Business Models Under Microfinance - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search

Business Models Under Microfinance
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
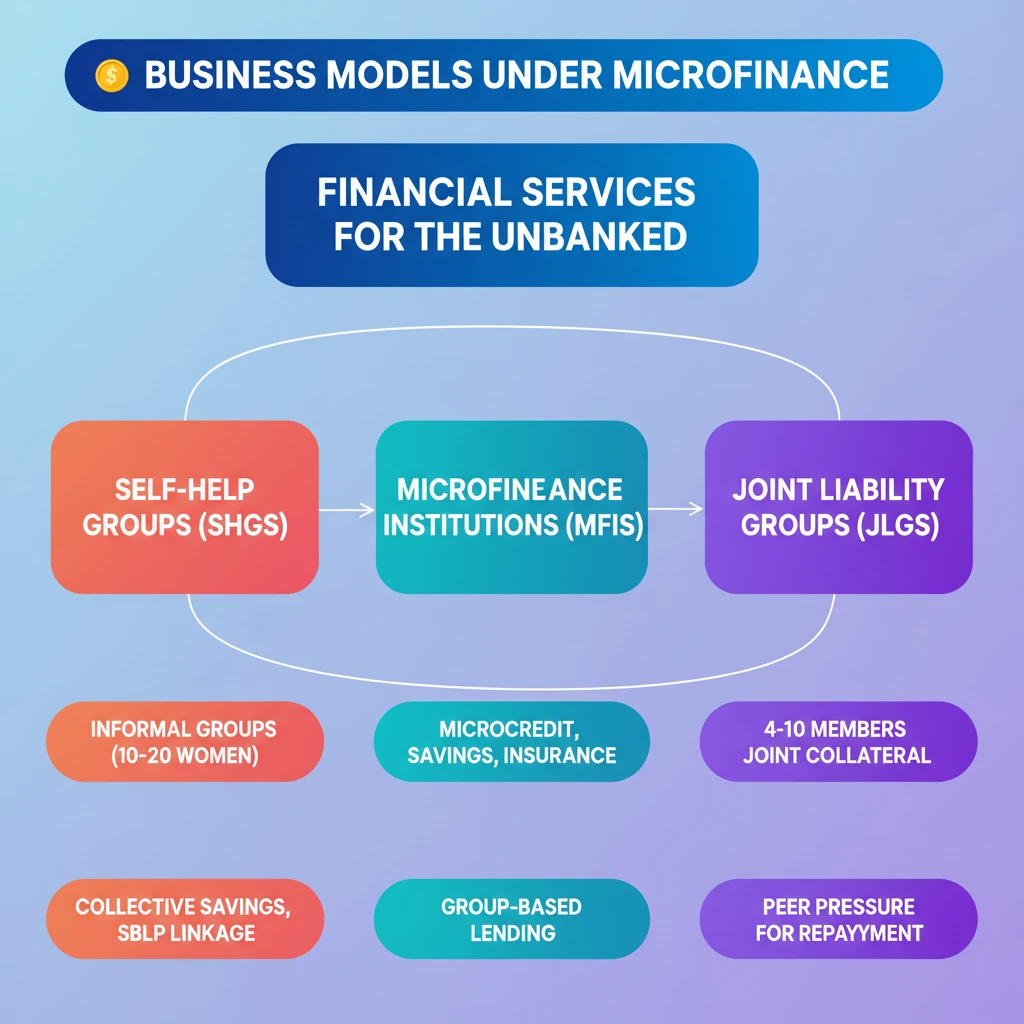
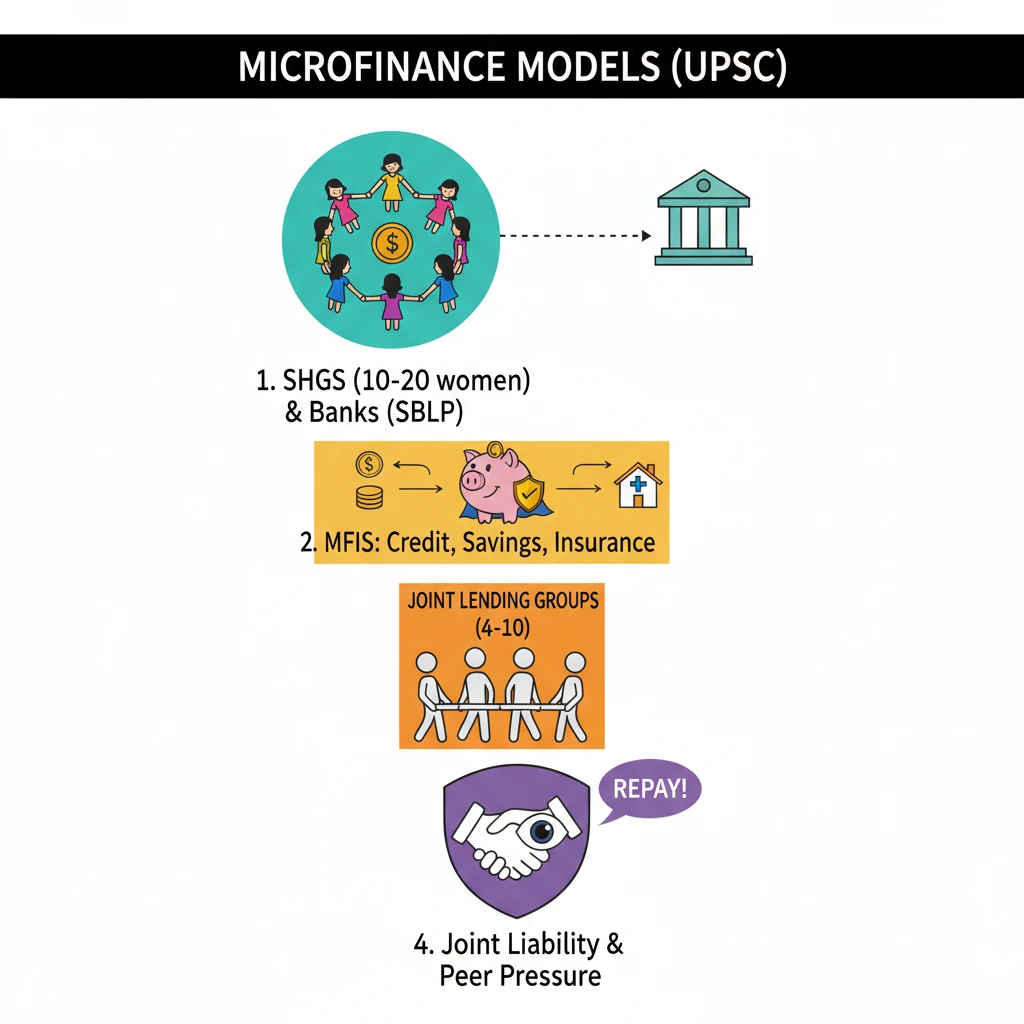
<h4>Introduction to Microfinance Business Models</h4><p><strong>Microfinance</strong> plays a crucial role in promoting financial inclusion by providing financial services to low-income individuals and groups who lack access to conventional banking. These services are often tailored to the specific needs of the poor, enabling them to engage in economic activities and improve their livelihoods.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The primary objective of <strong>microfinance business models</strong> is to deliver financial services efficiently and sustainably to the unbanked and underbanked populations, fostering economic empowerment and poverty reduction.</p></div><h4>Self-Help Groups (SHGs) Model</h4><p><strong>Self-Help Groups (SHGs)</strong> represent a significant and widespread model in India's microfinance landscape. These are typically informal associations of individuals, predominantly women, who come together for mutual support and collective savings.</p><p>An <strong>SHG</strong> usually consists of <strong>10 to 20 members</strong>. The members pool their small savings regularly, creating a common fund. This fund is then used to provide small loans to members for various productive or consumption purposes, often at reasonable interest rates.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Key Characteristics of SHGs:</strong><ul><li><strong>Informal Groups:</strong> Not legally registered entities initially.</li><li><strong>Member-Driven:</strong> Decisions on savings, lending, and repayment are made collectively by members.</li><li><strong>Focus on Women:</strong> A vast majority of SHGs are exclusively women's groups, empowering them financially and socially.</li></ul></p></div><p>The <strong>SHG-Bank Linkage Programme</strong> is a crucial initiative that connects these groups with formal financial institutions. Once an SHG demonstrates regular savings and sound internal lending practices, banks provide them with credit, which is then on-lent to members.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>The <strong>SHG-Bank Linkage Programme</strong> is vital for UPSC aspirants, especially for <strong>GS Paper III (Economy)</strong> and <strong>GS Paper I (Social Issues)</strong>, highlighting financial inclusion and women's empowerment.</p></div><h4>Microfinance Institutions (MFIs) Model</h4><p><strong>Microfinance Institutions (MFIs)</strong> are specialized financial entities that provide a broader range of financial services beyond just credit. They operate with a more formalized structure compared to SHGs, often registered as Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) or other legal forms.</p><p>MFIs offer various financial services, including <strong>microcredit</strong>, <strong>savings facilities</strong>, <strong>micro-insurance</strong>, and <strong>remittance services</strong>. Their goal is to cater to the diverse financial needs of low-income households and micro-entrepreneurs.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Services Offered by MFIs:</strong><ul><li><strong>Microcredit:</strong> Small loans for income-generating activities.</li><li><strong>Savings:</strong> Facilitating small deposits.</li><li><strong>Micro-insurance:</strong> Providing affordable insurance products (e.g., health, life, crop).</li><li><strong>Remittances:</strong> Enabling transfer of money, especially for migrant workers.</li></ul></p></div><p>Loans from MFIs are typically disbursed through a model known as <strong>Joint Lending Groups (JLGs)</strong>. These are informal groups, usually comprising <strong>4 to 10 individuals</strong>, who are involved in similar economic activities.</p><p>In a <strong>JLG</strong>, members collectively guarantee each other's loans. This mechanism of <strong>joint liability</strong> serves as a substitute for traditional collateral, which low-income borrowers often lack. The group's collective responsibility ensures higher repayment rates.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The <strong>joint liability mechanism</strong> in JLGs is a cornerstone of MFI operations, mitigating credit risk and fostering peer pressure for timely repayments, thereby ensuring the sustainability of microcredit programs.</p></div>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •Microfinance models (SHGs & MFIs) provide financial services to the unbanked.
- •SHGs are informal groups (10-20 women) saving collectively, linked to banks via SBLP.
- •MFIs offer microcredit, savings, insurance via Joint Lending Groups (JLGs) of 4-10 members.
- •JLGs use joint liability as collateral, fostering peer pressure for repayment.
- •Both models are crucial for financial inclusion, poverty alleviation, and women's empowerment in India.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•NABARD Annual Reports (for SHG-Bank Linkage Programme data)
•Reserve Bank of India (RBI) publications on Microfinance
•Ministry of Rural Development (MoRD) documents on NRLM