India’s Concerns on EU’s CBAM and Deforestation Norms - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
India’s Concerns on EU’s CBAM and Deforestation Norms
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
<h4>India's Concerns: EU's CBAM and Deforestation Norms</h4><p>India has expressed significant apprehension regarding two major European Union initiatives: the <strong>Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM)</strong> and the <strong>European Union Deforestation Regulation (EUDR)</strong>.</p><p>India's <strong>Finance Minister</strong> has characterized these measures as <strong>unilateral</strong>, <strong>arbitrary</strong>, and essentially <strong>trade barriers</strong> designed to negatively impact Indian industries.</p><h4>Understanding the Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM)</h4><div class="info-box"><p>The <strong>Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM)</strong> is a key instrument of the EU aimed at leveling the playing field regarding carbon emissions.</p><p>Its primary goal is to impose a fair price on the <strong>carbon emissions</strong> embedded in the production of certain <strong>carbon-intensive goods</strong> imported into the EU.</p><p>This mechanism also seeks to encourage cleaner industrial production practices in non-EU countries by incentivizing them to reduce their carbon footprint.</p></div><h4>Understanding the European Union Deforestation Regulation (EUDR)</h4><div class="info-box"><p>The <strong>European Union Deforestation Regulation (EUDR)</strong> mandates stringent requirements for operators and traders.</p><p>Those placing specified commodities on the EU market or exporting them must provide verifiable proof.</p><p>This proof must demonstrate that their products do not originate from recently <strong>deforested land</strong> and do not contribute to <strong>forest degradation</strong>.</p></div><div class="key-point-box"><p><strong>Key Point:</strong> Both <strong>CBAM</strong> and <strong>EUDR</strong> are perceived by India as protectionist measures, potentially hindering its export competitiveness and violating principles of free and fair trade.</p></div><div class="exam-tip-box"><p>⚡️ <strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Questions on <strong>international trade regulations</strong>, <strong>environmental diplomacy</strong>, and their impact on India's economy are common in <strong>GS-II</strong> and <strong>GS-III</strong>. Understand the implications for India's export sectors.</p></div>
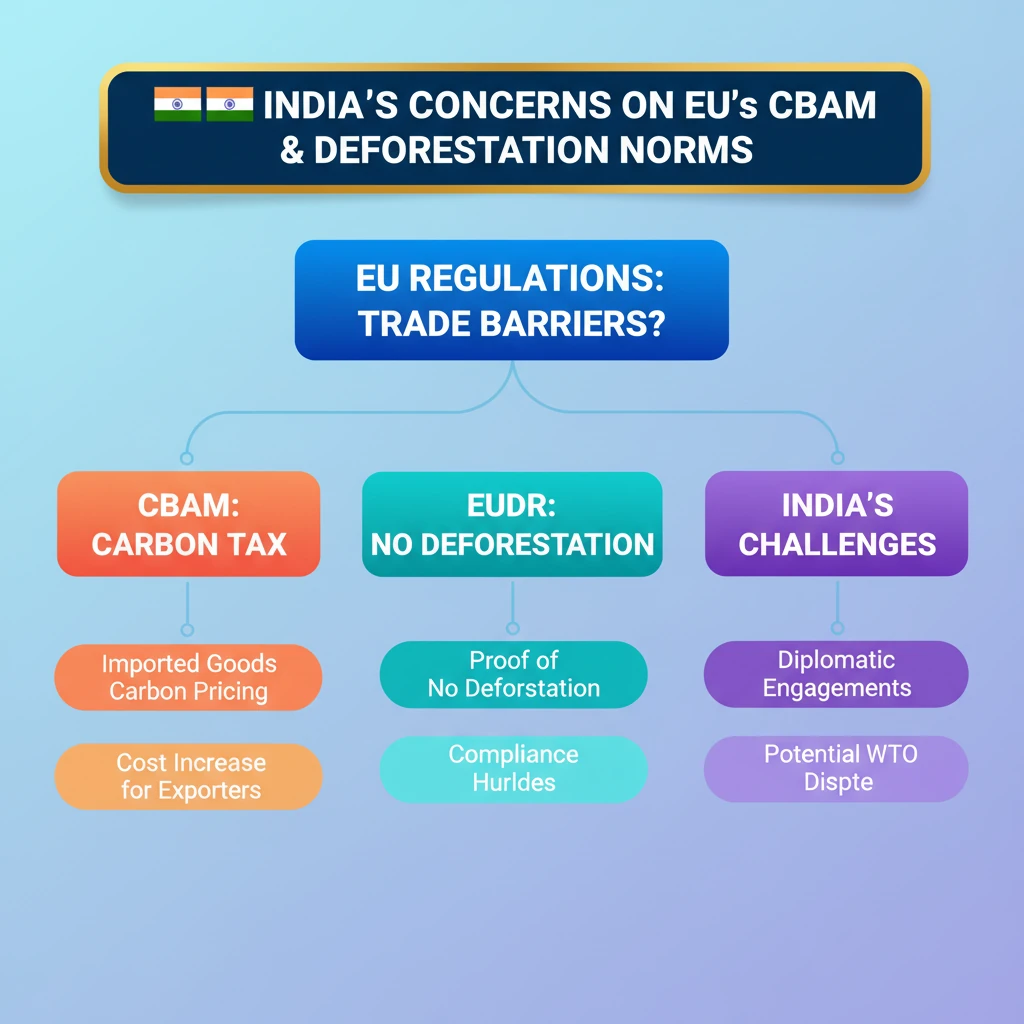
💡 Key Takeaways
- •India views EU's CBAM and EUDR as unilateral trade barriers.
- •CBAM aims to price carbon emissions in imported goods to the EU.
- •EUDR requires proof that products are not linked to recent deforestation.
- •Both regulations pose compliance challenges and potential cost increases for Indian exporters.
- •India is engaging diplomatically and considering WTO challenges.
- •These measures highlight the growing intersection of trade and environmental policy.
🧠 Memory Techniques
90% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•European Commission Official Websites (for CBAM and EUDR details)