What is the ‘Make in India’ Initiative? - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

What is the ‘Make in India’ Initiative?
Medium⏱️ 7 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
<h4>Introduction to Make in India</h4><p>The <strong>‘Make in India’</strong> initiative is a flagship program launched by the <strong>Government of India</strong>. Its primary aim is to transform India into a global manufacturing hub.</p><p>The campaign was initiated to attract and facilitate both domestic and foreign investment in various sectors across the country. It seeks to create a conducive environment for businesses to thrive.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>Key aspects of the initiative include fostering <strong>innovation</strong>, enhancing <strong>skill development</strong>, protecting <strong>intellectual property</strong>, and building world-class <strong>manufacturing infrastructure</strong>.</p></div><h4>Key Objectives of Make in India</h4><p>The initiative set ambitious targets to boost the manufacturing sector and its contribution to the Indian economy. These objectives were crucial for achieving sustainable economic growth and creating employment opportunities.</p><div class='info-box'><ul><li><strong>Increase Manufacturing Growth Rate:</strong> To achieve a growth rate of <strong>12-14% per annum</strong> in the manufacturing sector.</li><li><strong>Job Creation:</strong> To create <strong>100 million additional manufacturing jobs</strong>. Initially targeted by <strong>2022</strong>, this was later revised to <strong>2025</strong>.</li><li><strong>GDP Contribution:</strong> To increase the manufacturing sector’s contribution to <strong>India's GDP</strong> to <strong>25%</strong> by <strong>2025</strong>.</li></ul></div><h4>Pillars of ‘Make in India’</h4><p>The <strong>‘Make in India’</strong> initiative is built upon four foundational pillars designed to create a holistic ecosystem for manufacturing growth. These pillars address various aspects from policy to infrastructure.</p><h4>New Processes</h4><p>This pillar focuses on improving the regulatory and business environment to make India an attractive destination for manufacturing. It emphasizes streamlining procedures and reducing bureaucratic hurdles.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The government recognized the critical importance of <strong>‘ease of doing business’</strong> for fostering entrepreneurship. Various measures have been implemented to simplify regulations.</p></div><p>These improvements aim to create a more predictable and transparent business environment for both new <strong>startups</strong> and established <strong>enterprises</strong>.</p><h4>New Infrastructure</h4><p>Developing robust and modern infrastructure is vital for supporting a thriving manufacturing sector. This pillar focuses on physical and digital connectivity, as well as innovation ecosystems.</p><div class='info-box'><p>The government prioritized the development of <strong>industrial corridors</strong> and <strong>smart cities</strong> to provide world-class infrastructure. This includes better logistics, power, and connectivity.</p></div><p>Additionally, efforts were made to enhance <strong>innovation</strong> and <strong>research</strong> through streamlined registration systems and improved <strong>intellectual property rights (IPR) infrastructure</strong>. This supports indigenous R&D.</p><h4>New Sectors</h4><p>To attract investment and expand manufacturing capabilities, the initiative significantly opened up various sectors for foreign participation. This broadened the scope for international collaboration and technology transfer.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)</strong> norms were liberalized in key sectors, including <strong>Defence Production</strong>, <strong>Insurance</strong>, <strong>Medical Devices</strong>, <strong>Construction</strong>, and <strong>Railway infrastructure</strong>. This attracted global players.</p></div>
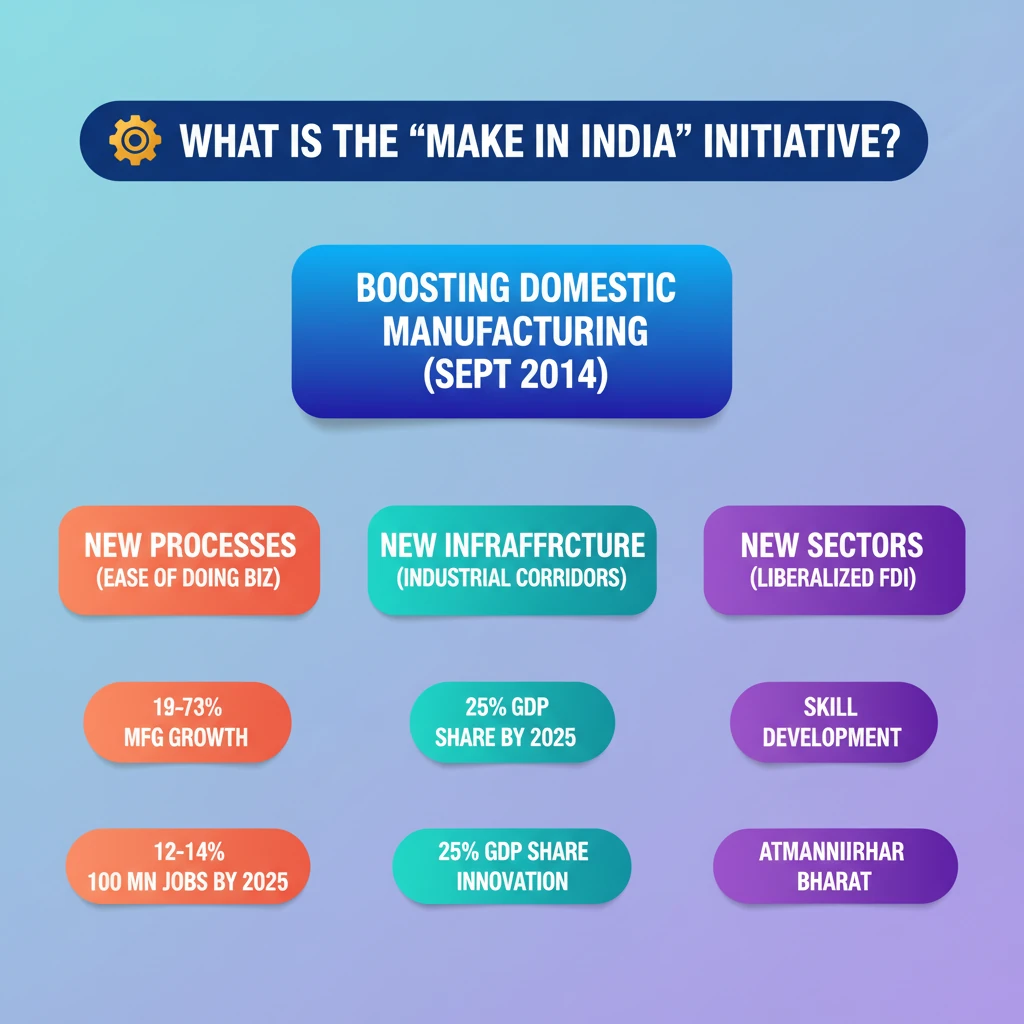
💡 Key Takeaways
- •<strong>‘Make in India’</strong> launched on <strong>Sept 25, 2014</strong>, to boost domestic manufacturing.
- •Objectives: <strong>12-14%</strong> manufacturing growth, <strong>100 million</strong> jobs by <strong>2025</strong>, <strong>25%</strong> manufacturing share in <strong>GDP</strong> by <strong>2025</strong>.
- •Four pillars: <strong>New Processes</strong> (ease of doing business), <strong>New Infrastructure</strong> (industrial corridors, IPR), <strong>New Sectors</strong> (liberalized FDI), <strong>New Mindset</strong> (government as facilitator).
- •Aims to facilitate investment, foster innovation, enhance skill development, and protect intellectual property.
- •Crucial for <strong>‘Atmanirbhar Bharat’</strong>, driving economic growth, and integrating India into global supply chains.
- •Supported by initiatives like <strong>Production Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes</strong> across various sectors.
🧠 Memory Techniques

98% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Press Information Bureau (PIB), Government of India
•NITI Aayog reports and publications
•Drishti IAS Economy Study Material