Eased FDI Policy for Space Sector - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Eased FDI Policy for Space Sector
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
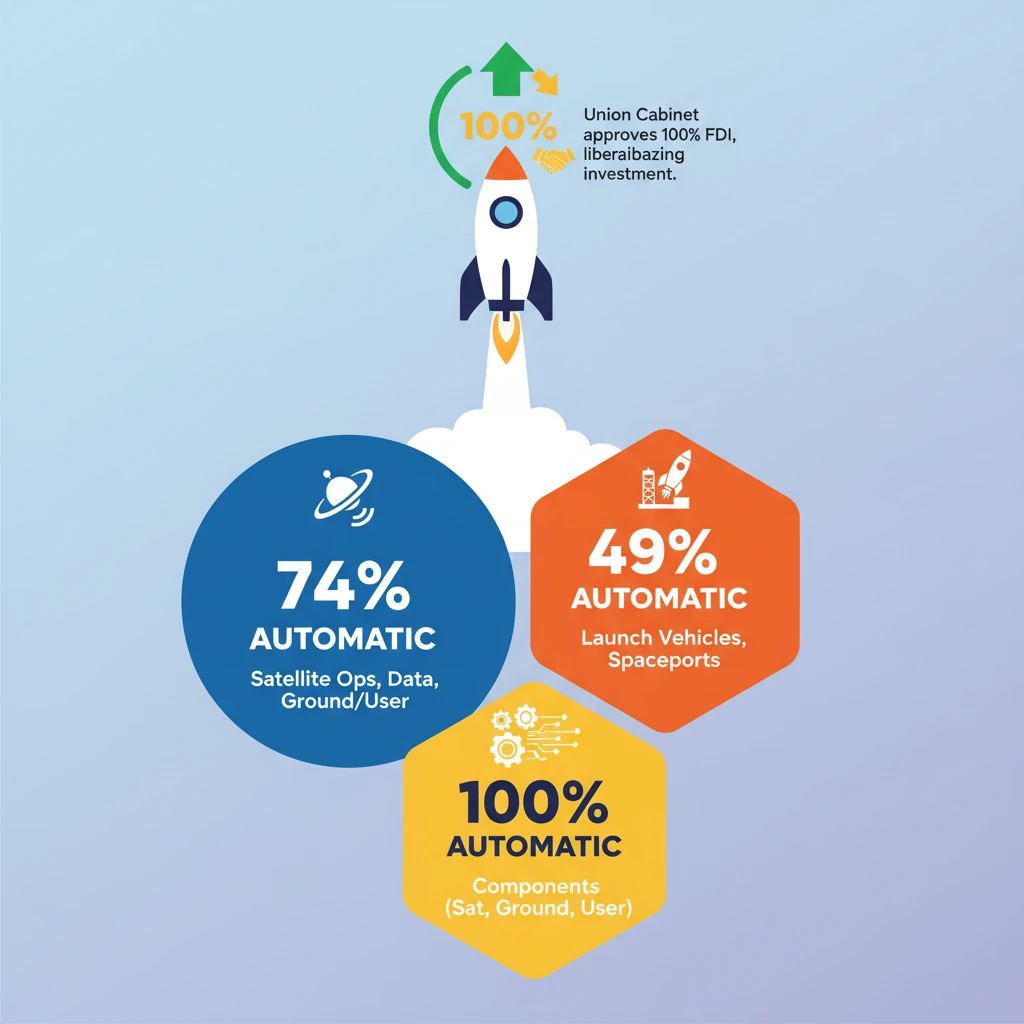
<h4>Eased FDI Policy for Space Sector: An Overview</h4><p>The <strong>Union Cabinet</strong> recently approved significant amendments to the existing <strong>Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) policy</strong> specifically for the <strong>space industry</strong>. This move aims to streamline investment processes and attract global capital into India's burgeoning space economy.</p><p>The primary objective behind these changes is to encourage greater participation from private entities and international investors. This is expected to boost technological advancements, create employment opportunities, and enhance India's global competitiveness in the space domain.</p><h4>Key Amendments in FDI Policy for Space Sector</h4><p>The amended policy now permits <strong>100% FDI</strong> in various segments of the space sector. This liberalisation is a strategic step to draw potential investors towards Indian space companies, fostering growth and innovation.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>100% FDI Permitted:</strong> The new policy allows <strong>100% Foreign Direct Investment</strong> across most segments of the Indian space sector, signifying a major shift towards a more open investment environment.</p></div><h4>Liberalised Entry Routes for Space Activities</h4><p>The entry routes for foreign investment have been significantly liberalised, with different thresholds for <strong>Automatic Route</strong> and <strong>Government Route</strong> approvals, depending on the specific activity:</p><div class='info-box'><ul><li><strong>Up to 74% under Automatic Route:</strong> This applies to activities such as <strong>Satellites – Manufacturing & Operation</strong>, <strong>Satellite Data Products</strong>, and development of <strong>Ground Segment & User Segment</strong>. Beyond 74%, the <strong>Government Route</strong> is required.</li><li><strong>Up to 49% under Automatic Route:</strong> This route is for investments in <strong>Launch Vehicles</strong>, their associated <strong>systems or sub-systems</strong>, and the <strong>Creation of Spaceports</strong>. Investments exceeding 49% will necessitate approval via the <strong>Government Route</strong>.</li><li><strong>Up to 100% under Automatic Route:</strong> For the <strong>Manufacturing of components and systems/sub-systems</strong> specifically for <strong>satellites, ground segment, and user segment</strong>, <strong>100% FDI</strong> is permitted under the <strong>Automatic Route</strong>.</li></ul></div><h4>Major Developments in India's Space Sector</h4><p>India currently holds a <strong>2-3% share</strong> of the <strong>global space economy</strong>, with aspirations to increase this to over <strong>10% by 2030</strong>. This growth trajectory is supported by the capabilities of <strong>ISRO</strong>, which stands as one of the <strong>six largest space agencies globally</strong>.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Global Space Economy Share:</strong> India's current share is <strong>2-3%</strong>, significantly lower than the <strong>US (40%)</strong> and <strong>UK (7%)</strong>. The goal is to reach <strong>>10% by 2030</strong>.</p></div><h4>Recent Major Successful Missions</h4><p>India's space prowess is evident through a series of highly successful missions:</p><ul><li><strong>Aditya L1:</strong> India's first dedicated solar mission, launched to study the Sun.</li><li><strong>Chandrayaan 3:</strong> Achieved a historic soft landing on the lunar south pole, making India the fourth nation to do so.</li><li><strong>Mars Orbiter Mission (Mangalyaan):</strong> India's inaugural interplanetary mission, successfully orbiting Mars.</li></ul><h4>Advancements in Launch Vehicles</h4><p>India has developed robust and versatile launch vehicle capabilities:</p><ul><li><strong>GSLV Mark III (LVM3):</strong> India's heaviest operational launch vehicle, capable of launching 4-ton class satellites into GTO.</li><li><strong>Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV):</strong> Designed for cost-effective and on-demand launch of small satellites.</li><li><strong>PSLV (Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle):</strong> A workhorse launch vehicle known for its reliability and versatility.</li></ul><h4>Missions for International Clients</h4><p>India has emerged as a preferred partner for international satellite launches:</p><ul><li><strong>TeleOS-2 (2023):</strong> Launched for <strong>Singapore</strong>, an Earth observation satellite.</li><li><strong>PSLV-C51 (2021):</strong> Successfully launched <strong>Brazil’s Amazonia-1 satellite</strong> along with 18 smaller co-passenger satellites.</li></ul><h4>Other Key Developments</h4><p>Beyond missions, several other initiatives are strengthening India's space ecosystem:</p><ul><li><strong>NavIC:</strong> India's independent regional satellite navigation system.</li><li><strong>Bhuvan:</strong> ISRO's geo-portal offering Earth observation data and services.</li><li><strong>Rise in Space Start-Ups:</strong> The number of Indian <strong>Space Start-Ups</strong> has significantly increased, reaching <strong>189 in 2023</strong>, indicating a vibrant private sector.</li></ul><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> The <strong>eased FDI policy</strong> is crucial for understanding India's push for <strong>private sector participation</strong> and <strong>technological self-reliance</strong> in strategic sectors. Connect this to <strong>economic reforms</strong> and <strong>global competitiveness</strong> for <strong>GS Paper 3</strong>.</p></div>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •Union Cabinet approved 100% FDI in India's space sector, liberalising investment routes.
- •Up to 74% FDI is automatic for satellite operations, data products, ground/user segments.
- •Up to 49% FDI is automatic for launch vehicles and spaceports.
- •100% FDI is automatic for manufacturing components for satellites, ground, and user segments.
- •India aims to increase its global space economy share from 2-3% to over 10% by 2030.
- •Policy supports ISRO's advancements, successful missions (Aditya L1, Chandrayaan 3), and growth of 189+ space start-ups.
- •Expected to attract investment, foster innovation, create jobs, and enhance India's global competitiveness in space.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Press Information Bureau (PIB) releases regarding Union Cabinet decisions on FDI policy
•ISRO official website for mission details and achievements