Small-Scale LNG - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
Small-Scale LNG
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
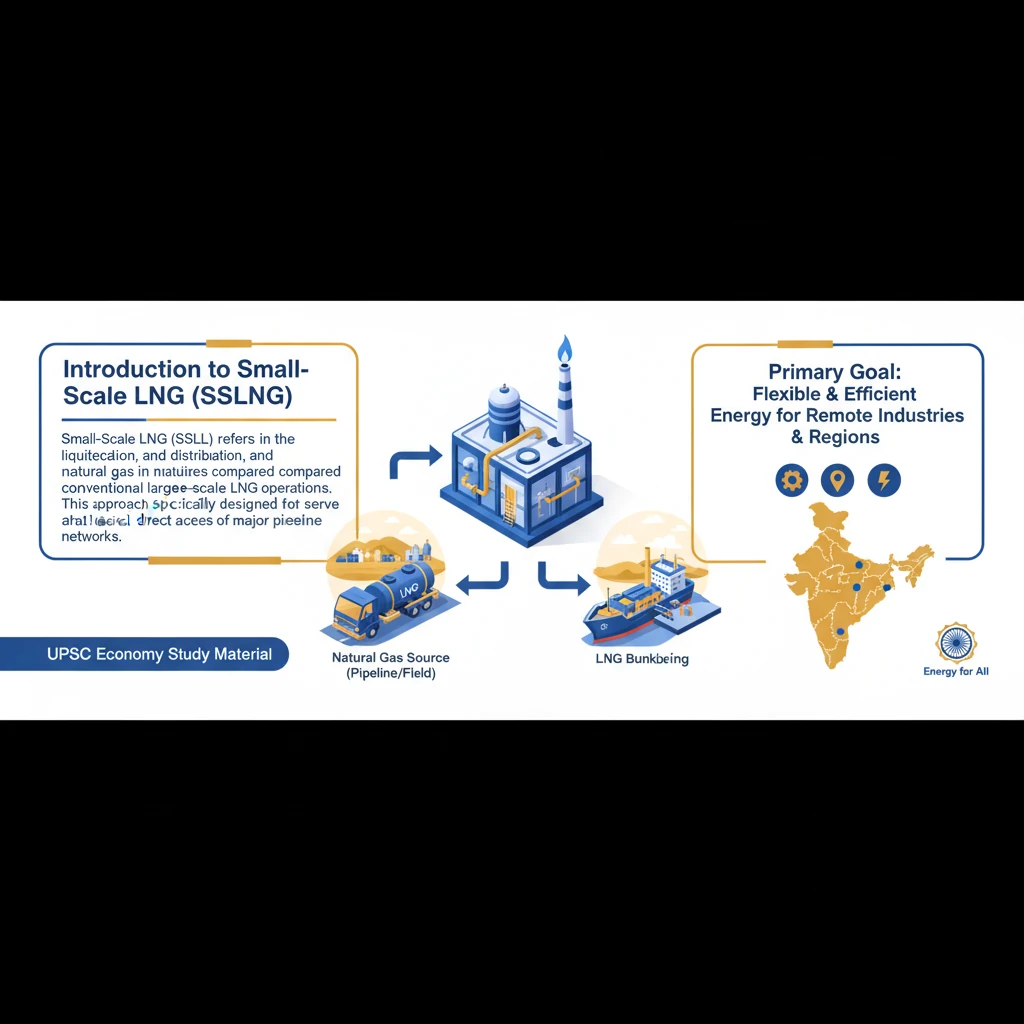
<h4>Introduction to Small-Scale LNG (SSLNG)</h4><p><strong>Small-Scale LNG (SSLNG)</strong> refers to the liquefaction, transportation, and distribution of <strong>natural gas</strong> in smaller volumes compared to conventional large-scale LNG operations. This approach is specifically designed to serve areas that lack direct access to major <strong>pipeline networks</strong>.</p><p>The primary goal of <strong>SSLNG</strong> is to provide a flexible and efficient energy solution for remote industries, communities, and specific transportation sectors. It bridges the gap where traditional pipeline infrastructure is not economically viable or physically feasible.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Key Characteristics of SSLNG:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Smaller Volumes:</strong> Typically involves capacities ranging from 10,000 to 500,000 tonnes per annum (TPA).</li><li><strong>Distributed Supply:</strong> Caters to dispersed demand points rather than large centralized markets.</li><li><strong>Flexible Logistics:</strong> Utilizes diverse transport modes like trucks and small vessels.</li></ul></div><h4>Operational Flow of Small-Scale LNG</h4><p>The supply chain for <strong>SSLNG</strong> often originates from existing <strong>large-scale LNG import terminals</strong>. At these terminals, a portion of the imported LNG is offloaded and then further distributed using specialized smaller logistics.</p><p>From these terminals, <strong>SSLNG</strong> can be supplied directly to various consumers. This involves transferring the <strong>liquefied natural gas</strong> into specialized transport carriers for onward delivery to end-users.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Transport and Delivery Methods:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Cryogenic Road Tankers:</strong> Specialized trucks designed to maintain LNG at extremely low temperatures for road transport.</li><li><strong>Small Vessels:</strong> Smaller LNG carriers or barges used for coastal or inland waterway transport to islands or remote ports.</li></ul></div><p>Upon reaching the consumer, the <strong>LNG</strong> can be utilized in two primary forms. It can be supplied directly as a <strong>liquid fuel</strong> for specific applications, such as marine bunkering or heavy-duty vehicles.</p><p>Alternatively, the <strong>LNG</strong> can be <strong>regasified</strong> at the consumption point. This process converts the liquid back into gaseous natural gas, making it suitable for traditional uses like power generation, industrial processes, or domestic consumption.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> <strong>SSLNG</strong> is crucial for India's energy security and achieving a 'gas-based economy' by extending the reach of natural gas beyond the conventional pipeline grid. It's a vital component for distributed energy solutions and reducing reliance on polluting fuels in remote areas. Expect questions on its role in infrastructure development and environmental sustainability. ⚡</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
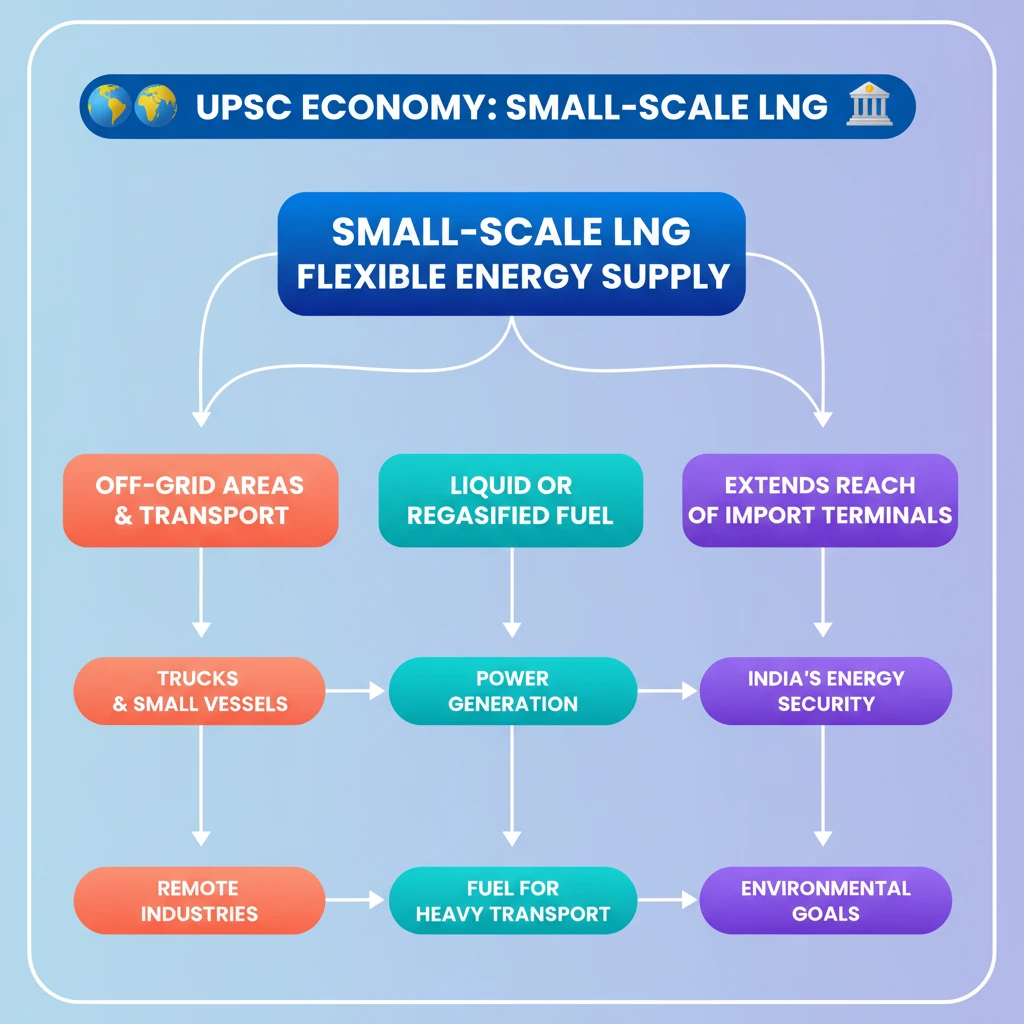
- •Small-Scale LNG (SSLNG) involves liquefying and transporting natural gas in smaller volumes.
- •It caters to areas without pipeline connections, using specialized trucks and small vessels.
- •SSLNG can supply LNG directly as a liquid or regasified for traditional uses.
- •It originates from large-scale LNG import terminals, extending their reach.
- •Crucial for India's energy security, environmental goals, and industrial decentralization.
- •Offers flexible and distributed energy solutions for remote and underserved markets.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas, Government of India reports
•Petroleum Planning & Analysis Cell (PPAC) data
•International Gas Union (IGU) reports on Small-Scale LNG
•Various industry publications and academic papers on LNG infrastructure