is considered one of the most vital polymers for human society due to its versatility and unique properties. Its primary source is a milky fluid known as <strong>latex</strong>.</p><p><strong>Latex</strong> is a whitish, milky fluid found in many plants, particularly the <strong>rubber tree</strong> (Hevea brasiliensis). This fluid is a complex emulsion containing not only rubber particles but also other organic compounds.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Composition of Latex:</strong> Besides rubber particles, <strong>latex</strong> contains <strong>proteins</strong>, <strong>starch</strong>, and <strong>alkaloids</strong>, among other substances.</p></div><h4>Synthetic Rubber: Production and Nature</h4><p>In contrast to its natural counterpart, <strong>Synthetic Rubber</strong> is a <strong>man-made</strong> material. It is produced through complex <strong>chemical processes</strong>, typically involving petroleum-based raw materials. This allows for tailored properties to suit specific industrial requirements.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>For UPSC, understand the fundamental distinction: <strong>Natural Rubber</strong> is plant-derived (biopolymer), while <strong>Synthetic Rubber</strong> is chemically manufactured (petroleum-derived). Focus on their unique properties and applications in <strong>GS Paper III: Economy</strong> and <strong>Science & Technology</strong>.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Rubber is an elastic material, capable of deforming and regaining its shape.
- •It is composed of polymers, primarily based on the organic compound isoprene.
- •Two main types exist: Natural Rubber (from plant latex) and Synthetic Rubber (man-made via chemical processes).
- •Latex is a milky fluid from plants, containing rubber, proteins, starch, and alkaloids.
- •Both natural and synthetic rubbers are vital for diverse industries like automotive, medical, and consumer goods.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•NCERT Science Textbooks (General Chemistry/Polymers)
•Britannica Encyclopedia (for historical context and general rubber facts)
•The Rubber Board of India website (for current relevance and statistics)