What is Compressed Natural Gas? - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

What is Compressed Natural Gas?
Easy⏱️ 8 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
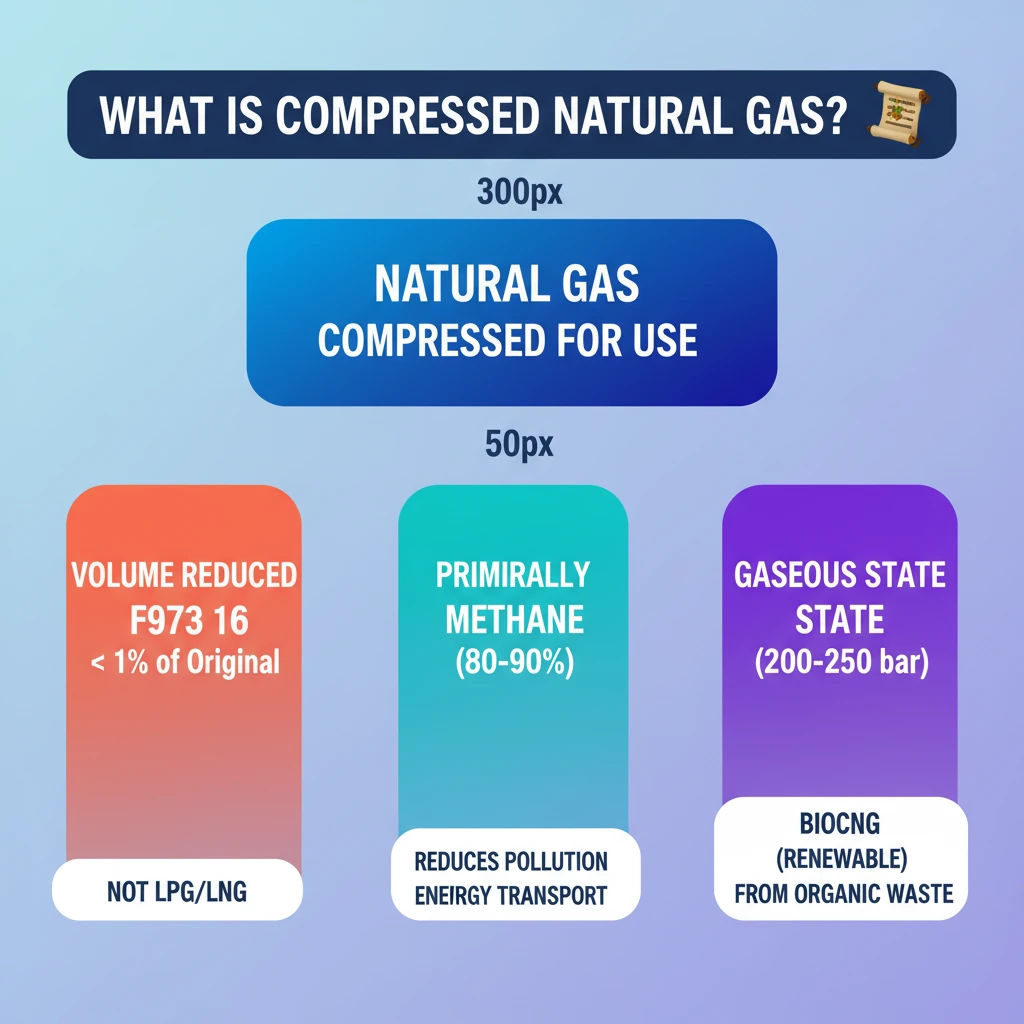
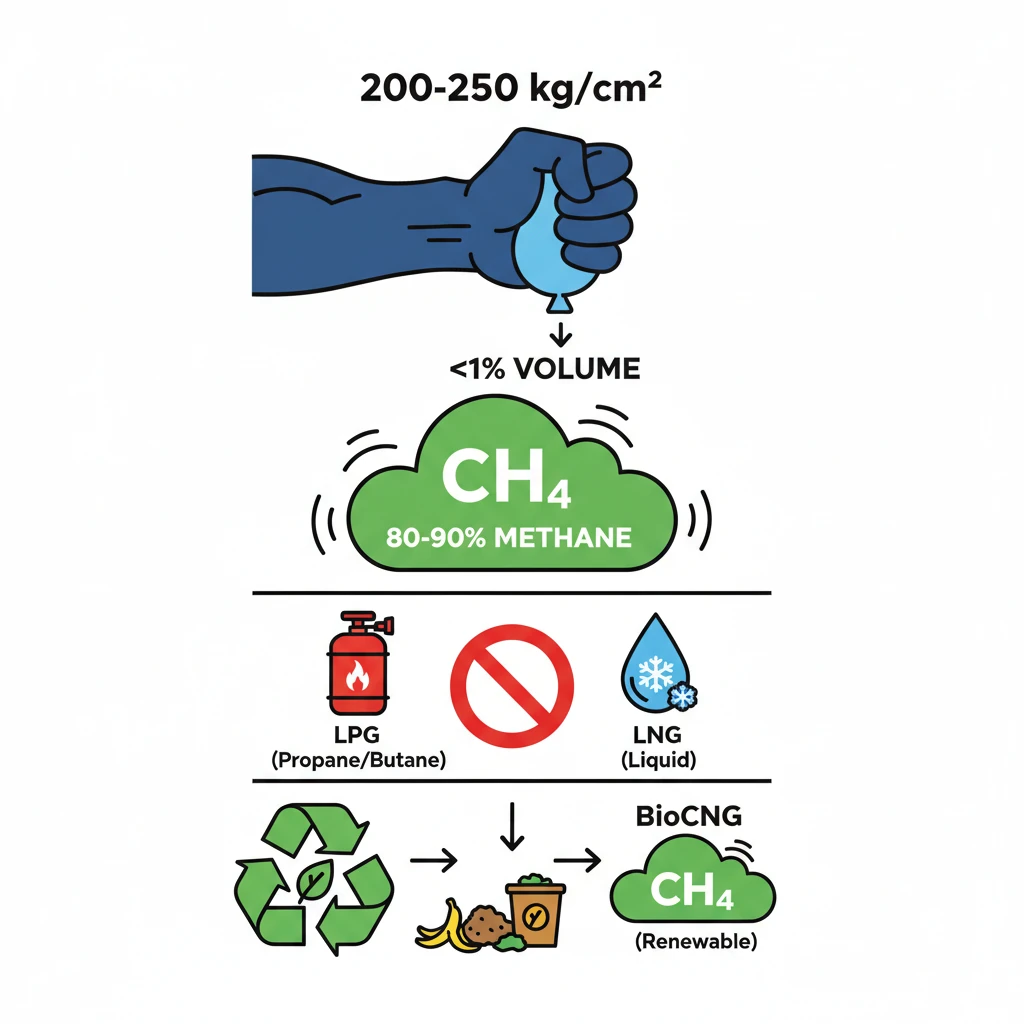
<h4>What is Compressed Natural Gas (CNG)?</h4><p><strong>Compressed Natural Gas (CNG)</strong> is essentially <strong>natural gas</strong> that has undergone a process of significant compression. This compression allows it to occupy a much smaller volume, making it suitable for storage in fuel tanks, particularly for vehicles.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Compression Details:</strong> <strong>CNG</strong> is typically compressed at very high pressures, ranging from <strong>200 to 250 kg/cm²</strong>. This intense compression reduces its volume to less than <strong>1%</strong> of its original size at atmospheric pressure, enabling efficient storage.</p></div><h4>Composition of CNG</h4><p>Unlike <strong>Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG)</strong>, which is a blend of compressed propane and butane, <strong>CNG</strong> has a distinct composition. It primarily consists of <strong>methane</strong>, making up <strong>80 to 90%</strong> of its content, and remains in a <strong>gaseous state</strong> even after compression.</p><h4>CNG vs. LNG: Key Differences</h4><p>The fundamental distinction between <strong>CNG</strong> and <strong>Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG)</strong> lies in their physical states. While <strong>CNG</strong> exists and is stored as a <strong>gas</strong>, <strong>LNG</strong> is natural gas cooled to an extremely low temperature to become a <strong>liquid</strong>, which is then regasified for use.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Physical State is Key:</strong> Remember that <strong>CNG</strong> is a <strong>gas under high pressure</strong>, whereas <strong>LNG</strong> is a <strong>liquid at cryogenic temperatures</strong>.</p></div><h4>Understanding BioCNG</h4><p><strong>BioCNG</strong>, also known as <strong>biomethane</strong>, represents a renewable and environmentally friendly alternative. It is a <strong>clean-burning transportation fuel</strong> derived from <strong>organic waste</strong> materials.</p><p>The production of <strong>BioCNG</strong> involves upgrading <strong>biogas</strong> to achieve the same quality as conventional natural gas. This process makes it a sustainable fuel source, contributing to waste management and renewable energy goals.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>BioCNG Attributes:</strong> It is a <strong>renewable fuel</strong>, produced from <strong>organic waste</strong>, and significantly contributes to reducing carbon footprint as a <strong>clean-burning fuel</strong>.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •CNG is natural gas compressed to 200-250 kg/cm², reducing its volume to less than 1%.
- •It primarily consists of 80-90% methane and remains in a gaseous state.
- •CNG differs from LPG (propane/butane mixture) and LNG (liquid natural gas).
- •BioCNG (biomethane) is a renewable, clean-burning fuel produced by upgrading biogas from organic waste.
- •CNG and BioCNG are crucial for cleaner urban transport, reducing air pollution, and enhancing energy security.
🧠 Memory Techniques
98% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas, Government of India official reports
•Petroleum Planning & Analysis Cell (PPAC) data
•National Biofuel Policy 2018 document