RBI to Review NBFCs - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

RBI to Review NBFCs
Medium⏱️ 9 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
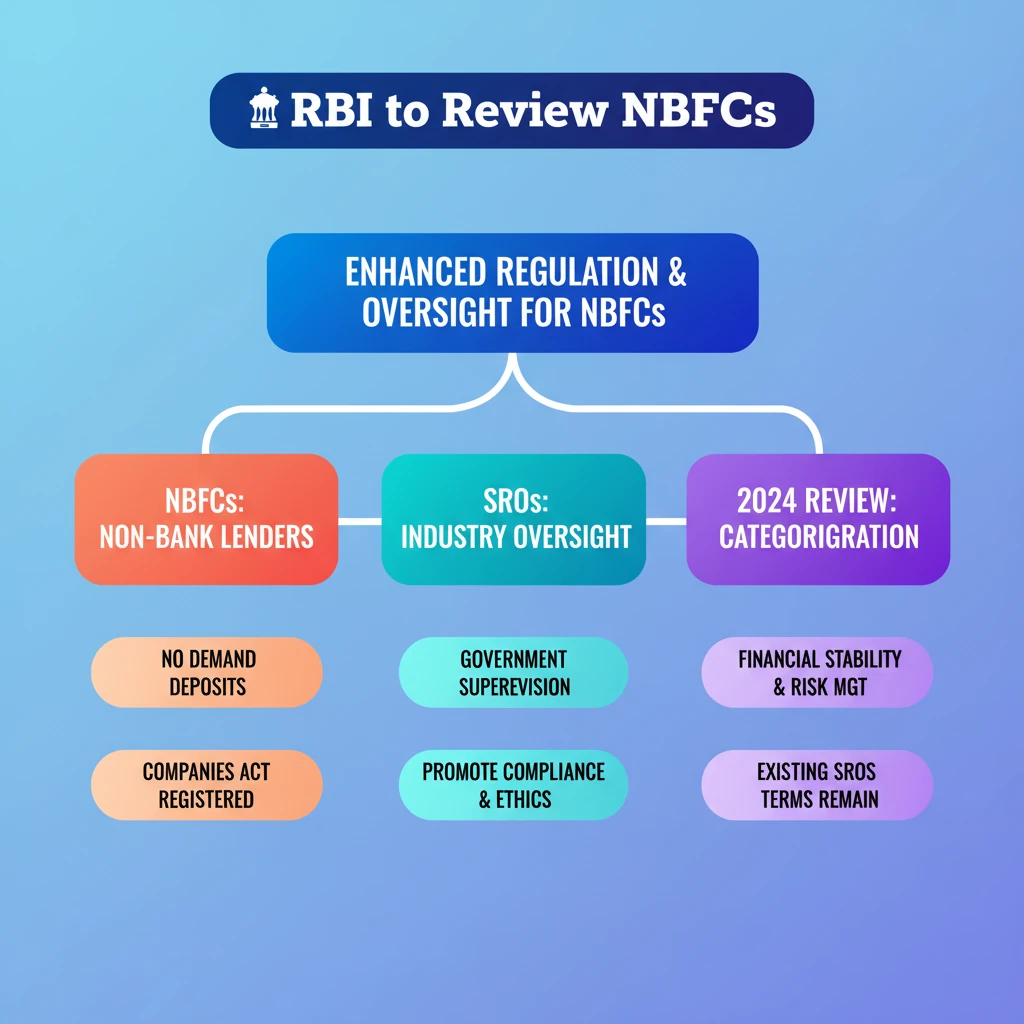
<h4>RBI's Review of NBFC Categorisation</h4><p>The <strong>Reserve Bank of India (RBI)</strong> is set to undertake a comprehensive review of the categorisation of <strong>Non-Banking Finance Companies (NBFCs)</strong> in <strong>2024</strong>. This initiative aims to refine the regulatory framework and ensure better oversight of the financial sector.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Note:</strong> Existing <strong>Self-Regulatory Organisations (SROs)</strong> recognised by the <strong>RBI</strong> will continue to be governed by their current terms and conditions. This framework will only be extended to them if specifically stated.</p></div><h4>Understanding Self-Regulatory Organisations (SROs)</h4><p><strong>Self-Regulatory Organisations (SROs)</strong> are entities established within specific industries or sectors. Their primary function is to regulate their members, often working in close collaboration with government regulators.</p><p>These organisations operate under the direct supervision of government regulators. Regulators delegate certain functions, relying on <strong>SROs</strong> to monitor and enforce compliance within their respective industries.</p><div class='info-box'><p>While government regulators maintain ultimate authority, they leverage <strong>SROs</strong> to manage the day-to-day compliance and ethical standards of their members.</p></div><h4>What are Non-Banking Finance Companies (NBFCs)?</h4><p>An <strong>NBFC</strong> is a company that is registered under either the <strong>Companies Act, 1956</strong>, or the <strong>Companies Act, 2013</strong>. They are actively involved in a variety of financial activities.</p><p>These activities include <strong>lending</strong>, making <strong>investments in securities</strong>, providing <strong>leasing services</strong>, and offering <strong>insurance products</strong>. Despite offering banking-like services, <strong>NBFCs</strong> do not possess a full banking license.</p><h4>Key Features of NBFCs</h4><p><strong>NBFCs</strong> offer a diverse range of financial services to individuals and businesses. These services cater to various needs across different segments of the economy.</p><ul><li>They provide <strong>personal loans</strong>, <strong>home loans</strong>, and <strong>vehicle loans</strong>.</li><li><strong>Gold loans</strong> and <strong>microfinance</strong> facilities are also prominent offerings.</li><li>Many <strong>NBFCs</strong> are involved in <strong>insurance</strong> and <strong>investment management</strong>.</li><li>They are permitted to accept <strong>public deposits</strong> for specific durations, ranging from a minimum of <strong>12 months</strong> to a maximum of <strong>60 months</strong>.</li></ul><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Crucial Distinction:</strong> Unlike commercial banks, <strong>NBFCs cannot accept demand deposits</strong>. This means they cannot offer facilities like current or savings accounts from which money can be withdrawn on demand.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •RBI to review NBFC categorisation in 2024 for enhanced regulation and oversight.
- •NBFCs are non-bank financial institutions registered under Companies Act, offering diverse services but cannot accept demand deposits.
- •SROs are industry bodies regulating members under government oversight, promoting compliance and ethical standards.
- •The review aims for better financial stability, risk management, and regulatory clarity for NBFCs.
- •Existing SROs' terms remain unless specifically extended by the new framework, highlighting their ongoing importance.
🧠 Memory Techniques

95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Reserve Bank of India (RBI) official communications (general knowledge)
•Companies Act, 1956/2013 (general knowledge)