Revised Currency Swap Framework for SAARC - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Revised Currency Swap Framework for SAARC
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
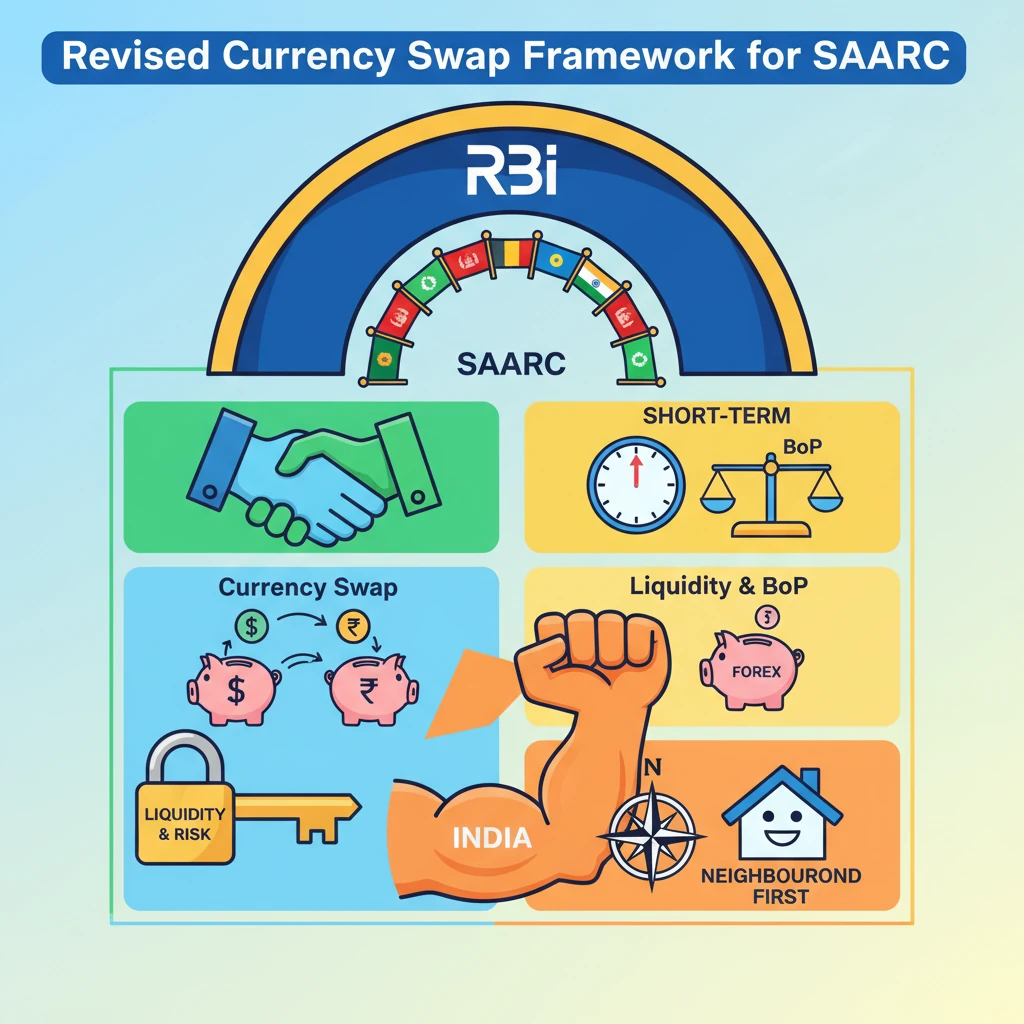
<h4>Introduction to Currency Swap Framework</h4><p>The <strong>Reserve Bank of India (RBI)</strong> has implemented a <strong>revised framework</strong> for <strong>currency swap arrangements</strong> specifically designed for the <strong>South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC)</strong> member countries. This initiative aims to provide financial stability and support within the region.</p><div class='info-box'><p>A <strong>currency swap</strong> is a transaction in which two parties exchange an equivalent amount of money in different currencies. They agree to swap principal and/or interest payments over a specified period, typically to manage foreign exchange risk or obtain lower interest rates in foreign currency borrowing.</p></div><h4>Purpose of the SAARC Currency Swap Framework</h4><p>The primary objective of this framework is to offer a <strong>backstop line of funding</strong> to <strong>SAARC nations</strong>. This funding is crucial for meeting their short-term foreign exchange liquidity requirements, especially during times of balance of payments (BoP) crises or external shocks.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The framework acts as a <strong>safety net</strong>, allowing member countries to draw upon a pre-agreed amount of foreign currency from the <strong>RBI</strong>, thus preventing potential financial instability.</p></div><h4>Evolution and Revision of the Framework</h4><p>Initially, the <strong>RBI</strong> had established a <strong>SAARC Currency Swap Facility</strong> in <strong>2012</strong>. This facility was part of India's commitment to fostering regional economic cooperation and stability. Over time, economic conditions and regional needs evolved, necessitating a review.</p><p>The decision to put in place a <strong>revised framework</strong> reflects a proactive approach by the <strong>RBI</strong> to enhance the effectiveness and accessibility of the swap arrangements for its neighbours. This revision ensures the framework remains relevant and robust.</p><h4>Key Features of the Revised Framework</h4><p>The revised framework introduces several improvements to make the currency swap facility more attractive and beneficial for <strong>SAARC members</strong>. These enhancements include increased financial limits and more flexible terms.</p><ul><li><strong>Increased Limits:</strong> The total corpus of the swap facility has been substantially increased, allowing for larger drawdowns by eligible countries.</li><li><strong>Longer Tenure:</strong> The maximum period for which a swap can be availed has been extended, providing more flexibility for countries to manage their liquidity.</li><li><strong>Wider Currency Options:</strong> While primarily denominated in <strong>US Dollars</strong>, the framework may also allow for swaps in <strong>Indian Rupees (INR)</strong>, further promoting the use of local currencies in regional trade.</li><li><strong>Simplified Procedures:</strong> Efforts have been made to streamline the application and approval processes, making it easier for countries to access funds quickly when needed.</li></ul><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>For <strong>UPSC Mains GS-II (International Relations)</strong> and <strong>GS-III (Economy)</strong>, understanding the <strong>SAARC Currency Swap Framework</strong> is vital. It demonstrates India's role in regional economic diplomacy and its commitment to multilateral institutions. Focus on the 'why' (stability, liquidity) and 'how' (RBI's role, features).</p></div>
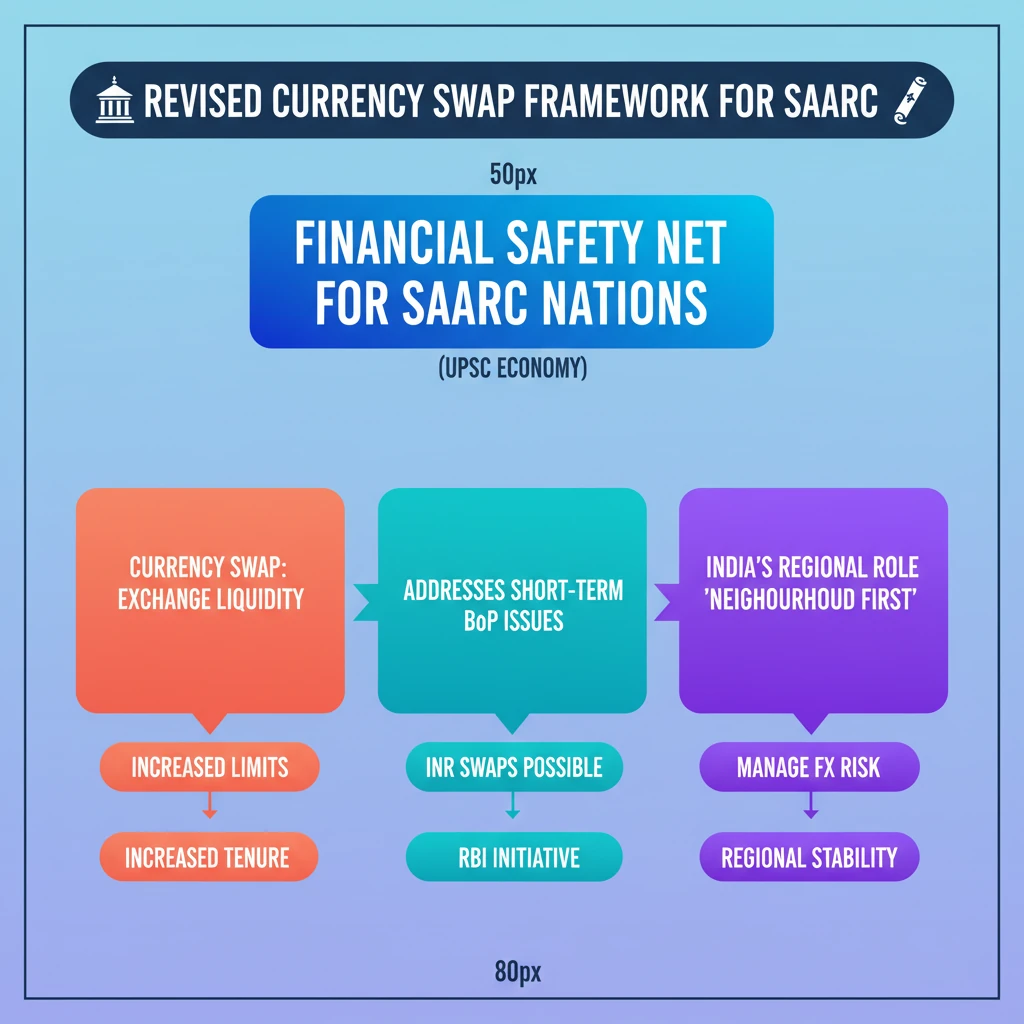
💡 Key Takeaways
- •RBI's Revised Currency Swap Framework provides a financial safety net for SAARC nations.
- •A currency swap is an exchange of principal/interest in different currencies to manage liquidity or risk.
- •The framework aims to address short-term foreign exchange liquidity and Balance of Payments (BoP) issues.
- •It enhances India's role in regional economic stability and aligns with the 'Neighbourhood First' policy.
- •Key features include increased limits, longer tenure, and potential for INR swaps.
- •It helps SAARC countries reduce reliance on volatile international markets and manage currency volatility.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Economic Survey of India (various years)
•Financial news outlets (e.g., The Hindu, Livemint, Business Standard)
•Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) publications on SAARC and regional cooperation