Environmental Ship Index (ESI): Main Characteristics - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Environmental Ship Index (ESI): Main Characteristics
Medium⏱️ 5 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
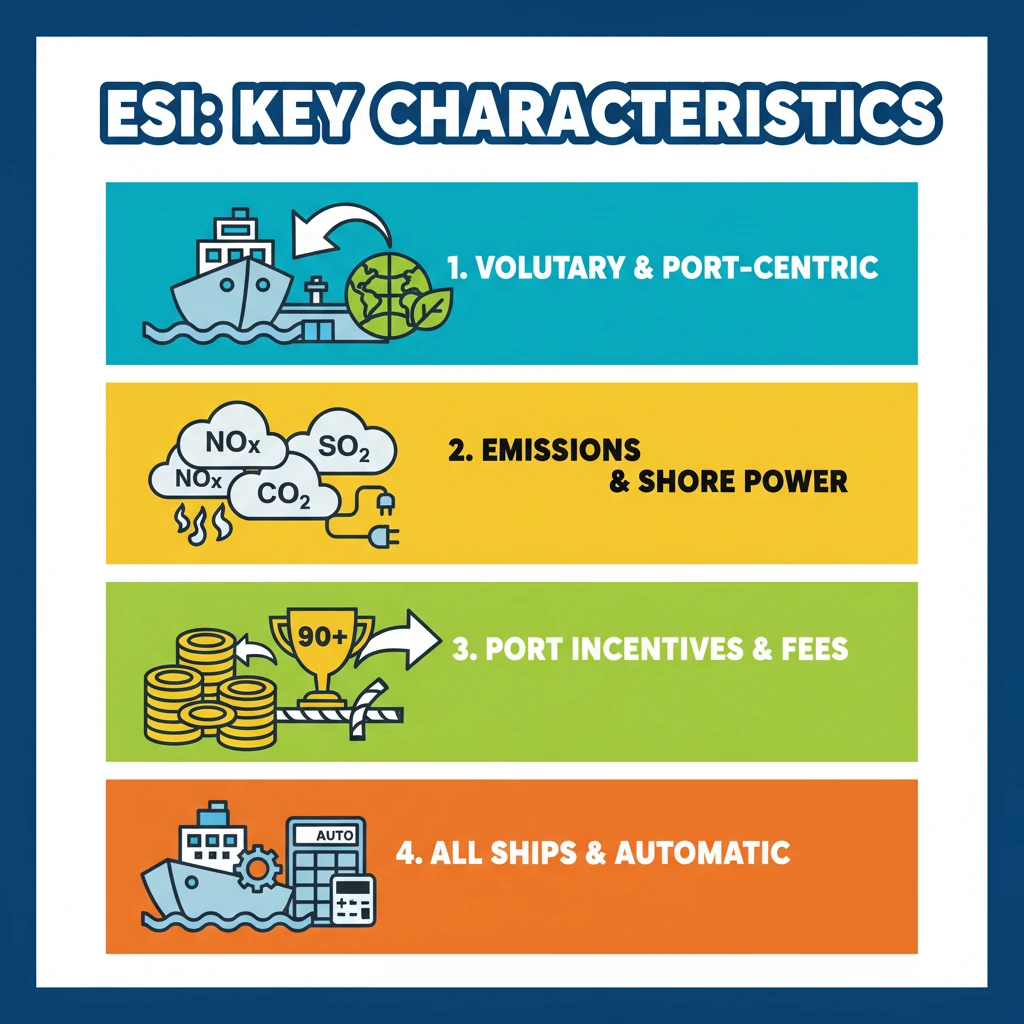
<h4>Understanding the Environmental Ship Index (ESI)</h4><p>The <strong>Environmental Ship Index (ESI)</strong> is a crucial tool designed to evaluate and incentivize the environmental performance of ships. It provides a transparent mechanism for ports and other stakeholders to reward vessels that exceed regulatory environmental standards.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The <strong>ESI</strong> primarily focuses on emissions of <strong>Nitrogen Oxides (NOx)</strong>, <strong>Sulphur Oxides (SOx)</strong>, and <strong>Carbon Dioxide (CO2)</strong>, as well as the ship's <strong>on-shore power capabilities</strong>.</p></div><h4>Port-Centric System</h4><p>One of the primary characteristics of the <strong>ESI</strong> is its design as a <strong>port-centric system</strong>. This means it is specifically engineered to operate as a framework for environmental performance evaluation from <strong>ports to ports</strong>, facilitating localized and regional incentives.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The system allows individual ports or port authorities to tailor their incentive programs based on their specific environmental goals and local air quality requirements.</p></div><h4>Voluntary Participation</h4><p>Participation in the <strong>Environmental Ship Index</strong> program is entirely <strong>voluntary</strong>. Shipowners choose to demonstrate the environmental performance of their vessels, encouraging proactive engagement beyond mandatory regulations.</p><p>This voluntary nature fosters a competitive environment where shipowners can gain advantages by investing in cleaner technologies and operational practices.</p><h4>Broad Applicability</h4><p>The <strong>ESI</strong> is designed to be highly versatile and can be applied to <strong>all types of seagoing ships</strong>. This broad applicability extends irrespective of the vessel's <strong>size</strong>, <strong>function</strong>, or <strong>flag state</strong>, ensuring a wide reach for environmental improvement.</p><p>From large container ships to smaller cargo vessels, any ship can be assessed under the ESI framework, promoting a unified approach to cleaner shipping.</p><h4>Automated Calculation and Maintenance</h4><p>A significant feature of the <strong>ESI</strong> is its <strong>automated calculation and maintenance</strong>. This ensures consistency, accuracy, and efficiency in assessing a vessel's environmental performance without extensive manual intervention.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The index is typically calculated based on reported data concerning engine emissions, fuel consumption, and other environmental parameters, which are then verified.</p></div><h4>Incentive Mechanism</h4><p>The <strong>ESI</strong> serves as a robust <strong>incentive mechanism</strong>. Ports and port authorities are empowered to offer various benefits to ships achieving higher <strong>ESI scores</strong>, thereby rewarding superior environmental performance.</p><p>Common incentives include <strong>reduced port fees</strong>, <strong>priority berthing</strong>, or other financial advantages. These incentives motivate shipowners to invest in greener technologies and sustainable operations.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>Understanding the <strong>voluntary nature</strong> and <strong>incentive structure</strong> of ESI is crucial for UPSC Mains answers, especially when discussing policy instruments for environmental governance in shipping (<strong>GS-III: Environment</strong>).</p></div>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •ESI is a voluntary, port-centric system for evaluating ship environmental performance.
- •It covers NOx, SOx, CO2 emissions, and on-shore power capabilities.
- •Ports offer incentives (e.g., reduced fees) for higher ESI scores.
- •Applicable to all seagoing ships, calculated automatically.
- •Promotes cleaner shipping beyond mandatory regulations, driving innovation.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Port of Rotterdam Official Website - Environmental Incentives
•International Maritime Organization (IMO) - MARPOL Convention details
•Various academic articles and reports on green shipping and port sustainability