What are the Initiatives Shaping India’s Energy Transition? - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
What are the Initiatives Shaping India’s Energy Transition?
Medium⏱️ 8 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
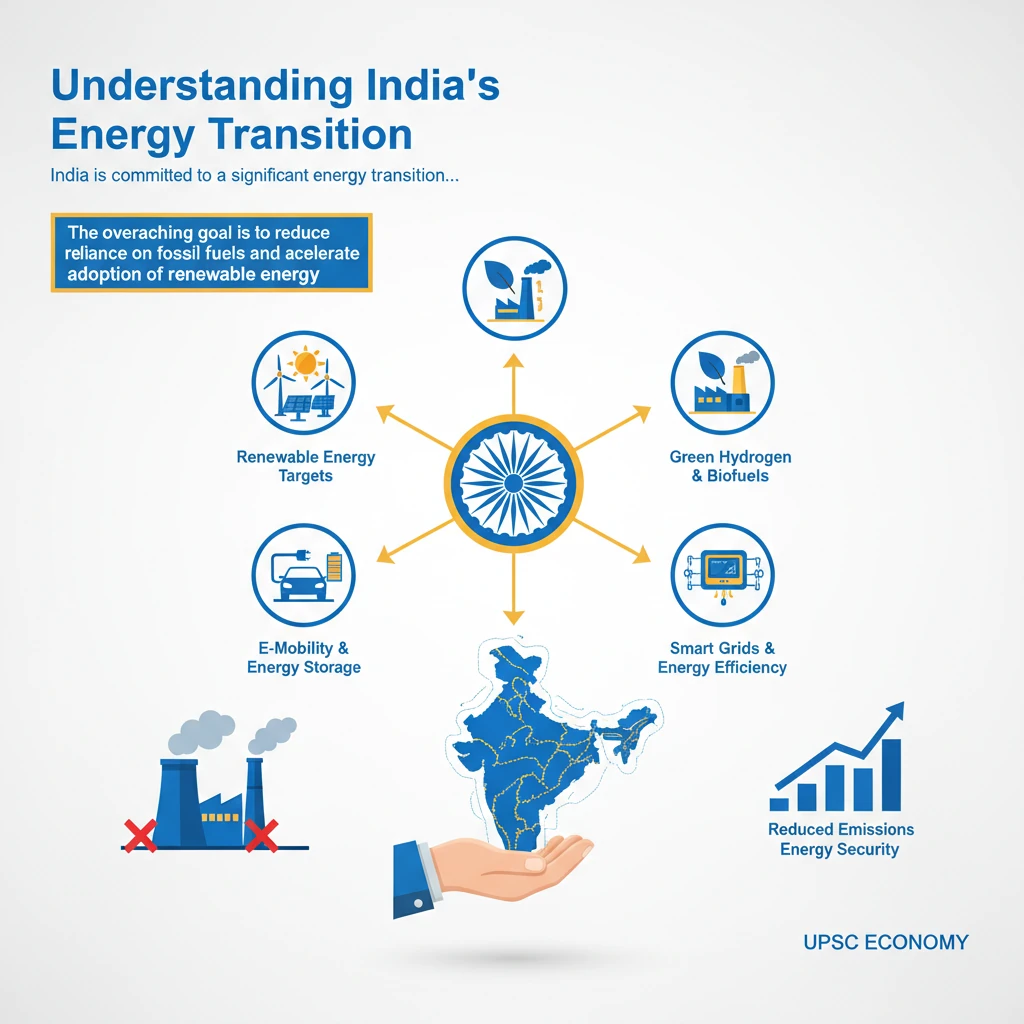
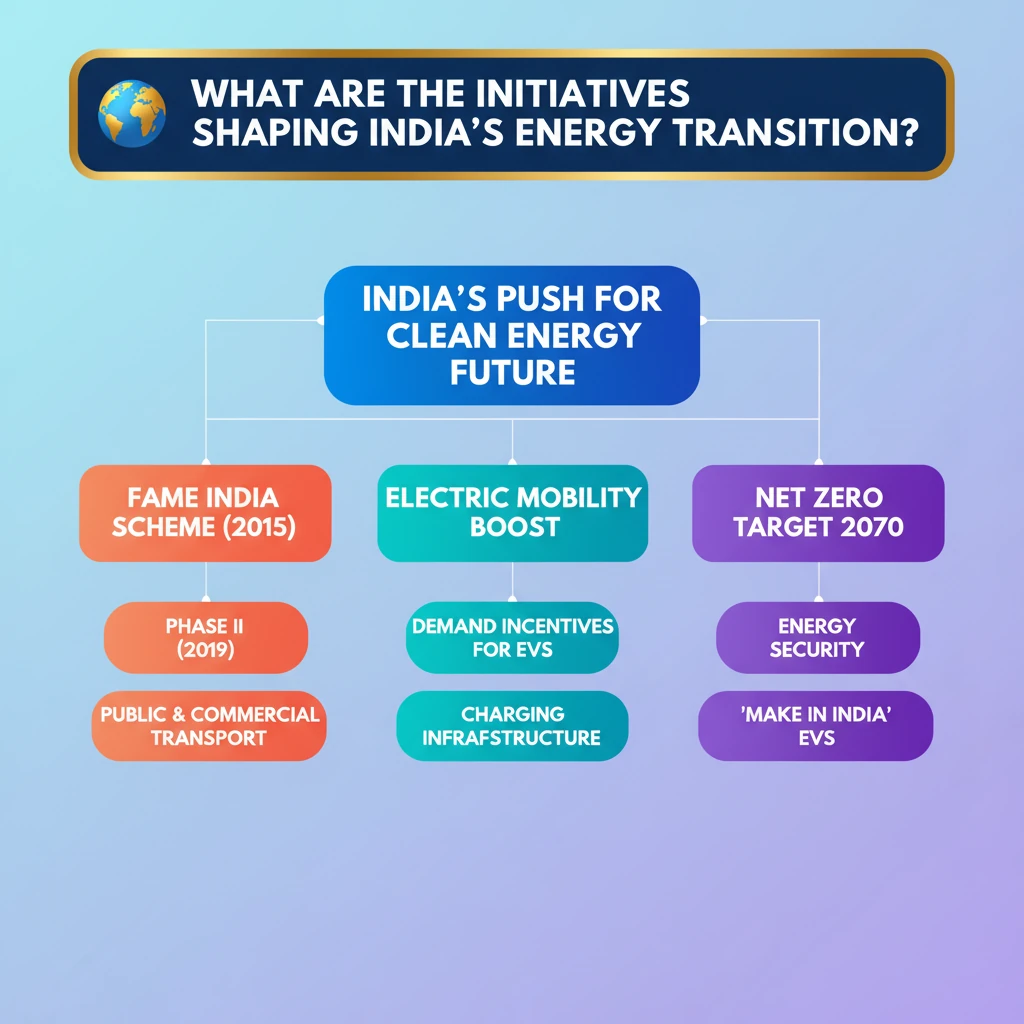
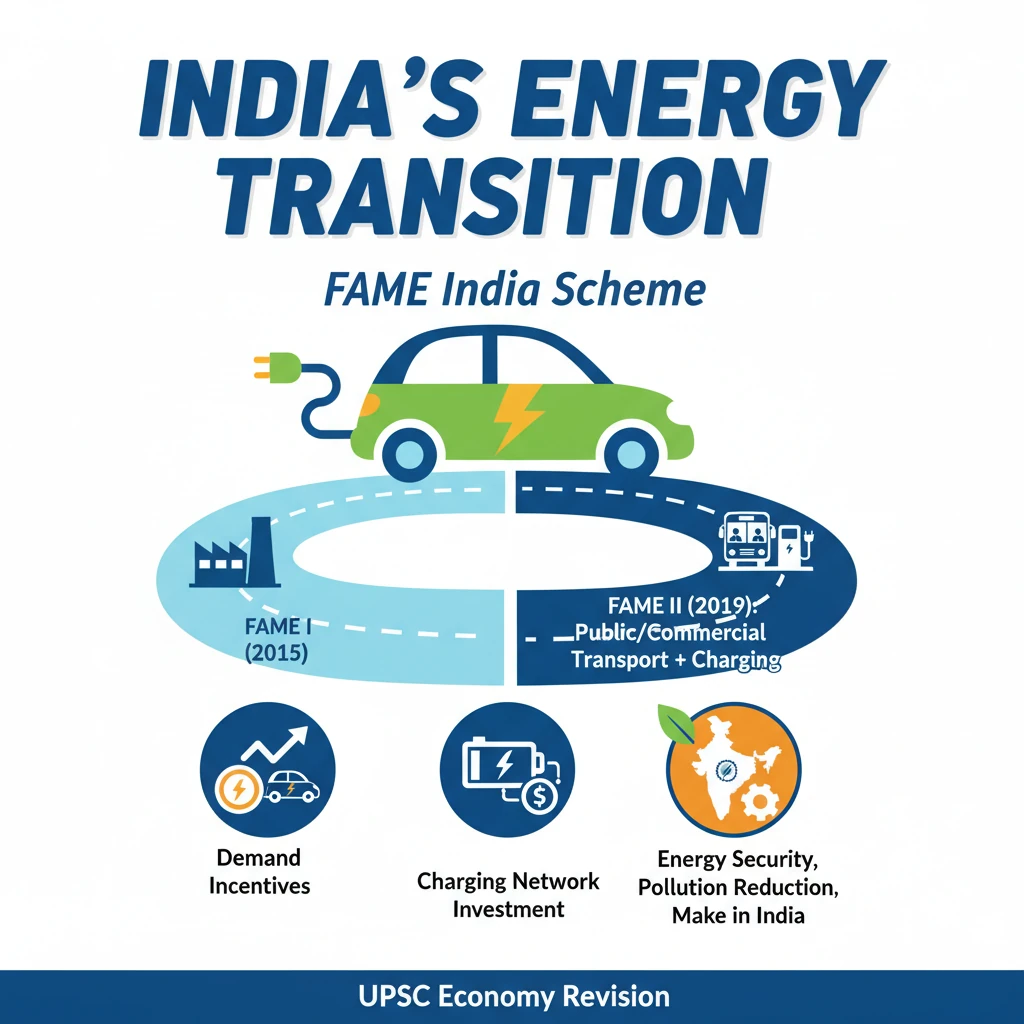
<h4>Understanding India's Energy Transition</h4><p>India is committed to a significant <strong>energy transition</strong>, aiming to shift its energy mix towards cleaner and more sustainable sources. This transition is crucial for achieving energy security, reducing air pollution, and meeting international climate commitments.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p>The overarching goal is to reduce reliance on <strong>fossil fuels</strong> and accelerate the adoption of <strong>renewable energy</strong> and <strong>electric mobility</strong> across various sectors.</p></div><h4>The FAME India Scheme: A Catalyst for E-Mobility</h4><p>The <strong>Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of (Hybrid) & Electric Vehicles (FAME) India Scheme</strong> is a flagship initiative by the Government of India. It falls under the <strong>National Electric Mobility Mission Plan (NEMMP) 2020</strong>, launched in <strong>2015</strong>.</p><p>Its primary objective is to promote the manufacturing of electric and hybrid vehicles and encourage their faster adoption by providing financial incentives and developing supporting infrastructure.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>FAME India</strong> is implemented by the <strong>Ministry of Heavy Industries</strong>. It aims to reduce the country's dependence on fossil fuels and address environmental concerns.</p></div><h4>Phases of FAME India</h4><p>The scheme has been implemented in two phases, each with specific targets and focus areas.</p><ul><li><strong>FAME India Phase I (2015-2019):</strong> Focused on demand creation, technology development, pilot projects, and charging infrastructure. It supported various vehicle segments, including two-wheelers, three-wheelers, four-wheelers, and buses.</li><li><strong>FAME India Phase II (2019-present):</strong> Aims for a more ambitious push towards electrification, with a budget of <strong>₹10,000 crore</strong> for a period of three years, extended multiple times. It primarily focuses on public and commercial transport.</li></ul><h4>Key Components of FAME India Phase II</h4><p><strong>FAME II</strong> has a well-defined strategy to achieve its goals, primarily through demand incentives and infrastructure development.</p><ol><li><strong>Demand Incentives:</strong> Subsidies are provided for the purchase of electric vehicles, particularly electric two-wheelers, three-wheelers, four-wheelers, and buses. The focus is on encouraging the shift from internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles.</li><li><strong>Charging Infrastructure:</strong> Significant emphasis is placed on establishing a robust network of <strong>charging stations</strong> across the country. This includes both public and private charging facilities to alleviate range anxiety among potential EV buyers.</li><li><strong>Inter-Ministerial Coordination:</strong> The scheme involves coordination with various ministries and state governments to create a conducive ecosystem for electric mobility.</li></ol><div class='exam-tip-box'><p>For <strong>UPSC Mains GS-III</strong>, understanding the phased approach and specific components of FAME II is crucial. It demonstrates a structured policy intervention for a national objective.</p></div><h4>Impact and Future Outlook</h4><p>FAME India has played a pivotal role in accelerating the adoption of EVs in India. It has led to increased sales of electric two-wheelers and buses, and a growing interest in electric cars.</p><p>The scheme is a cornerstone of India's strategy to achieve its <strong>net-zero emissions target by 2070</strong> and reduce its import bill for crude oil.</p>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •FAME India Scheme (2015) promotes faster adoption and manufacturing of electric and hybrid vehicles.
- •It operates in two phases, with FAME II (2019) focusing on public and commercial transport and charging infrastructure.
- •Key components include demand incentives for EVs and significant investment in charging networks.
- •FAME contributes to India's energy security, reduces pollution, and supports 'Make in India' for EVs.
- •It is a crucial initiative for achieving India's climate commitments, including Net Zero by 2070.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content
📚 Reference Sources
•NITI Aayog reports on Electric Mobility
•Press Information Bureau (PIB) releases on FAME India
•Economic Survey of India (latest editions)