What are the Regional Rural Banks? - Economy | UPSC Learning
Topics
0 topics • 0 completed
🔍
No topics match your search
What are the Regional Rural Banks?
Easy⏱️ 6 min read
economy
📖 Introduction
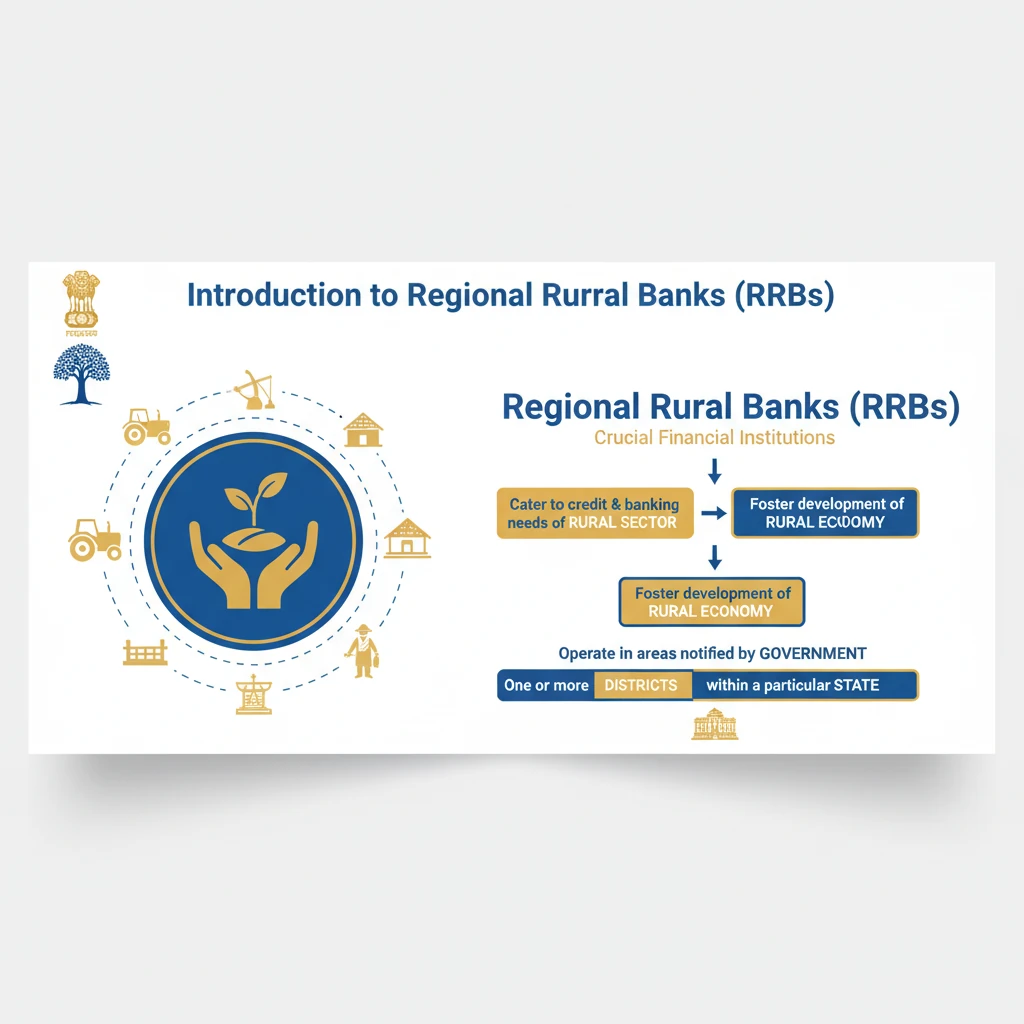
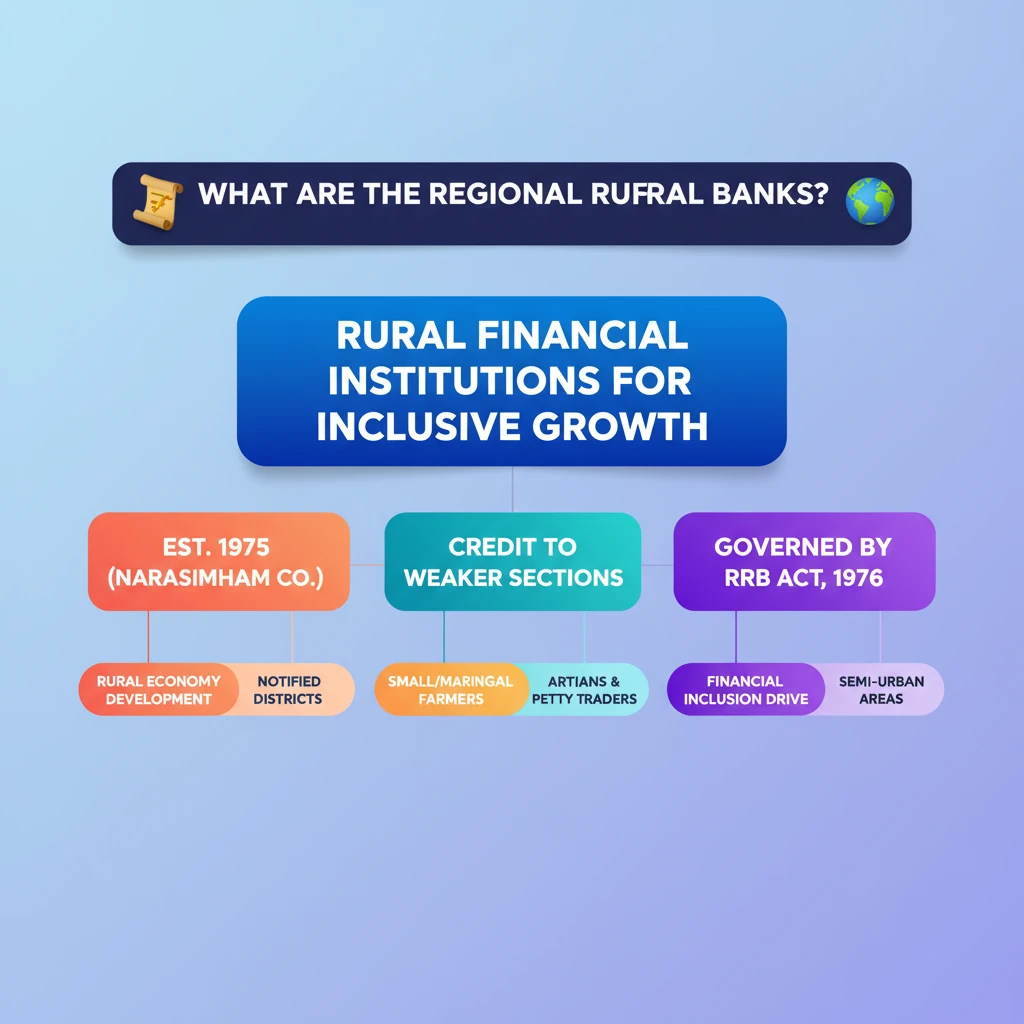
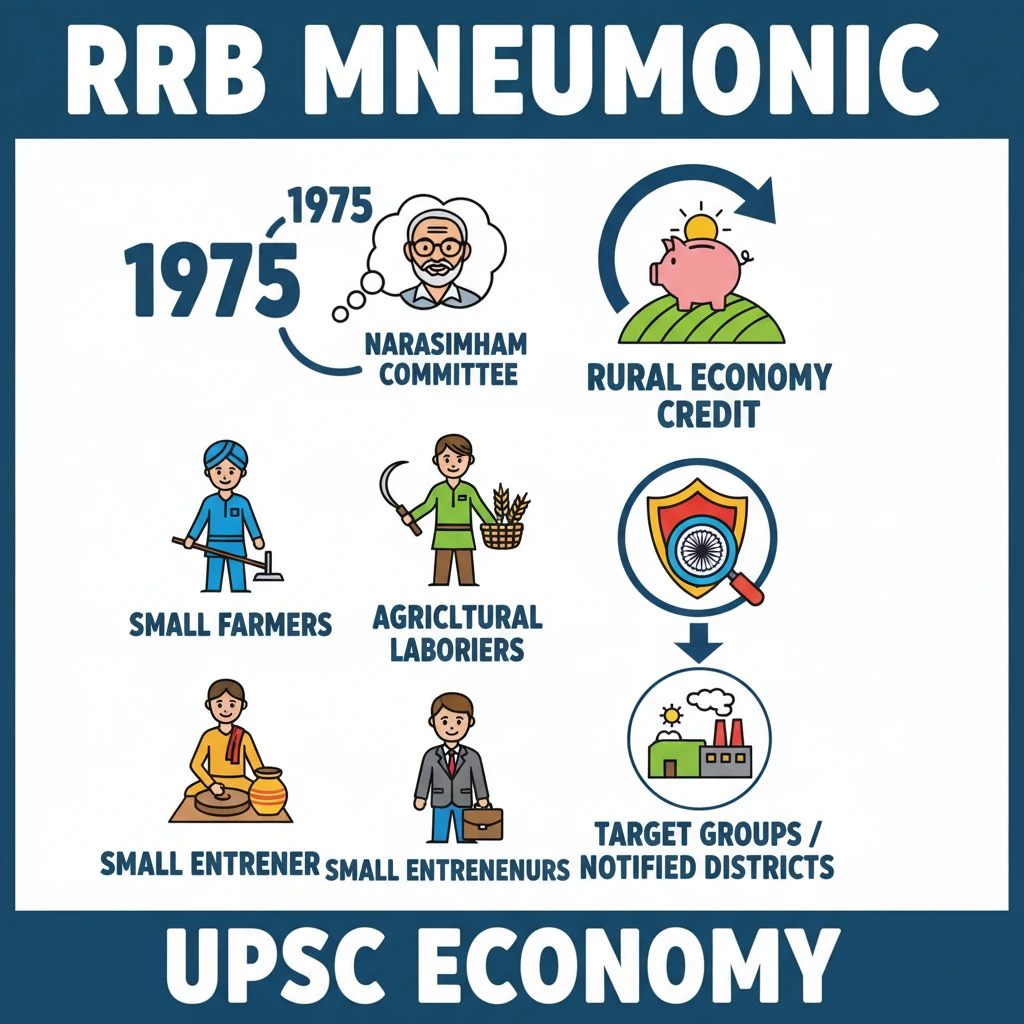
<h4>Introduction to Regional Rural Banks (RRBs)</h4><p><strong>Regional Rural Banks (RRBs)</strong> are crucial financial institutions established to cater to the credit and banking needs of the <strong>rural sector</strong> in India. Their primary objective is to foster the development of the <strong>rural economy</strong>.</p><p>These banks operate specifically in areas notified by the <strong>Government</strong>, typically covering one or more <strong>districts</strong> within a particular <strong>State</strong>.</p><div class='key-point-box'><p><strong>Key Point:</strong> RRBs bridge the gap in financial services for underserved rural populations, promoting inclusive growth.</p></div><h4>Genesis and Establishment</h4><p>The establishment of <strong>Regional Rural Banks</strong> was a direct recommendation of the <strong>Narasimham Committee</strong> on <strong>rural credit</strong> in <strong>1975</strong>. This committee played a pivotal role in shaping India's rural financial architecture.</p><div class='info-box'><p><strong>Fact:</strong> RRBs were formally established in <strong>1975</strong> under the specific provisions of the <strong>Regional Rural Banks Act, 1976</strong>. This legislative framework provided the legal basis for their operations.</p></div><h4>Core Objectives and Mandate</h4><p>The fundamental aim of RRBs is to develop the <strong>rural economy</strong> by providing essential <strong>credit</strong> and other financial facilities. This support is directed towards various segments of the rural populace.</p><ul><li><strong>Small and marginal farmers:</strong> Offering loans for agricultural activities and related needs.</li><li><strong>Agricultural laborers:</strong> Providing financial assistance for livelihood and consumption.</li><li><strong>Artisans:</strong> Supporting traditional crafts and small-scale production units.</li><li><strong>Small entrepreneurs:</strong> Facilitating the growth of micro-enterprises in rural and semi-urban areas.</li></ul><p>By extending these facilities, RRBs actively support key sectors such as <strong>agriculture</strong>, <strong>trade</strong>, <strong>commerce</strong>, and <strong>industry</strong> within <strong>rural and semi-urban areas</strong>.</p><div class='exam-tip-box'><p><strong>UPSC Insight:</strong> Understanding the genesis (<strong>Narasimham Committee</strong>) and the core beneficiaries of RRBs is vital for Mains answers on financial inclusion and rural development (<strong>GS Paper III</strong>).</p></div><h4>Operational Scope</h4><p>RRBs have a defined operational jurisdiction. They function in specific geographical areas that are officially notified by the <strong>Government</strong>.</p><p>Each RRB's operational reach is limited, typically encompassing one or more <strong>districts</strong> within a single <strong>State</strong>, ensuring focused and localized service delivery.</p>
💡 Key Takeaways
- •RRBs were established in 1975 based on the Narasimham Committee's recommendation.
- •Their primary goal is to develop the rural economy by providing credit to specific target groups.
- •Key beneficiaries include small/marginal farmers, agricultural laborers, artisans, and small entrepreneurs.
- •Operate in notified districts within a state, focusing on rural and semi-urban areas.
- •Governed by the RRB Act, 1976, they are crucial for financial inclusion and rural development.
🧠 Memory Techniques
95% Verified Content