Energy Sector: Transition, Minerals, Renewables & Key Developments - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Energy Sector: Transition, Minerals, Renewables & Key Developments
Medium⏱️ 15 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
<h4>Balancing Energy Transition & Security</h4><p>India is actively navigating the complex challenge of achieving <strong>energy transition</strong> towards cleaner sources while simultaneously ensuring robust <strong>energy security</strong> for its growing population and economy. This involves a multi-pronged strategy.</p><p>The focus is on reducing reliance on fossil fuels while meeting increasing energy demand. This balance is crucial for both environmental sustainability and economic stability.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Energy Transition:</strong> Shift from fossil fuels to renewable and low-carbon energy sources.</p><p><strong>Energy Security:</strong> Uninterrupted availability of energy sources at an affordable price.</p></div><h4>National Critical Mineral Mission</h4><p>The <strong>National Critical Mineral Mission</strong> is a strategic initiative aimed at securing the supply chain for essential minerals. These minerals are vital for various advanced technologies, including those used in renewable energy and electric vehicles.</p><p>Ensuring domestic availability and diversified sourcing of these <strong>critical minerals</strong> reduces India's vulnerability to global supply disruptions and geopolitical tensions. This is a key component of India's long-term energy and industrial strategy.</p><h4>Chhattisgarh Links Forest Ecosystem to Green GDP</h4><p><strong>Chhattisgarh</strong> has pioneered an initiative to link its <strong>forest ecosystem</strong> directly to the concept of <strong>Green GDP</strong>. This approach recognizes the economic value of natural resources and environmental services.</p><p>By integrating the value of forests into economic accounting, Chhattisgarh aims to promote sustainable resource management. This move highlights the importance of ecological health for economic well-being and aligns with global sustainability goals.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Green GDP:</strong> A measure of economic growth that accounts for the environmental consequences of that growth, including the depletion of natural resources and degradation of the environment.</p></div><h4>Push for Hybrid Electric Vehicles</h4><p>India is actively promoting <strong>Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs)</strong> as an interim solution in its transition towards full electrification of the transport sector. HEVs combine a conventional internal combustion engine with an electric propulsion system.</p><p>This push aims to reduce fuel consumption and vehicular emissions, offering a stepping stone before widespread adoption of Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs). Government incentives and policy support are crucial for their market penetration.</p><h4>India’s First Small-Scale LNG Unit in Madhya Pradesh</h4><p>India inaugurated its <strong>first small-scale Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) unit</strong> in <strong>Madhya Pradesh</strong>. This development marks a significant step towards expanding natural gas infrastructure and its accessibility.</p><p>Small-scale LNG units facilitate the supply of natural gas to remote and underserved areas, where large pipeline infrastructure is not feasible. This enhances energy access and promotes cleaner fuel usage in diverse regions.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>LNG:</strong> Natural gas cooled to a liquid state, making it easier to store and transport. It is a cleaner-burning fossil fuel compared to coal or oil.</p></div><h4>India Emerges as Third-Largest Solar Power Producer in 2023</h4><p>In <strong>2023</strong>, India achieved a significant milestone by becoming the <strong>third-largest solar power producer globally</strong>. This demonstrates the nation's rapid progress in renewable energy deployment.</p><p>This achievement is a result of aggressive policy support, declining solar panel costs, and increased investment in solar energy projects. It underscores India's commitment to its climate targets and energy transition goals.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>This fact is crucial for Mains answers on renewable energy, climate change, and economic development. Quote it to show India's leadership. (<strong>GS Paper III: Economy, Environment</strong>)</p></div><h4>ETHANOL 100</h4><p><strong>ETHANOL 100</strong> refers to pure ethanol fuel, which is being explored as a potential alternative to traditional petrol. India is significantly pushing for <strong>ethanol blending</strong> in petrol to reduce reliance on crude oil imports and cut emissions.</p><p>The development of <strong>ETHANOL 100</strong> technology and infrastructure would allow vehicles to run entirely on ethanol, offering a more sustainable and domestically sourced fuel option. This aligns with the government's biofuel policy objectives.</p><h4>Indian Oil Market Outlook to 2030: IEA</h4><p>The <strong>International Energy Agency (IEA)</strong> released its <strong>Indian Oil Market Outlook to 2030</strong>, providing critical insights into India's projected oil demand, supply, and refining capacity. Such reports are vital for policy planning.</p><p>The outlook likely highlights India's increasing energy needs, its strategic importance in global oil markets, and the challenges and opportunities in balancing economic growth with energy security and environmental goals.</p>
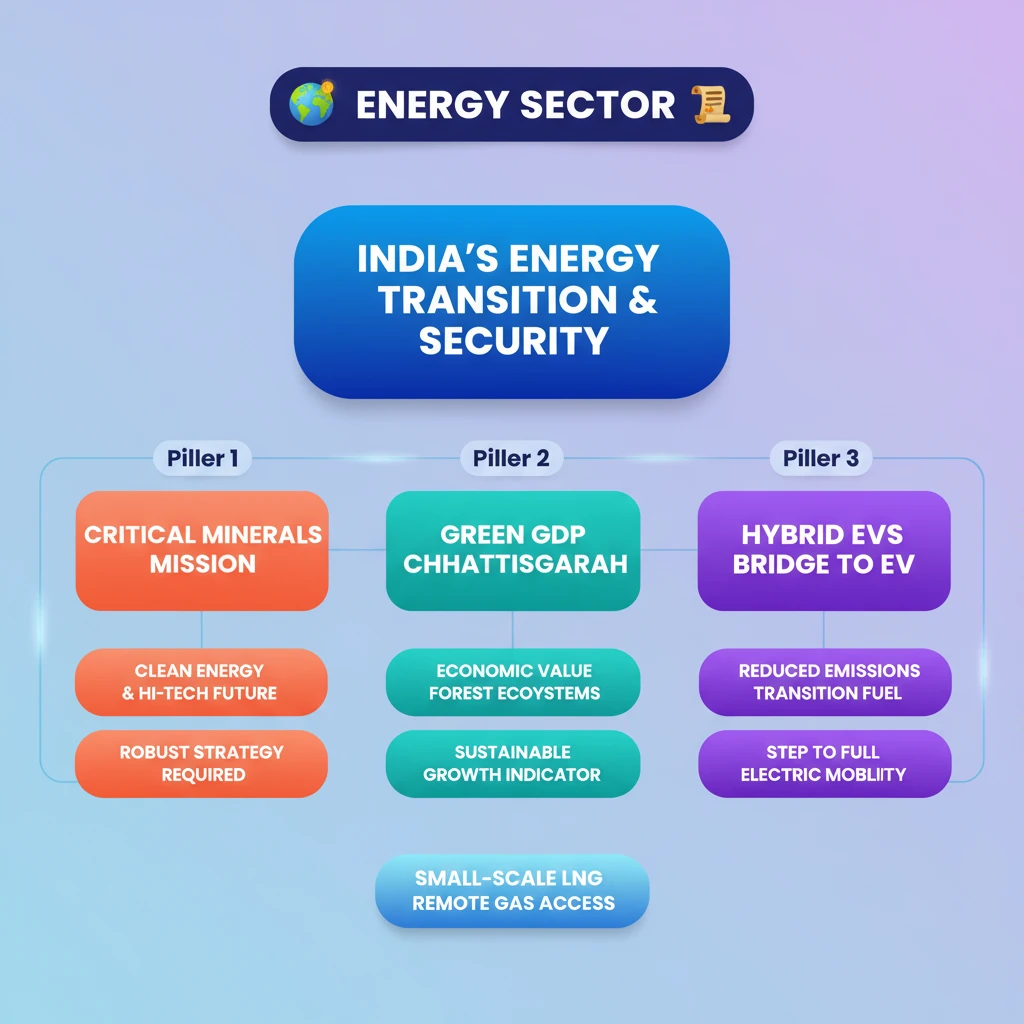
💡 Key Takeaways
- •India balances energy transition with energy security, crucial for sustainable growth.
- •Critical minerals are vital for India's clean energy and high-tech future, necessitating a robust mission.
- •Chhattisgarh's Green GDP initiative highlights the economic value of forest ecosystems.
- •Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) serve as a bridge to full electric mobility, reducing emissions.
- •Small-scale LNG units are expanding natural gas access to remote areas, promoting cleaner fuel.
- •India is the 3rd largest solar power producer globally (2023), demonstrating rapid renewable energy growth.
- •Ethanol blending (E20 by 2025) and ETHANOL 100 are key to reducing oil imports and emissions.
- •IEA's outlooks provide critical insights for India's long-term energy planning and policy formulation.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Ministry of Power, Government of India reports
•International Energy Agency (IEA) publications on India
•Press Information Bureau (PIB) releases
•NITI Aayog documents on energy policy