What are the Pros and Cons of Cryptocurrency? - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

What are the Pros and Cons of Cryptocurrency?
Medium⏱️ 10 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
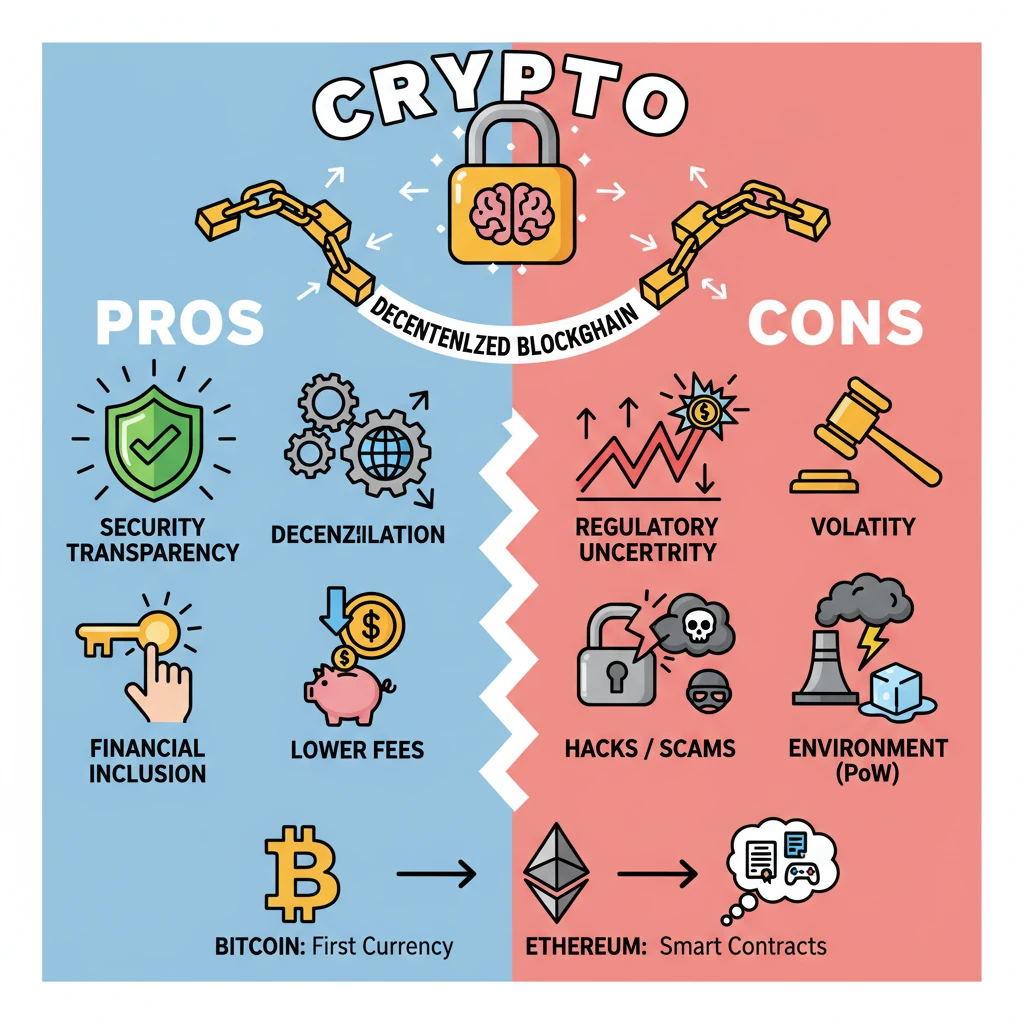
<h4>Introduction to Cryptocurrency</h4><p><strong>Cryptocurrency</strong> is a digital or virtual currency secured by <strong>cryptography</strong>, making it nearly impossible to counterfeit or double-spend. Many cryptocurrencies are decentralized networks based on <strong>blockchain technology</strong>, a distributed ledger enforced by a disparate network of computers.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Key Concept:</strong> Cryptocurrencies operate independently of a central bank or government, offering a new paradigm for financial transactions and value storage.</p></div><h4>Pros of Cryptocurrency</h4><h4>Blockchain-Driven Security and Transparency</h4><p>Cryptocurrencies leverage <strong>Blockchain technology</strong>, which offers enhanced <strong>security</strong>, <strong>transparency</strong>, and <strong>efficiency</strong> in financial transactions. Each transaction is immutably recorded on a public ledger, visible to all participants.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The cryptographic nature of blockchain ensures that once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered or removed, providing a high level of integrity.</p></div><h4>Decentralization and Autonomy</h4><p>Most cryptocurrencies are <strong>decentralized</strong>, meaning they are not subject to government or financial institution control. This offers users greater <strong>autonomy</strong> over their funds and transactions, free from traditional banking intermediaries.</p><p>This decentralized structure aims to reduce the risk of single points of failure and censorship, often associated with centralized financial systems.</p><h4>Potentially Lower Transaction Fees</h4><p>Traditional banking systems often involve various fees for international transfers and other services. Cryptocurrencies can offer <strong>lower transaction fees</strong>, especially for cross-border payments, by cutting out intermediaries.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>While often lower, transaction fees in cryptocurrencies like <strong>Bitcoin</strong> can fluctuate significantly based on network congestion, a point to consider in Mains answers.</p></div><h4>Financial Inclusion</h4><p>Cryptocurrencies can provide access to financial services for the <strong>unbanked population</strong> worldwide. Individuals without traditional bank accounts can participate in the digital economy using only a smartphone and internet access.</p><p>This aspect holds significant potential for developing economies, promoting broader economic participation.</p><h4>Faster Cross-Border Transactions</h4><p>International bank transfers can take days to clear due to various intermediaries and time zone differences. Cryptocurrency transactions, particularly with newer technologies, can be processed and settled much faster, often within minutes or hours.</p><h4>Potential Hedge Against Inflation</h4><p>Some cryptocurrencies, like <strong>Bitcoin</strong>, have a limited supply, mimicking scarce commodities like gold. Proponents argue this makes them a potential <strong>hedge against inflation</strong>, especially in economies with unstable fiat currencies.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Note:</strong> The effectiveness of cryptocurrencies as an inflation hedge is a subject of ongoing debate and depends heavily on market dynamics and regulatory environments.</p></div><h4>Cons of Cryptocurrency</h4><h4>High Price Volatility</h4><p>One of the most significant drawbacks is the extreme <strong>price volatility</strong> of cryptocurrencies. Their values can fluctuate wildly within short periods, leading to substantial gains or losses for investors.</p><p>This volatility makes them risky as a stable store of value or a medium of exchange for everyday transactions.</p><h4>Regulatory Uncertainty and Risks</h4><p>The regulatory landscape for cryptocurrencies remains largely undefined or inconsistent across different countries. This <strong>regulatory uncertainty</strong> poses risks for businesses and investors, hindering widespread adoption and stability.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>UPSC often asks about the government's stance and potential regulations on cryptocurrencies in India (e.g., <strong>RBI's views</strong>, proposed bills). Be aware of the evolving policy environment.</p></div><h4>Security Vulnerabilities and Scams</h4><p>Despite blockchain's inherent security, cryptocurrency users are susceptible to various <strong>security risks</strong>, including exchange hacks, phishing scams, and wallet compromises. Recovery of stolen funds is often impossible due to the irreversible nature of transactions.</p><p>The nascent nature of the industry also attracts fraudulent schemes and Ponzi schemes, leading to significant financial losses for unsuspecting individuals.</p><h4>Environmental Concerns</h4><p>The energy consumption associated with <strong>Proof-of-Work (PoW)</strong> cryptocurrencies, like <strong>Bitcoin</strong>, is substantial. The mining process requires immense computational power, leading to significant <strong>environmental concerns</strong> regarding carbon footprint.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Alternative:</strong> Newer cryptocurrencies and upgrades (e.g., <strong>Ethereum's shift to Proof-of-Stake</strong>) aim to address these environmental impacts by using more energy-efficient consensus mechanisms.</p></div><h4>Scalability Issues</h4><p>Many prominent cryptocurrencies face <strong>scalability issues</strong>, meaning their networks can only process a limited number of transactions per second. This can lead to network congestion and higher transaction fees during peak times, hindering their use for mass adoption.</p><h4>Potential for Illicit Activities</h4><p>The anonymity or pseudo-anonymity offered by cryptocurrencies can be exploited for <strong>illicit activities</strong> such as money laundering, drug trafficking, and ransomware payments. This poses challenges for law enforcement agencies globally.</p><h4>Complexity and User-Friendliness</h4><p>For many, understanding and using cryptocurrencies involves a steep learning curve. The technical jargon, wallet management, and private key security can be daunting, hindering adoption by the general public.</p>

💡 Key Takeaways
- •Cryptocurrencies are decentralized digital assets secured by cryptography, operating on blockchain technology.
- •Pros include enhanced security, transparency, decentralization, lower transaction fees, and financial inclusion.
- •Cons involve high volatility, regulatory uncertainty, security risks (hacks/scams), environmental concerns (PoW), and potential for illicit use.
- •Bitcoin was the first, Ethereum introduced smart contracts, expanding blockchain's utility beyond just currency.
- •India is cautious of private cryptocurrencies but actively developing its own Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC).
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•Reports from the Ministry of Finance, Government of India on crypto taxation
•IMF and World Bank reports on digital currencies and financial inclusion
•Academic papers and reputable financial news outlets (e.g., Bloomberg, Reuters, The Economic Times) on cryptocurrency trends and technology
•Whitepapers of prominent cryptocurrencies (Bitcoin, Ethereum)