Infrastructure and Development - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Infrastructure and Development
Medium⏱️ 12 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
<h4>Understanding Infrastructure and Development</h4><p><strong>Infrastructure</strong> refers to the fundamental facilities and systems serving a country, city, or area, including the services and facilities necessary for its economy to function. It encompasses a wide range of sectors such as transport, energy, communication, and social services like health and education.</p><p>The development of robust infrastructure is a critical prerequisite for sustained <strong>economic growth</strong> and social progress. It facilitates trade, attracts investment, creates employment, and improves the overall quality of life for citizens.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Key Infrastructure Sectors:</strong></p><ul><li><strong>Economic Infrastructure:</strong> Roads, railways, ports, airports, power, telecommunications, irrigation.</li><li><strong>Social Infrastructure:</strong> Education, healthcare, sanitation, housing, water supply.</li></ul></div><h4>Infrastructure Development in India</h4><p>India has historically faced significant challenges in developing adequate infrastructure to support its large and growing population and economy. Post-independence, various <strong>Five-Year Plans</strong> focused on building foundational infrastructure, primarily through public sector investments.</p><p>In recent decades, there has been a growing emphasis on accelerating infrastructure development through a mix of public, private, and hybrid financing models. Initiatives like the <strong>National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP)</strong> and <strong>PM Gati Shakti</strong> aim to streamline planning and execution.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Importance of Infrastructure for India:</strong></p><ul><li>Boosts <strong>manufacturing</strong> and services sectors.</li><li>Enhances <strong>connectivity</strong> and reduces logistics costs.</li><li>Attracts <strong>Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)</strong>.</li><li>Generates large-scale <strong>employment opportunities</strong>.</li><li>Improves access to essential <strong>social services</strong>.</li></ul></div><h4>Raising of Asset Monetisation Target</h4><p><strong>Asset Monetisation</strong> is a strategy employed by the government to unlock the value of underutilised or non-core public assets. Instead of selling assets, it involves transferring revenue rights to private parties for a specified transaction period in return for an upfront payment, a revenue share, or investment in the asset.</p><p>The Indian government has set ambitious targets for asset monetisation, particularly through the <strong>National Monetisation Pipeline (NMP)</strong>. This initiative aims to generate significant resources for new infrastructure creation by leveraging existing brownfield assets.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>UPSC often asks about innovative financing mechanisms for infrastructure. Understanding <strong>asset monetisation</strong>, its objectives, and challenges is crucial for both Prelims and Mains, especially in <strong>GS Paper III (Economy)</strong>.</p></div><p>The core objective of increasing the asset monetisation target is to bridge the infrastructure funding gap. It seeks to bring in private sector efficiency, technology, and capital into the operation and maintenance of public assets, while the ownership remains with the government.</p>
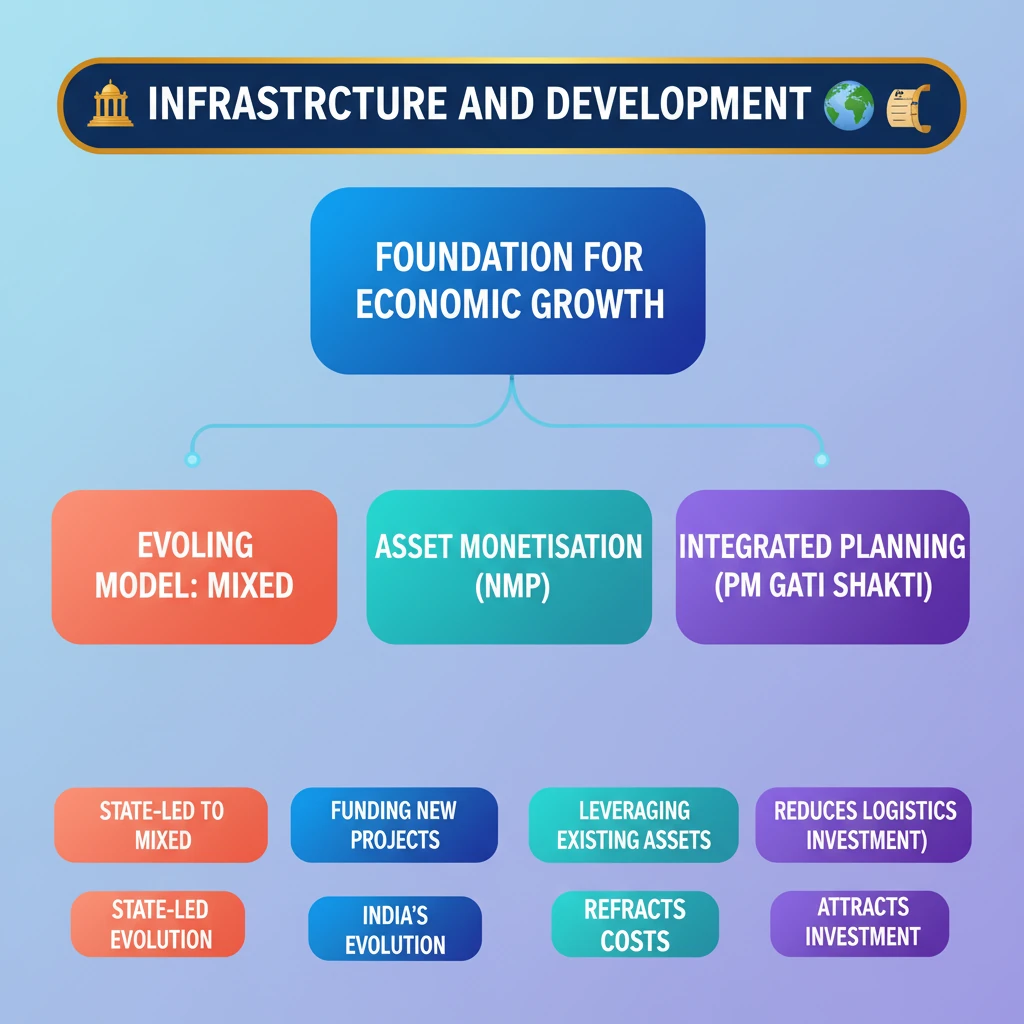
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Infrastructure is foundational for economic growth and social development.
- •India's infrastructure development has evolved from state-led to a mixed model.
- •Asset Monetisation (via NMP) is a key strategy to fund new infrastructure by leveraging existing assets.
- •PM Gati Shakti ensures integrated planning and execution of infrastructure projects.
- •Robust infrastructure improves competitiveness, reduces logistics costs, and attracts investment.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Ministry of Finance, Government of India (Economic Survey)
•Press Information Bureau (PIB) releases on PM Gati Shakti
•Reserve Bank of India (RBI) publications on infrastructure financing