Local Currency Trade between India-Indonesia - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
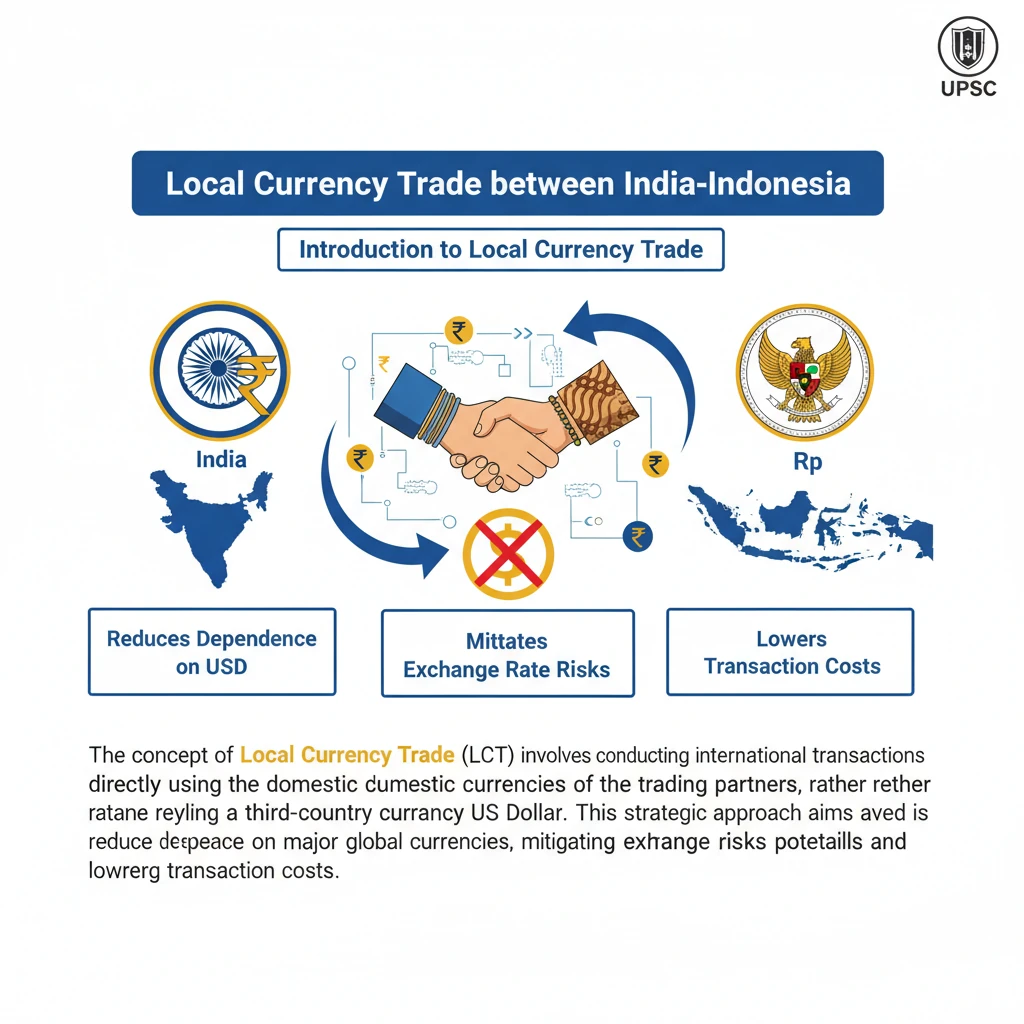
Local Currency Trade between India-Indonesia
Medium⏱️ 5 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
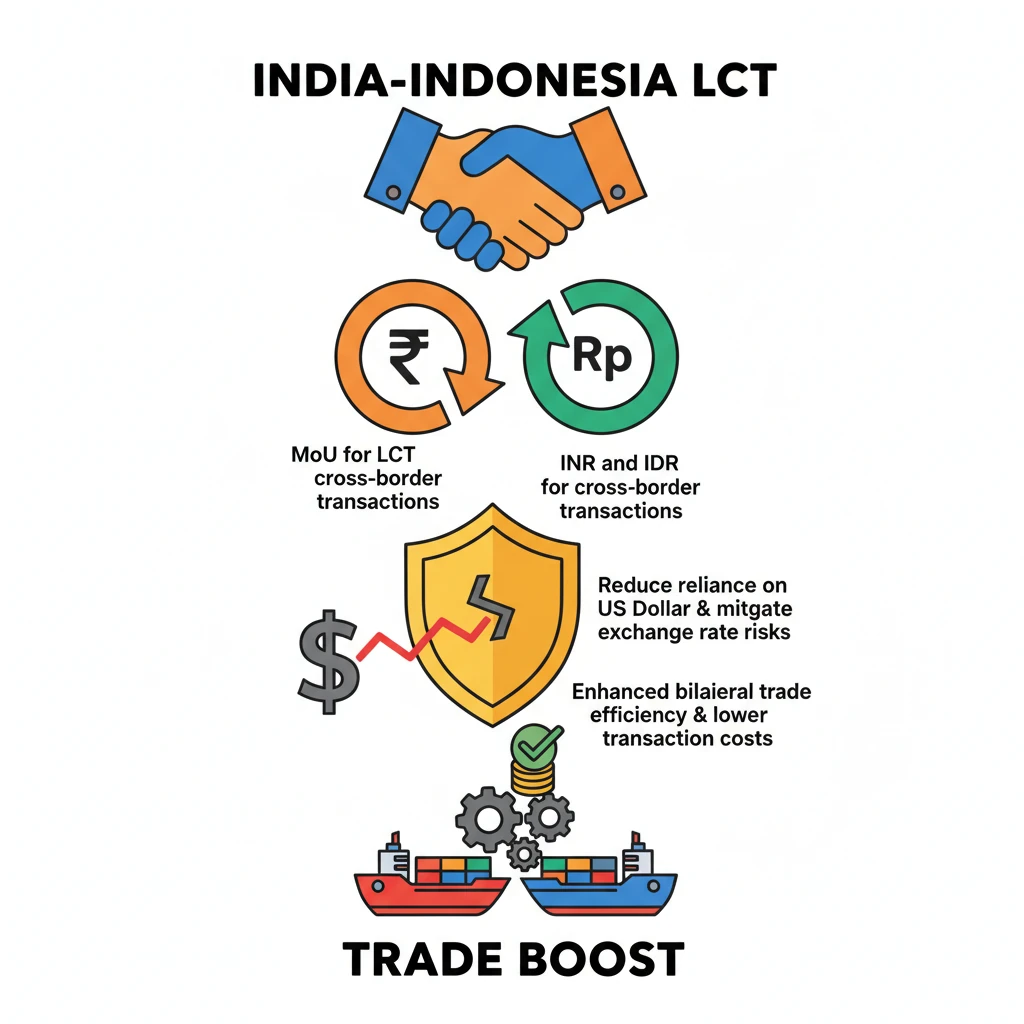
<h4>Introduction to Local Currency Trade</h4><p>The concept of <strong>Local Currency Trade (LCT)</strong> involves conducting international transactions directly using the domestic currencies of the trading partners, rather than relying on a third-country currency like the <strong>US Dollar</strong>.</p><p>This strategic approach aims to reduce dependence on major global currencies, thereby mitigating <strong>exchange rate risks</strong> and potentially lowering <strong>transaction costs</strong> for businesses engaged in cross-border commerce.</p><h4>India-Indonesia MoU for Local Currency Settlement</h4><p>The <strong>Reserve Bank of India (RBI)</strong> and <strong>Bank Indonesia (BI)</strong> have formally signed a significant agreement, a <strong>Memorandum of Understanding (MoU)</strong>.</p><p>This MoU establishes a robust framework specifically designed to facilitate and actively promote the use of their respective local currencies in bilateral trade and financial transactions.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Key Currencies Involved:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Indian Rupee (INR)</strong></li><li><strong>Indonesian Rupiah (IDR)</strong></li></ul></div><p>The primary objective of this newly established framework is to encourage the direct use of the <strong>INR</strong> and <strong>IDR</strong> for various <strong>cross-border transactions</strong> occurring between India and Indonesia.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>This initiative represents a crucial step towards enhancing <strong>bilateral trade efficiency</strong> and strengthening <strong>economic ties</strong>, reducing the need for conversion into external currencies.</p></div><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>UPSC often focuses on India's efforts towards the <strong>internationalization of the Rupee</strong> and reducing <strong>dollar dependence</strong>. This MoU serves as a prime, current example for such topics.</p></div>
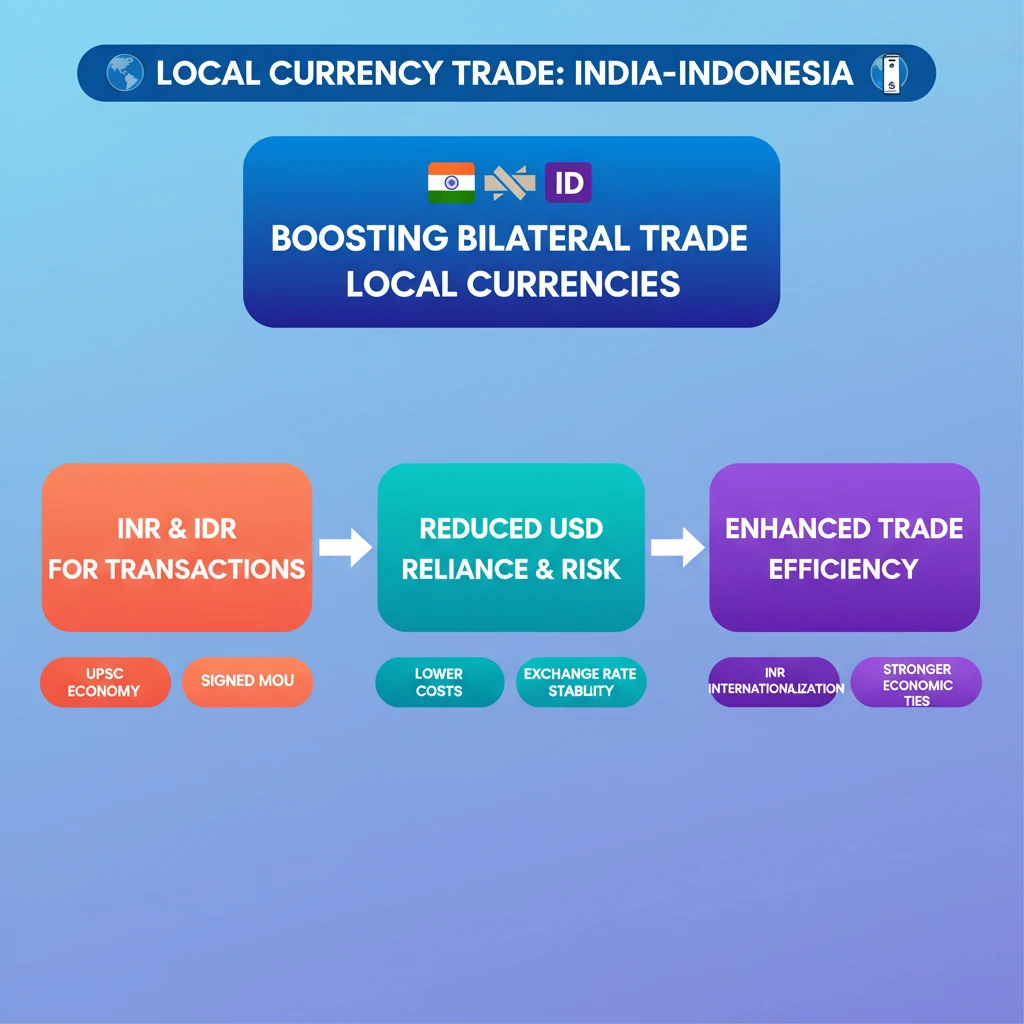
💡 Key Takeaways
- •India and Indonesia signed an MoU for Local Currency Trade (LCT).
- •The framework promotes using Indian Rupee (INR) and Indonesian Rupiah (IDR) for cross-border transactions.
- •Aims to reduce reliance on the US Dollar and mitigate exchange rate risks.
- •Enhances bilateral trade efficiency and lowers transaction costs for businesses.
- •Supports the internationalization of the Indian Rupee and strengthens economic ties.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Bank Indonesia (BI) Official Statements
•Ministry of External Affairs (MEA), Government of India
•Economic Survey of India