How did Cooperatives Evolve in India? - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
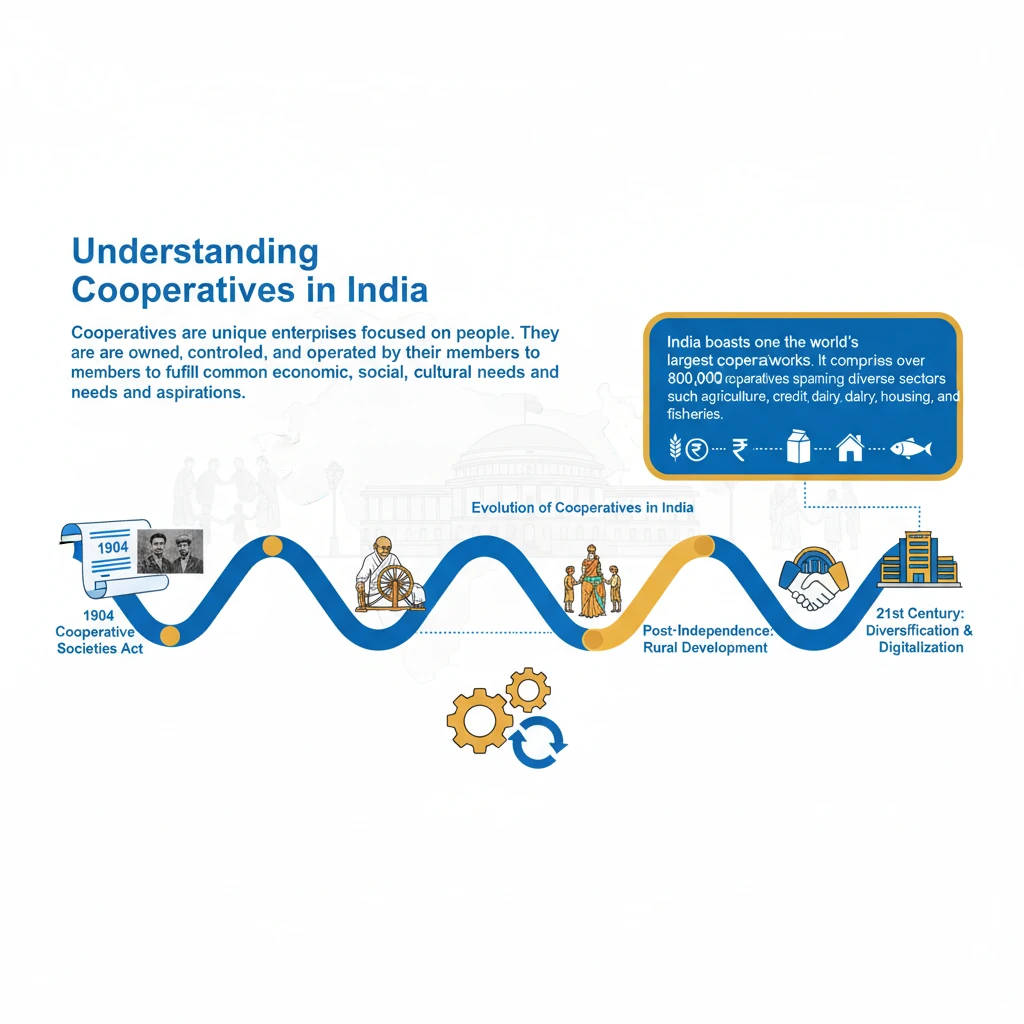
How did Cooperatives Evolve in India?
Medium⏱️ 10 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
<h4>Introduction to Cooperatives in India</h4><p><strong>Cooperatives</strong> are unique, <strong>people-centred enterprises</strong>. They are owned, controlled, and run by and for their members to realize their common economic, social, and cultural needs and aspirations.</p><p>India boasts one of the <strong>world's largest cooperative networks</strong>, with over <strong>800,000 cooperatives</strong> spread across diverse sectors like agriculture, credit, dairy, housing, and fisheries.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The cooperative sector makes significant contributions to the Indian economy, including:<ul><li><strong>20%</strong> in agricultural loans</li><li><strong>35%</strong> in fertilizer distribution</li><li><strong>31%</strong> in sugar production</li><li><strong>13%</strong> in wheat purchase</li><li><strong>20%</strong> in paddy purchase</li></ul></p></div><h4>Cooperatives in the Pre-Independence Era</h4><p>The foundation for the cooperative movement in India was laid in the early 20th century, primarily to address agrarian distress and rural indebtedness.</p><ol><li><p><strong>Indian Famine Commission (1901)</strong>: Its recommendations led to the enactment of the first cooperative law.</p></li><li><p><strong>Cooperative Credit Societies Act, 1904</strong>: This was the first significant legislation, focusing on providing credit to farmers and artisans.</p></li><li><p><strong>Cooperative Societies Act, 1912</strong>: An amendment to the 1904 Act, expanding its scope beyond credit to include non-credit cooperatives.</p></li></ol><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Maclagan Committee (1915)</strong>: Headed by <strong>Sir Edward Maclagan</strong>, this committee was appointed to study and report on the economic and financial soundness of the cooperative movement.</p></div><p>The <strong>Montague-Chelmsford Reforms of 1919</strong> brought a significant change by making <strong>co-operation a provincial subject</strong>. This decentralization gave further impetus to the movement, allowing provinces to tailor laws to local needs.</p><p>During the <strong>Poor Economic Depression of 1929</strong>, various committees were appointed in provinces like <strong>Madras, Bombay, Travancore, Mysore, Gwalior</strong>, and <strong>Punjab</strong> to examine possibilities for restructuring cooperative societies.</p><p><strong>Gandhian Socialist Philosophy</strong> played a crucial role. Mahatma Gandhi believed cooperation was necessary for the creation of a <strong>socialistic society</strong> and complete <strong>decentralisation of power</strong>.</p><p>He was of the opinion that cooperation was one of the important means to empower people. His practical applications include the <strong>‘Phoenix Settlement’</strong> and <strong>‘Tolstoy Farm’</strong> in South Africa, established on cooperative principles.</p><h4>Cooperatives in Post-Independence India</h4><p>Post-independence, cooperatives were seen as integral to nation-building and comprehensive rural development.</p><ol><li><p><strong>First Five-Year Plan (1951-56)</strong>: This plan strongly highlighted the promotion of cooperatives for <strong>comprehensive community development</strong> across the country.</p></li><li><p><strong>Multi-State Co-operative Societies Act, 2002</strong>: This act provided the legal framework for the formation and functioning of cooperatives operating across multiple states.</p></li><li><p><strong>Multi-State Co-operative Societies (Amendment) Act, 2022</strong>: This amendment introduced the <strong>Co-operative Election Authority</strong> to oversee board elections in multi-state co-operative societies, ensuring transparency.</p></li></ol><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>97th Constitutional Amendment Act of 2011</strong>: This landmark amendment significantly strengthened the cooperative movement by:</p><ul><li>Establishing the <strong>right to form cooperative societies</strong> as a <strong>fundamental right</strong> (<strong>Article 19(1)(c)</strong>).</li><li>Introducing a new <strong>Directive Principle of State Policy (DPSP)</strong> on Cooperative Societies (<strong>Article 43-B</strong>).</li><li>Adding a new <strong>Part IX-B</strong> to the Constitution, titled <strong>“The Co-operative Societies”</strong> (<strong>Articles 243-ZH to 243-ZT</strong>).</li><li>Empowering Parliament to enact laws governing <strong>Multi-State Cooperative Societies (MSCS)</strong> and delegating authority to state legislatures for other cooperative societies.</li></ul></div><p><strong>Establishment of Union Ministry of Cooperation (2021)</strong>: This new ministry was created to provide a separate administrative, legal, and policy framework for strengthening the cooperative movement in India, previously overseen by the Ministry of Agriculture.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>The evolution of cooperatives showcases a blend of legislative action, committee recommendations, and constitutional reforms, reflecting their growing importance in India's socio-economic fabric. Questions often focus on the <strong>97th Amendment</strong> and the role of the <strong>Ministry of Cooperation</strong>.</p></div>
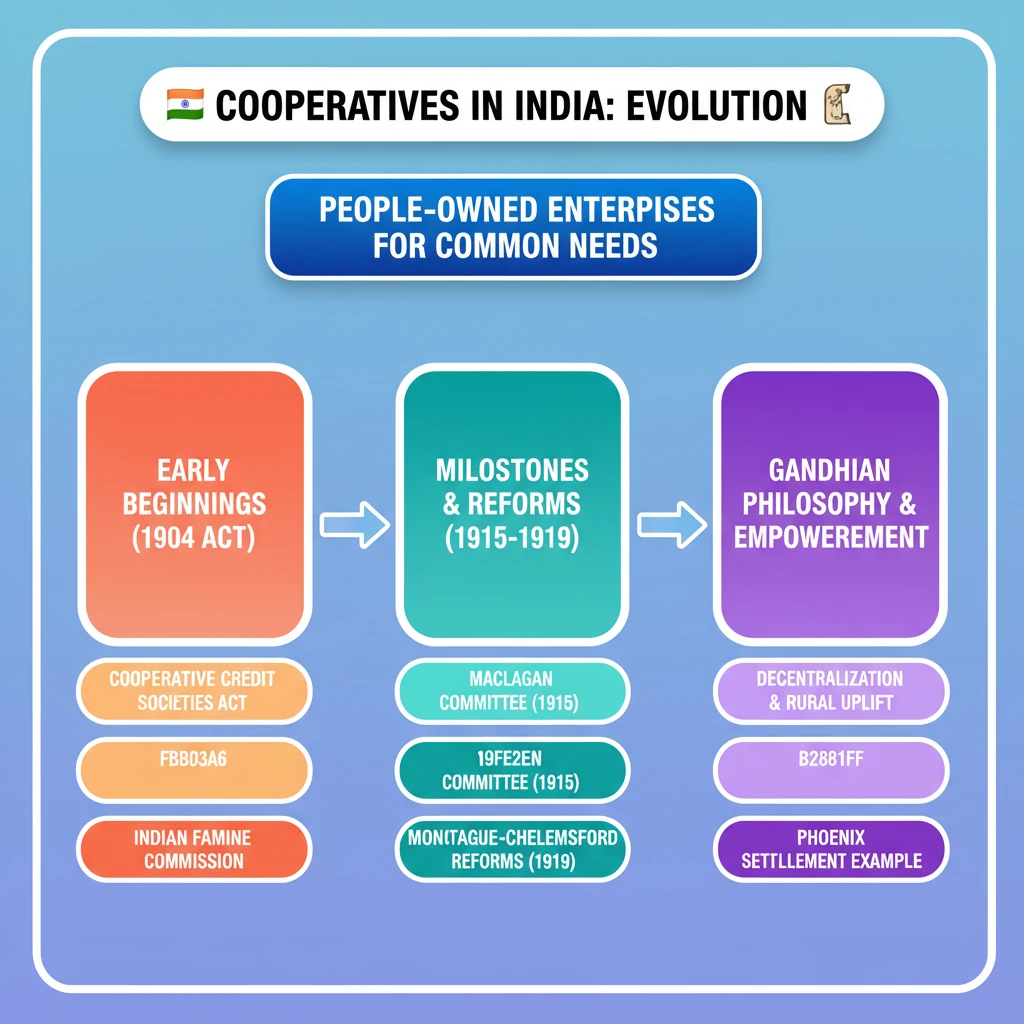
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Cooperatives are member-owned, democratically controlled enterprises fulfilling common needs.
- •India has one of the largest cooperative networks globally, with significant contributions to agriculture and credit.
- •Pre-independence evolution saw key acts (1904, 1912) and the Maclagan Committee, with cooperation becoming a provincial subject in 1919.
- •Gandhian philosophy championed cooperatives for decentralization and empowerment.
- •Post-independence, the First Five-Year Plan promoted cooperatives for community development.
- •The 97th Constitutional Amendment Act, 2011, made forming cooperatives a fundamental right and added Part IX-B.
- •The Union Ministry of Cooperation (2021) was established to strengthen the sector.
- •Cooperatives are crucial for rural development, financial inclusion, and inclusive growth in modern India.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•The Constitution of India (97th Amendment Act, 2011)
•Ministry of Cooperation, Government of India official website
•NCERT Economics Textbooks (relevant chapters on Indian Economy)